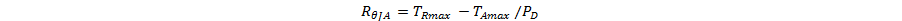SNVS225H February 2003 – June 2015 LP3871 , LP3874
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- KTT|5
Orderable Information
9 Power Supply Recommendations
9.1 Power Dissipation
LP3871 and LP3874 can deliver a continuous current of 0.8 A over the full operating temperature range. A heatsink may be required depending on the maximum power dissipation and maximum ambient temperature of the application. Under all possible conditions, the junction temperature must be within the range specified under operating conditions. The total power dissipation of the device is given by:
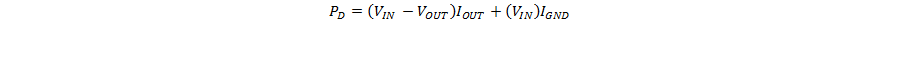
where
- IGND is the operating ground current of the device (specified under Electrical Characteristics).
The maximum allowable temperature rise (TRmax) depends on the maximum ambient temperature (TAmax) of the application, and the maximum allowable junction temperature (TJmax):
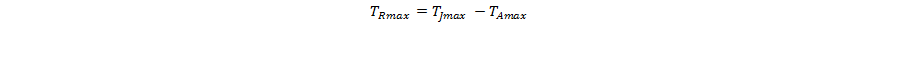
The maximum allowable value for junction to ambient thermal resistance, RθJA, can be calculated using the formula: