SLLSEL7B October 2014 – April 2024 DRV8848
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
6.3.4 Current Regulation
The current through the motor windings is regulated by a fixed-off-time PWM current regulation circuit. With DC brushed motors, current regulation can be used to limit the stall current (which is also the startup current) of the motor.
Current regulation works as follows:
When an H-bridge is enabled, current rises through the winding at a rate dependent on the supply voltage and inductance of the winding. If the current reaches the current chopping threshold, the bridge disables the current for a time tOFF before starting the next PWM cycle. Note that immediately after the current is enabled, the voltage on the xISEN pin is ignored for some time (tBLANK) before enabling the current sense circuitry. This blanking time also sets the minimum on-time of the PWM cycle.
The PWM chopping current is set by a comparator which compares the voltage across a current sense resistor, connected to the xISEN pin, with a reference voltage. The reference voltage is derived from the voltage applied to the VREF pin and the voltage is VVREF / 6.6. The VREF pin can be tied on board to the 3.3V – VINT pin, or the VREF pin can be externally forced to a desired VREF voltage.
The full scale chopping current in a winding is calculated as follows:
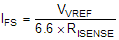
where
- IFS is the regulated current.
- VVREF is the voltage on the VREF pin.
- RISENSE is the resistance of the sense resistor.
Example: If VVREF is 3.3V and a 500mΩ sense resistor is used, the full-scale chopping current is 3.3V / (6.6 × 500mΩ) = 1A.
Note that if the current control is not needed, the xISEN pins can be connected directly to ground. In this case, VREF is connected to VINT.