SNVS209G November 2002 – May 2019 LM2733
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the External Capacitors
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.3 Selecting the Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Feedforward Compensation
- 8.2.2.5 Selecting Diodes
- 8.2.2.6 Setting the Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.7 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.8 Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.9 Inductance Value
- 8.2.2.10 Maximum Switch Current
- 8.2.2.11 Calculating Load Current
- 8.2.2.12 Design Parameters VSW and ISW
- 8.2.2.13 Thermal Considerations
- 8.2.2.14 Minimum Inductance
- 8.2.2.15 Inductor Suppliers
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified: VIN = 5 V, VSHDN = 5 V, IL = 0 A, TJ = 25°C.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(3) | TYP(4) | MAX(3) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 2.7 | 14 | V | |
| ISW | Switch current limit | See(5) | 1 | 1.5 | A | |
| RDS(ON) | Switch ON resistance | ISW = 100 mA | 500 | 650 | mΩ | |
| SHDNTH | Shutdown threshold | Device ON, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 1.5 | V | ||
| Device OFF, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 0.50 | |||||
| ISHDN | Shutdown pin bias current | VSHDN = 0 | 0 | µA | ||
| VSHDN = 5 V | 0 | |||||
| VSHDN = 5 V, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 2 | |||||
| VFB | Feedback pin reference voltage | VIN = 3 V | 1.230 | V | ||
| VIN = 3 V, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 1.205 | 1.255 | ||||
| IFB | Feedback pin bias current | VFB = 1.23 V | 60 | nA | ||
| IQ | Quiescent current | VSHDN = 5 V, Switching "X" | 2.1 | mA | ||
| VSHDN = 5 V, Switching "X", −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 3 | |||||
| VSHDN = 5 V, Switching "Y" | 1.1 | |||||
| VSHDN = 5 V, Switching "Y", −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 2 | |||||
| VSHDN = 5 V, Not Switching | 400 | µA | ||||
| VSHDN = 5 V, Not Switching, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 500 | |||||
| VSHDN = 0 | 0.024 | 1 | ||||
| Δ VFBΔVIN | FB voltage line regulation | 2.7 V ≤ VIN ≤ 14 V | 0.02 | %/V | ||
| FSW | Switching frequency | “X” Option | 1.6 | MHz | ||
| “X” Option, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 1.15 | 1.85 | ||||
| “Y” Option | 0.60 | |||||
| “Y” Option, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 0.40 | 0.8 | ||||
| DMAX | Maximum duty cycle | “X” Option | 93% | |||
| “X” Option, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 87% | |||||
| “Y” Option | 96% | |||||
| “Y” Option, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C | 93% | |||||
| IL | Switch leakage | Not Switching VSW = 5 V | 1 | µA | ||
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the component may occur. Electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device outside of the limits set forth under the operating ratings which specify the intended range of operating conditions.
(2) The maximum power dissipation which can be safely dissipated for any application is a function of the maximum junction temperature, TJ(MAX) = 125°C, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance for the SOT-23 package, RθJ-A = 210°C/W, and the ambient temperature, TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature for designs using this device can be calculated using the formula: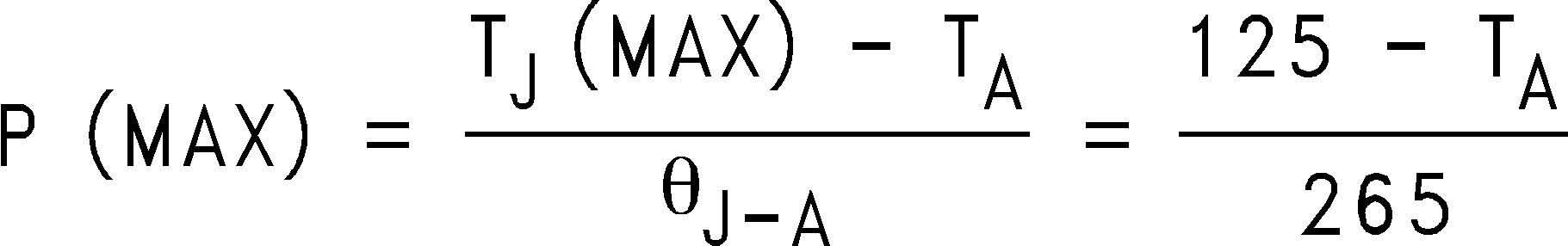 If power dissipation exceeds the maximum specified above, the internal thermal protection circuitry protects the device by reducing the output voltage as required to maintain a safe junction temperature.
If power dissipation exceeds the maximum specified above, the internal thermal protection circuitry protects the device by reducing the output voltage as required to maintain a safe junction temperature.
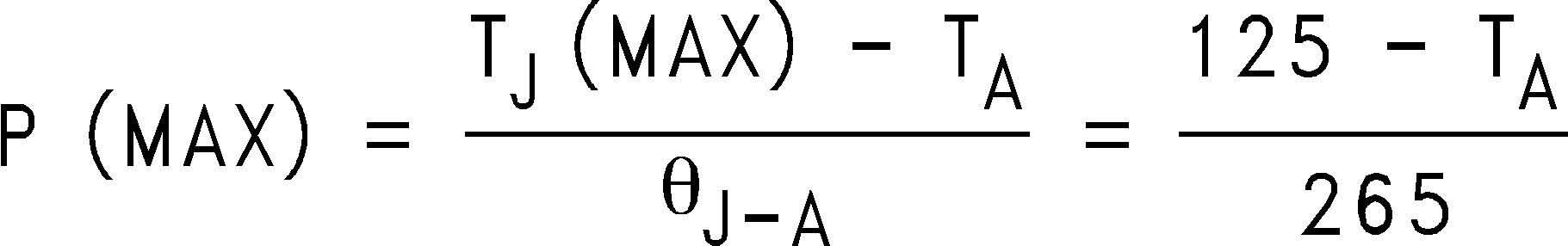 If power dissipation exceeds the maximum specified above, the internal thermal protection circuitry protects the device by reducing the output voltage as required to maintain a safe junction temperature.
If power dissipation exceeds the maximum specified above, the internal thermal protection circuitry protects the device by reducing the output voltage as required to maintain a safe junction temperature.(3) Limits are specified by testing, statistical correlation, or design.
(4) Typical values are derived from the mean value of a large quantity of samples tested during characterization and represent the most likely expected value of the parameter at room temperature.
(5) Switch current limit is dependent on duty cycle (see Typical Characteristics). Limits shown are for duty cycles ≤ 50%.