SNVSA43B August 2014 – September 2017 LM43600
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematic
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Controlled Step-Down Regulator
- 8.3.2 Light Load Operation
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Enable (ENABLE)
- 8.3.5 VCC, UVLO and BIAS
- 8.3.6 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking (SS/TRK)
- 8.3.7 Switching Frequency (RT) and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.8 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 8.3.9 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 8.3.10 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 8.3.11 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 8.3.12 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Applications and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 9.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.4 Input Capacitors
- 9.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.7 Feedforward Capacitor
- 9.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 9.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor
- 9.2.2.10 BIAS Capacitors
- 9.2.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitors
- 9.2.2.12 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 9.2.2.13 PGOOD
- 9.2.3 Application Performance Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltages | VIN to PGND | –0.3 | 42 | V |
| EN to PGND | –0.3 | VIN + 0.3 | ||
| FB, RT, SS/TRK to AGND | –0.3 | 3.6 | ||
| PGOOD to AGND | –0.3 | 15 | ||
| SYNC to AGND | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||
| BIAS to AGND | –0.3 | 30 | ||
| AGND to PGND | –0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| Output voltages | SW to PGND | –0.3 | VIN + 0.3 | V |
| SW to PGND less than 10ns Transients | –3.5 | 42 | ||
| CBOOT to SW | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||
| VCC to AGND | –0.3 | 3.6 | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltages | VIN to PGND | 3.5 | 36 | V |
| EN | –0.3 | VIN | ||
| FB | –0.3 | 1.1 | ||
| PGOOD | –0.3 | 12 | ||
| BIAS input not used | –0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| BIAS input used | 3.3 | VIN or 28(2) | ||
| AGND to PGND | –0.1 | 0.1 | ||
| Output Voltage | VOUT | 1 | 28 | V |
| Output Current | IOUT | 0 | 0.5 | A |
| Temperature | Operating junction temperature range, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C |
(1) Recommended Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is intended to be functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits. For specified specifications, see Electrical Characteristics.
(2) Whichever is lower.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1)(2) | LM43600 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (HTSSOP) | |||
| 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 39.9(3) | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 26.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 21.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.8 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 21.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.3 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
(2) The package thermal impedance is calculated in accordance with JESD 51-7 standard with a 4-layer board and 1 W power dissipation.
(3) RθJA is highly related to PCB layout and heat sinking. See Figure 107 for measured RθJA vs PCB area from a 2-layer board and a 4-layer board.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Limits apply over the recommended operating junction temperature (TJ) range of –40°C to 125°C, unless otherwise stated. Minimum and Maximum limits are specified through test, design or statistical correlation. Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm at TJ = 25°C, and are provided for reference purposes only. Unless otherwise stated, the following conditions apply: VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, FS = 500 kHz.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VIN PINS) | ||||||
| VIN-MIN-ST | Minimum input voltage for start-up | 3.8 | V | |||
| ISHDN | Shutdown quiescent current | VEN = 0 V | 1.1 | 3.1 | µA | |
| IQ-NONSW | Operating quiescent current (non-switching) from VIN | VEN = 3.3 V VFB = 1.5 V VBIAS = 3.4 V external |
6 | 11 | µA | |
| IBIAS-NONSW | Operating quiescent current (non-switching) from external VBIAS | VEN = 3.3 V VFB = 1.5 V VBIAS = 3.4 V external |
85 | 140 | µA | |
| IQ-SW | Operating quiescent current (switching) | VEN = 3.3 V IOUT = 0 A RT = open VBIAS = VOUT = 3.3 V RFBT = 1 Meg |
33 | µA | ||
| ENABLE (EN PIN) | ||||||
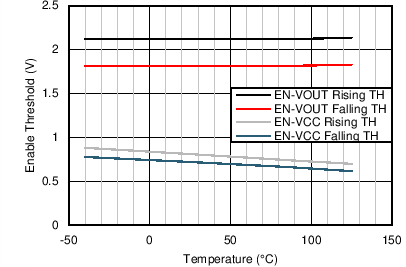
| VEN-VCC-H | Voltage level to enable the internal LDO output VCC | VENABLE high level | 1.2 | V | ||
| VEN-VCC-L | Voltage level to disable the internal LDO output VCC | VENABLE low level | 0.4 | V | ||
| VEN-VOUT-H | Precision enable level for switching and regulator output: VOUT | VENABLE high level | 2 | 2.1 | 2.42 | V |
| VEN-VOUT-HYS | Hysteresis voltage between VOUT precision enable and disable thresholds | VENABLE hysteresis | –305 | mV | ||
| ILKG-EN | Enable input leakage current | VEN = 3.3 V | 0.8 | 1.75 | µA | |
| INTERNAL LDO (VCC PIN AND BIAS PIN) | ||||||
| VCC | Internal LDO output voltage VCC | VIN ≥ 3.8 V | 3.3 | V | ||
| VCC-UVLO | Undervoltage lockout (UVLO) thresholds for VCC | VCC rising threshold | 3.14 | V | ||
| Hysteresis voltage between rising and falling thresholds | –567 | mV | ||||
| VBIAS-ON | Internal LDO input change over threshold to BIAS | VBIAS rising threshold | 2.96 | 3.2 | V | |
| Hysteresis voltage between rising and falling thresholds | –74 | mV | ||||
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE (FB PIN) | ||||||
| VFB | Feedback voltage | TJ = 25°C | 1.009 | 1.016 | 1.023 | V |
| TJ = –40°C to 85°C | 0.999 | 1.016 | 1.031 | |||
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 0.999 | 1.016 | 1.039 | |||
| ILKG-FB | Input leakage current at FB pin | FB = 1.011 V | 0.2 | 65 | nA | |
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| TSD (1) | Thermal shutdown | Shutdown threshold | 160 | °C | ||
| Recovery threshold | 150 | °C | ||||
| CURRENT LIMIT AND HICCUP | ||||||
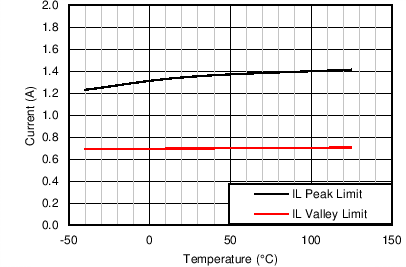
| IHS-LIMIT | Peak inductor current limit | 1.04 | 1.33 | 1.56 | A | |
| ILS-LIMIT | Inductor current valley limit | 0.46 | 0.60 | 0.75 | A | |
| SOFT START (SS/TRK PIN) | ||||||
| ISSC | Soft-start charge current | 1.17 | 2.2 | 2.85 | µA | |
| RSSD | Soft-start discharge resistance | UVLO, TSD, OCP, or EN = 0 V | 16 | kΩ | ||
| POWER GOOD (PGOOD PIN) | ||||||
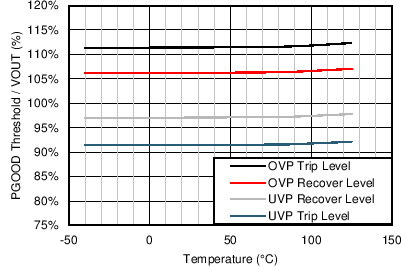
| VPGOOD-HIGH | Power-good flag overvoltage tripping threshold | % of FB voltage | 110% | 113% | ||
| VPGOOD-LOW | Power-good flag undervoltage tripping threshold | % of FB voltage | 83% | 90% | ||
| VPGOOD-HYS | Power-good flag recovery hysteresis | % of FB voltage | 6% | |||
| RPGOOD | PGOOD pin pulldown resistance when power bad | VEN = 3.3 V | 40 | 125 | Ω | |
| VEN = 0 V | 60 | 150 | ||||
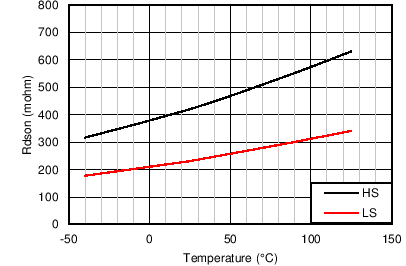
| MOSFETS (2) | ||||||
| RDS-ON-HS | High-side MOSFET ON-resistance | IOUT = 0.5 A VBIAS = VOUT = 3.3 V |
419 | mΩ | ||
| RDS-ON-LS | Low-side MOSFET ON-resistance | IOUT = 0.5 A VBIAS = VOUT = 3.3 V |
231 | mΩ | ||
(1) Specified by design.
(2) Measured at package pins.
7.6 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CURRENT LIMIT AND HICCUP | |||||
| NOC | Hiccup wait cycles when LS current limit tripped | 32 | Cycles | ||
| TOC | Hiccup retry delay time | 5.5 | ms | ||
| SOFT START (SS/TRK PIN) | |||||
| TSS | Internal soft-start time when SS pin open circuit | 3.86 | ms | ||
| POWER GOOD (PGOOD PIN) | |||||
| TPGOOD-RISE | Power-good flag rising transition deglitch delay | 220 | µs | ||
| TPGOOD-FALL | Power-good flag falling transition deglitch delay | 220 | µs | ||
7.7 Switching Characteristics
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW (SW PIN) | ||||||
| tON-MIN(1) | Minimum high side MOSFET ON time | 125 | 165 | ns | ||
| tOFF-MIN(1) | Minimum high side MOSFET OFF time | 200 | 250 | ns | ||
| OSCILLATOR (SW PINS AND SYNC PIN) | ||||||
| FOSC-DEFAULT | Oscillator default frequency | RT pin open circuit | 445 | 500 | 570 | kHz |
| FADJ | Minimum adjustable frequency | With 1% resistors at RT pin | 200 | kHz | ||
| Maximum adjustable frequency | 2200 | kHz | ||||
| Frequency adjust accuracy | 10% | |||||
| VSYNC-HIGH | Sync clock high level threshold | 2 | V | |||
| VSYNC-LOW | Sync clock low level threshold | 0.4 | V | |||
| DSYNC-MAX | Sync clock maximum duty cycle | 90% | ||||
| DSYNC-MIN | Sync clock minimum duty cycle | 10% | ||||
| TSYNC-MIN | Minimum sync clock ON-time and OFF-time | 80 | ns | |||
(1) Specified by design.
7.8 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, FS = 500 kHz, L = 22 µH, COUT = 100 µF, CFF = 33 pF. See Application Performance Curves for bill of materials (BOM) for other VOUT and FSW combinations.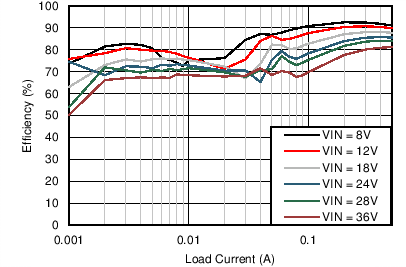
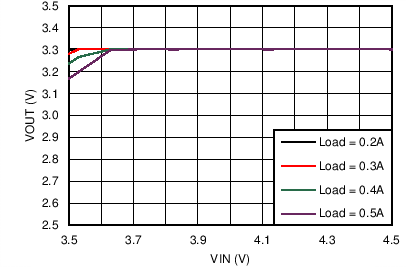
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
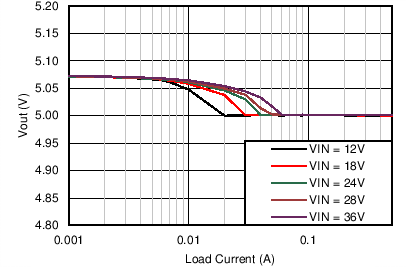
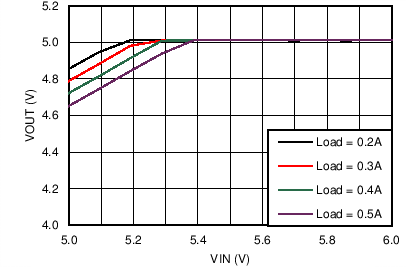
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
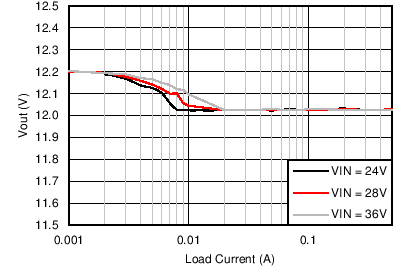
| VOUT = 12 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
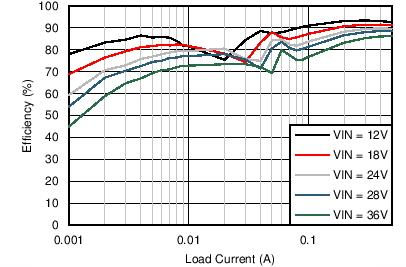
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
| VOUT = 12 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
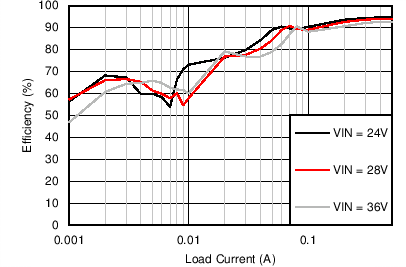
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
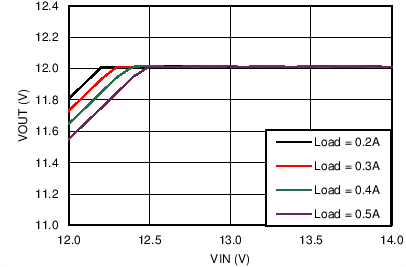
| VOUT = 12 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
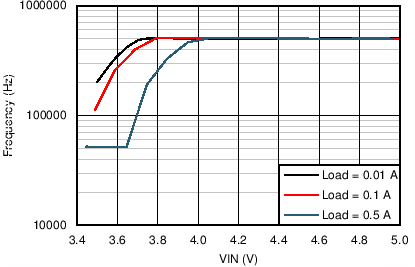
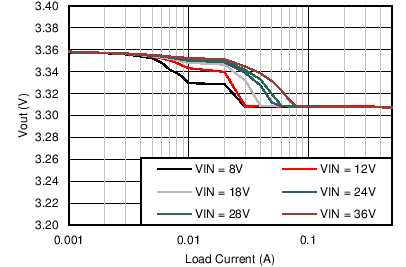
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
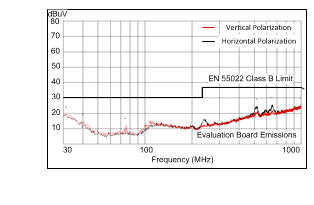
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz | IOUT = 0.5 A |
| Measured on the LM43600PWPEVM with default BOM. No input filter used. | ||
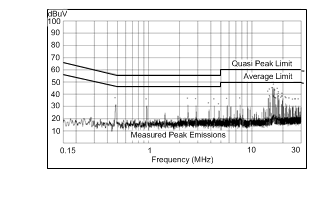
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz | IOUT = 0.5 A |
| Measured on the LM43600PWPEVM with default BOM. Input filter: Lin = 1 µH Cd = 47 µF CIN4 = 68 µF | ||
| VIN = 12 V | VOUT = 3.3 V | FS = 500 kHz |
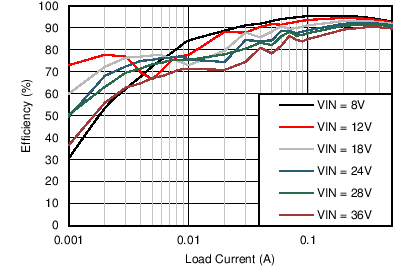
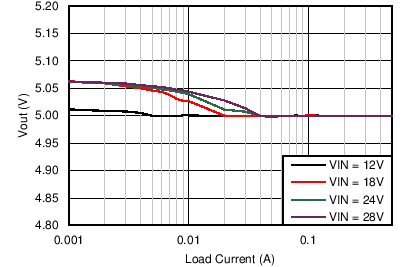
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 200 kHz |
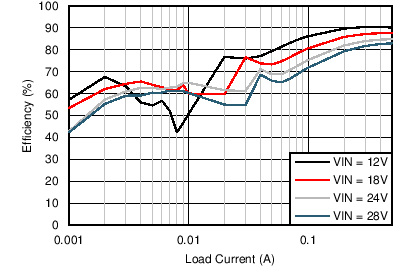
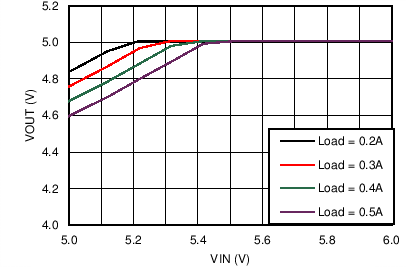
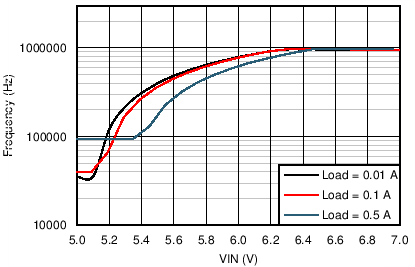
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 1 MHz |
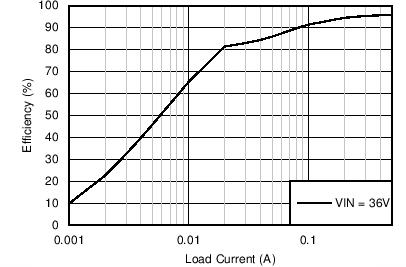
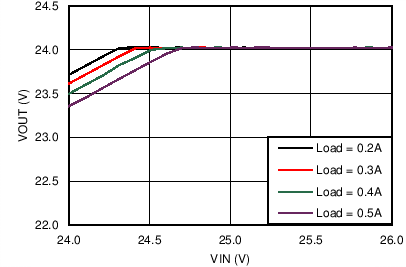
| VOUT = 24 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
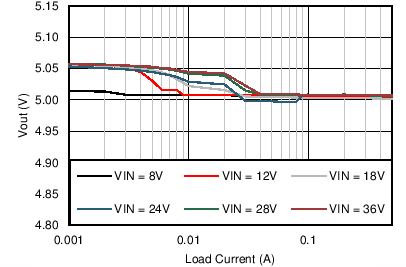
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 200 kHz |
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 1 MHz |
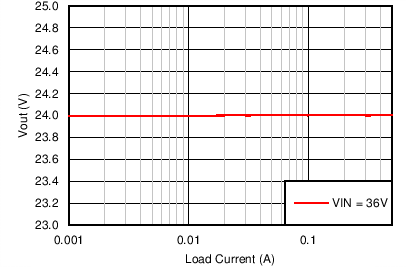
| VOUT = 24 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 200 kHz |
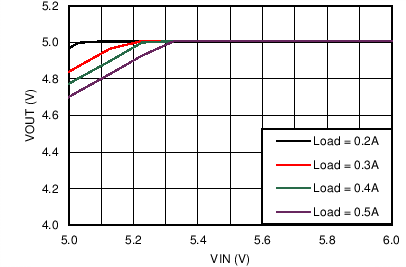
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 1 MHz |
| VOUT = 24 V | FSW = 500 kHz |
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 1 MHz |
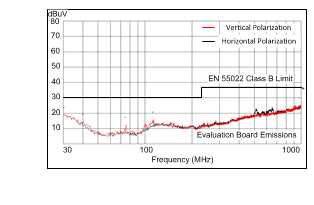
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 500 kHz | IOUT = 0.5 A |
| Measured on the LM43600PWPEVM with L = 44 µH, COUT = 66 µF, CFF = 33 pF. No input filter used. | ||
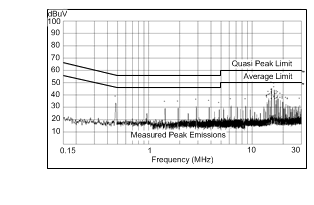
| VOUT = 5 V | FSW = 500 kHz | IOUT = 0.5 A |
| Measured on the LM43600PWPEVM with L = 44 µH, COUT = 66 µF, CFF = 33 pF. Input filter Lin = 1 µH Cd = 47 µF CIN4 = 68 µF | ||
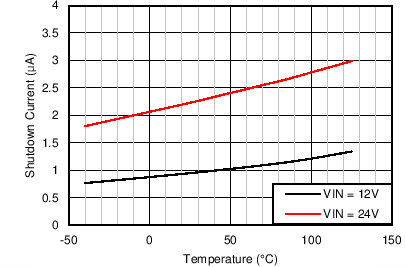
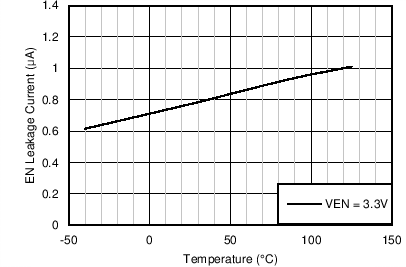
Junction Temperature
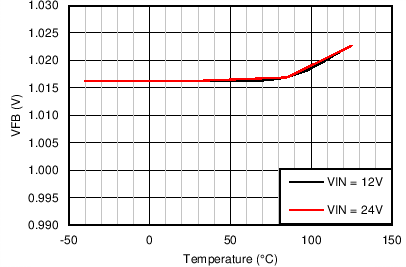
i.
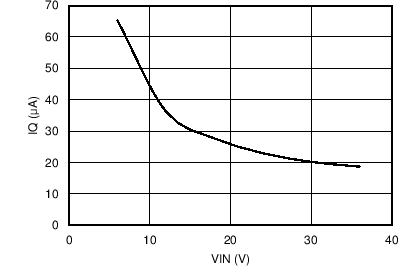
Figure 32. Operation IQ vs VIN with BIAS Connected to VOUT
| VOUT = 3.3 V | FSW = 500 kHz | IOUT = 0 A |