SBOS374E November 2006 – September 2017 INA200 , INA201 , INA202
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
- Connect the input pins to the sensing resistor using a Kelvin or 4-wire connection. This connection technique ensures that only the current-sensing resistor impedance is detected between the input pins. Poor routing of the current-sensing resistor commonly results in additional resistance present between the input pins. Given the very-low-ohmic value of the current resistor, any additional high-current carrying impedance causes significant measurement errors.
- The power-supply bypass capacitor must be placed as close as possible to the supply and ground pins. The recommended value of this bypass capacitor is 0.1 μF. Additional decoupling capacitance can be added to compensate for noisy or high-impedance power supplies.
10.2 Layout Example
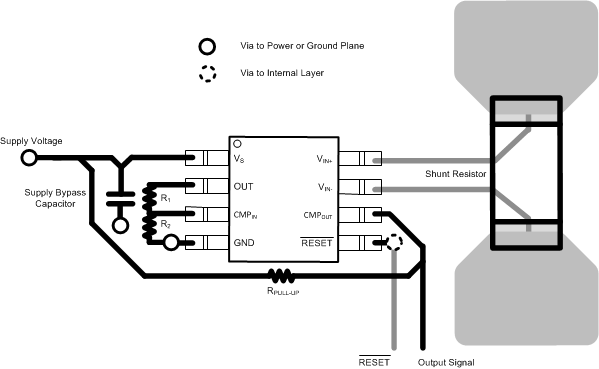 Figure 39. INA20x Layout Example
Figure 39. INA20x Layout Example