SLVSH53 December 2023 MCT8315Z
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 PWM Control Mode (1x PWM Mode)
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 Step-Down Mixed-Mode Buck Regulator
- 8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.6 Charge Pump
- 8.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.8 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.9 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.10 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.11 Active Demagnetization
- 8.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 8.3.13 Hall Comparators (Analog Hall Inputs)
- 8.3.14 Advance Angle
- 8.3.15 FGOUT Signal
- 8.3.16
Protections
- 8.3.16.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (NPOR)
- 8.3.16.2 AVDD Undervoltage Lockout (AVDD_UV)
- 8.3.16.3 Buck Undervoltage Lockout (BUCK_UV)
- 8.3.16.4 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.16.5 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 8.3.16.6 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.16.7 Buck Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.16.8 Motor Lock (MTR_LOCK)
- 8.3.16.9 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.16.10 Thermal Shutdown (OTSD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RRY|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RRY|32
Orderable Information
8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
A 3.3-V linear regulator is integrated into the MCT8315Z family of devices and is available for use by external circuitry. The AVDD regulator is used for powering up the internal digital circuitry of the device and additionally, this regulator can also provide the supply voltage for a low-power MCU or other circuitry supporting low current (up to 30 mA). The output of the AVDD regulator should be bypassed near the AVDD pin with a X5R or X7R, 1-µF, 6.3-V ceramic capacitor routed directly back to the adjacent AGND ground pin.
The AVDD nominal, no-load output voltage is 3.3 V.
 Figure 8-15 AVDD Linear Regulator Block
Diagram
Figure 8-15 AVDD Linear Regulator Block
DiagramUse Equation 1 to calculate the power dissipated in the device by the AVDD linear regulator with VM as supply (BUCK_PS_DIS = 1b)
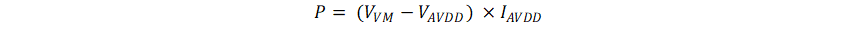
For example, at a VVM of 24 V, drawing 20 mA out of AVDD results in a LDO power dissipation as shown in Equation 2.
Use Equation 3 to calculate the power dissipated in the device by the AVDD linear regulator with buck output as supply (BUCK_PS_DIS = 0b)
For example, at a VFB_BK of 5 V, drawing 20 mA out of AVDD results in a LDO power dissipation as shown in Equation 4.