SLVSCP2F January 2015 – June 2020 DRV10975
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Motor Parameters
- 8.4.2 Starting the Motor Under Different Initial Conditions
- 8.4.3 Motor Start Sequence
- 8.4.4 Start-Up Current Setting
- 8.4.5 Closed Loop
- 8.4.6 Current Limit
- 8.4.7 Lock Detect and Fault Handling
- 8.4.8 AVS Function
- 8.4.9 PWM Output
- 8.4.10 FG Customized Configuration
- 8.4.11
Diagnostics and Visibility
- 8.4.11.1 Motor Status Readback
- 8.4.11.2 Motor Speed Readback
- 8.4.11.3 Motor Electrical Period Readback
- 8.4.11.4 BEMF Constant Readback
- 8.4.11.5 Motor Estimated Position by IPD
- 8.4.11.6 Supply Voltage Readback
- 8.4.11.7 Speed Command Readback
- 8.4.11.8 Speed Command Buffer Readback
- 8.4.11.9 Fault Diagnostics
- 8.5 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|24
Orderable Information
8.4.10.1 FG Output Frequency
The FG output frequency can be configured by FGcycle[1:0]. The default FG toggles once every electrical cycle (FGcycle = 00). Many applications configure the FG output so that it provides two pulses for every mechanical rotation of the motor. The configuration bits provided in DRV10975 can accomplish this for 4-pole, 6-pole, 8-pole, and 12-pole motors, as shown in Figure 35.
Figure 35 shows the DRV10975 has been configured to provide FG pulses once every electrical cycle (4 pole), twice every three electrical cycle (6 pole), once every two electrical cycles (8 pole), and once every three electrical cycles (12 pole).
Note that when it is set to 2 FG pulses every three electrical cycles, the FG output is not 50% duty cycle. Motor speed is able to be measured by monitoring the rising edge of the FG output.
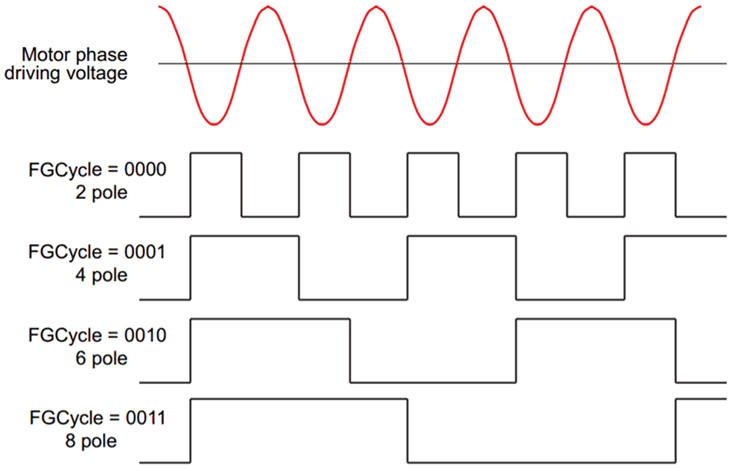 Figure 35. FG Frequency Divider
Figure 35. FG Frequency Divider