SNVSA13C April 2014 – April 2019 LM46002
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency, Peak-Current-Mode-Controlled, Step-Down Regulator
- 7.3.2 Light Load Operation
- 7.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.4 Enable (ENABLE)
- 7.3.5 VCC, UVLO, and BIAS
- 7.3.6 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking (SS/TRK)
- 7.3.7 Switching Frequency (RT) and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 7.3.8 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time, and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 7.3.9 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.10 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.11 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 7.3.12 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.2.10 BIAS Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitors
- 8.2.2.12 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.13 PGOOD
- 8.2.3 Application Performance Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|16
Orderable Information
8.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
The first criterion for selecting an output inductor is the inductance itself. In most buck converters, this value is based on the desired peak-to-peak ripple current, ΔiL, that flows in the inductor along with the DC load current. As with switching frequency, the selection of the inductor is a tradeoff between size and cost. Higher inductance gives lower ripple current and hence lower output voltage ripple with the same output capacitors. Lower inductance could result in smaller, less expensive component. An inductance that gives a ripple current of 20% to 40% of the 2 A at the typical supply voltage is a good starting point. ΔiL = (1/5 to 2/5) × IOUT. The peak-to-peak inductor current ripple can be found by Equation 13, and the range of inductance can be found by Equation 14 with the typical input voltage used as VIN.
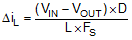
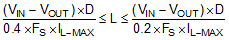
D is the duty cycle of the converter which in a buck converter it can be approximated as D = VOUT / VIN, assuming no loss power conversion. By calculating in terms of amperes, volts, and megahertz, the inductance value comes out in micro henries. The inductor ripple current ratio is defined by:
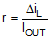
The second criterion is the inductor saturation current rating. The inductor must be rated to handle the maximum load current plus the ripple current:
The LM46002 has both valley current limit and peak current limit. During an instantaneous short, the peak inductor current can be high due to a momentary increase in duty cycle. The inductor current rating must be higher than the HS current limit. It is advised to select an inductor with a larger core saturation margin and preferably a softer rolloff of the inductance value over load current.
In general, lower inductance in switching power supplies is the best choice because it usually corresponds to faster transient response, smaller DCR, and reduced size for more compact designs. But an inductance that is too low can generate an inductor current ripple that is too large so that overcurrent protection at the full load could be falsely triggered. It also generates more conduction loss, since the RMS current is slightly higher relative that with lower current ripple at the same DC current. Larger inductor current ripple also implies larger output voltage ripple with the same output capacitors. With peak-current-mode control, TI does not recommend having an inductor current ripple that is too small. Enough inductor current ripple improves signal-to-noise ratio on the current comparator and makes the control loop more immune to noise.
Once the inductance is determined, the type of inductor must be selected. Ferrite designs have very low core losses and are preferable at high switching frequencies, so design goals can concentrate on copper loss and preventing saturation. Ferrite core material saturates hard, which means that inductance collapses abruptly when the peak design current is exceeded. The ‘hard’ saturation results in an abrupt increase in inductor ripple current and consequent output voltage ripple. Do not allow the core to saturate!
For the design example, a standard 10-μH inductor from Wurth, Coiltronics, or Vishay can be used for the 3.3-V output with plenty of current-rating margin.