SBOS479A March 2009 – April 2018 OPA356-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
To achieve a maximally-flat, second-order Butterworth frequency response, the feedback pole must be set to:
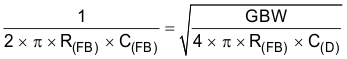
Use Equation 2 to calculate the bandwidth.
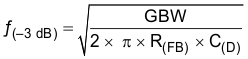
For other transimpedance bandwidths, consider the high-speed CMOS OPA380 (90-MHz GBW), OPA354
(100-MHz GBW), OPA300 (180-MHz GBW), OPA355 (200-MHz GBW), or OPA656 and OPA657 (400-MHz GBW).
For single-supply applications, the +INx input can be biased with a positive DC voltage to allow the output to reach true zero when the photodiode is not exposed to any light, and respond without the added delay that results from coming out of the negative rail; this configuration is shown in Figure 30. This bias voltage appears across the photodiode, providing a reverse bias for faster operation.
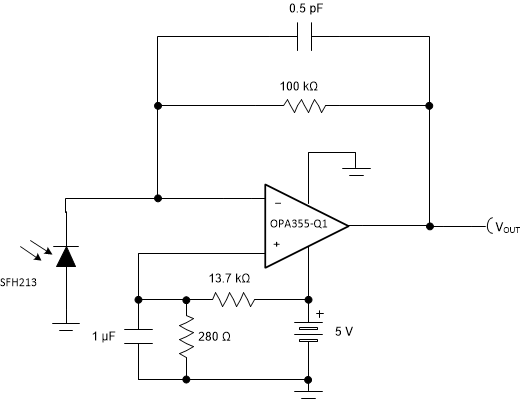 Figure 30. Single-Supply Transimpedance Amplifier
Figure 30. Single-Supply Transimpedance Amplifier
For additional information, see the Compensate Transimpedance Amplifiers Intuitively application bulletin.