SNVS676I August 2010 – April 2018 LM5119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 High Voltage Start-Up Regulator
- 7.3.2 UVLO
- 7.3.3 Enable 2
- 7.3.4 Oscillator and Sync Capability
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifiers and PWM Comparators
- 7.3.6 Ramp Generator
- 7.3.7 Current Limit
- 7.3.8 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 7.3.9 Soft Start
- 7.3.10 HO and LO Output Drivers
- 7.3.11 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.12 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Timing Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor
- 8.2.1.2.3 Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Ramp Resistor and Ramp Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.7 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.10 Restart Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Output Voltage Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 UVLO Divider
- 8.2.1.2.13 MOSFET Snubber
- 8.2.1.2.14 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Two-Phase Design Example
- 8.2.1
Dual-output Design Example
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTV|32
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
RTV Package
32-Pin WQFN
Top View
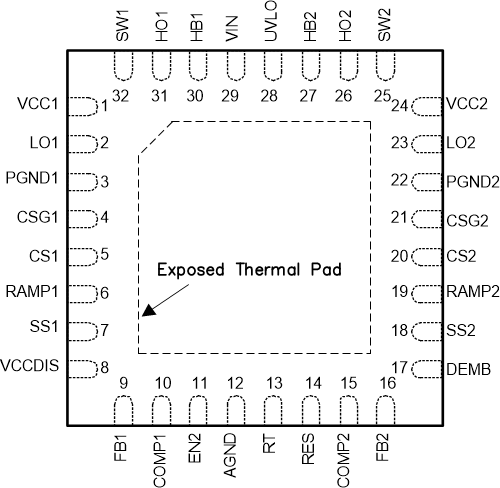
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AGND | 12 | G | Analog ground. Return for the internal 0.8-V voltage reference and analog circuits. |
| COMP1 | 10 | O | Output of the channel1 internal error amplifier. The loop compensation network must be connected between this pin and the FB1 pin. |
| COMP2 | 15 | O | Output of the channel2 internal error amplifier. The loop compensation network must be connected between this pin and the FB2 pin. |
| CS1 | 5 | I | Current sense amplifier input. Connect to the high side of the channel1 current sense resistor. |
| CS2 | 20 | I | Current sense amplifier input. Connect to the high side of the channel2 current sense resistor. |
| CSG1 | 4 | I | Kelvin ground connection to the external current sense resistor. Connect directly to the low side of the channel1 current sense resistor. |
| CSG2 | 21 | I | Kelvin ground connection to the external current sense resistor. Connect directly to the low side of the channel2 current sense resistor. |
| DEMB | 17 | I | Logic input that enables diode emulation when in the low state. In diode emulation mode, the low-side MOSFET is latched off for the remainder of the PWM cycle when the buck inductor current reverses direction (current flow from output to ground). When DEMB is high, diode emulation is disabled allowing current to flow in either direction through the low-side MOSFET. A 50-kΩ pulldown resistor internal to the LM5119 holds DEMB pin low and enables diode emulation if the pin is left floating. |
| EN2 | 11 | I | If the EN2 pin is low, channel2 is disabled. Channel1 and all other functions remain active. The EN2 has a 50-kΩ pullup resistor to enable channel2 when the pin is left floating. |
| FB1 | 9 | I | Feedback input and inverting input of the channel1 internal error amplifier. A resistor divider from the channel1 output to this pin sets the output voltage level. The regulation threshold at the FB1 pin is 0.8 V. |
| FB2 | 16 | I | Feedback input and inverting input of the channel2 internal error amplifier. A resistor divider from the channel2 output to this pin sets the output voltage level. The regulation threshold at the FB2 pin is 0.8 V. |
| HB1 | 30 | P | High-side driver supply for bootstrap gate drive. Connect to the cathode of the channel1 external bootstrap diode and to the bootstrap capacitor. The bootstrap capacitor supplies current to charge the high-side MOSFET gate and must be placed as close to controller as possible. |
| HB2 | 27 | P | High-side driver supply for bootstrap gate drive. Connect to the cathode of the channel2 external bootstrap diode and to the bootstrap capacitor. The bootstrap capacitor supplies current to charge the high-side MOSFET gate and must be placed as close to the controller as possible. |
| HO1 | 31 | O | High-side MOSFET gate drive output. Connect to the gate of the channel1 high-side MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| HO2 | 26 | O | High-side MOSFET gate drive output. Connect to the gate of the channel2 high-side MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| LO1 | 2 | O | Low-side MOSFET gate drive output. Connect to the gate of the channel1 low-side synchronous MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| LO2 | 23 | O | Low-side MOSFET gate drive output. Connect to the gate of the channel2 low-side synchronous MOSFET through a short, low inductance path. |
| PGND1 | 3 | G | Power ground return pin for low-side MOSFET gate driver. Connect directly to the low side of the channel1 current sense resistor. |
| PGND2 | 22 | G | Power ground return pin for low-side MOSFET gate driver. Connect directly to the low side of the channel2 current sense resistor. |
| RAMP1 | 6 | I | PWM ramp signal. An external resistor and capacitor connected between the SW1 pin, the RAMP1 pin and the AGND pin sets the channel1 PWM ramp slope. Proper selection of component values produces a RAMP1 signal that emulates the current in the buck inductor. |
| RAMP2 | 19 | I | PWM ramp signal. An external resistor and capacitor connected between the SW2 pin, the RAMP2 pin and the AGND pin sets the channel2 PWM ramp slope. Proper selection of component values produces a RAMP2 signal that emulates the current in the buck inductor. |
| RES | 14 | O | The restart timer pin for an external capacitor that configures the hiccup mode current limiting. A capacitor on the RES pin determines the time the controller remains off before automatically restarting in hiccup mode. The two regulator channels operate independently. One channel may operate in normal mode while the other is in hiccup mode overload protection. The hiccup mode commences when either channel experiences 256 consecutive PWM cycles with cycle-by-cycle current limiting. After this occurs, a 10-µA current source charges the RES pin capacitor to the 1.25-V threshold which restarts the overloaded channel. |
| RT | 13 | I | The internal oscillator is set with a single resistor between RT and AGND. The recommended maximum oscillator frequency is 1.5 MHz which corresponds to a maximum switching frequency of 750 kHz for either channel. The internal oscillator can be synchronized to an external clock by coupling a positive pulse into RT through a small coupling capacitor. |
| SS1 | 7 | I | An external capacitor and an internal 10-µA current source set the ramp rate of the channel1 error amp reference. The SS1 pin is held low when VCC1 or VCC2 < 4.9 V, UVLO < 1.25 V or during thermal shutdown. |
| SS2 | 18 | I | An external capacitor and an internal 10-µA current source set the ramp rate of the channel2 error amp reference. The SS2 pin is held low when VCC1 or VCC2 < 4.9 V, UVLO < 1.25 V or during thermal shutdown. |
| SW1 | 32 | I/O | Switching node of the buck regulator. Connect to channel1 bootstrap capacitor, the source terminal of the high-side MOSFET and the drain terminal of the low-side MOSFET. |
| SW2 | 25 | I/O | Switching node of the buck regulator. Connect to channel2 bootstrap capacitor, the source terminal of the high-side MOSFET and the drain terminal of the low-side MOSFET. |
| UVLO | 28 | I | Undervoltage lockout programming pin. If the UVLO pin is below 0.4 V, the regulator is in the shutdown mode with all function disabled. If the UVLO pin is greater than 0.4 V and below 1.25 V, the regulator is in standby mode with the VCC regulators operational, the SS pins grounded and no switching at the HO and LO outputs. If the UVLO pin voltage is above 1.25 V, the SS pins are allowed to ramp and pulse width modulated gate drive signals are delivered at the LO and HO pins. A 20-µA current source is enabled when UVLO exceeds 1.25 V and flows through the external UVLO resistors to provide hysteresis. |
| VCCDIS | 8 | I | Optional input that disables the internal VCC regulators when external biasing is supplied. If VCCDIS > 1.25 V, the internal VCC regulators are disabled. The externally supplied bias must be coupled to the VCC pins through a diode. VCCDIS has a 500-kΩ pulldown resistor to ground to enable the VCC regulators when the pin is left floating. The pulldown resistor can be overridden by pulling VCCDIS above 1.25 V with a resistor divider connected to the external bias supply. |
| VIN | 29 | P | Supply voltage input source for the VCC regulators. |
| Thermal Pad | — | Thermal pad of WQFN package. No internal electrical connections. Solder to the ground plane to reduce thermal resistance. | |
(1) G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output, P = Power