SBASA67 June 2023 OPT4060
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DTS|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
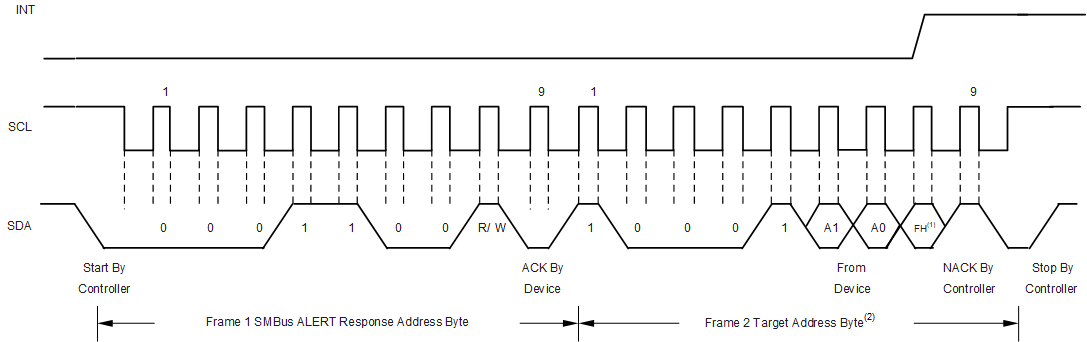
8.5.2.4 SMBus Alert Response
The SMBus alert response provides a quick identification for which device issued the interrupt. Without this alert response capability, the processor does not know which device pulled the interrupt line when there are multiple target devices connected.
The OPT4060 is designed to respond to the SMBus alert response address, when in the latched window-style comparison mode. The OPT4060 does not respond to the SMBus alert response when in transparent mode.
Figure 8-7 shows the OPT4060 device behavior to the SMBus alert response. When the interrupt line to the processor is pulled to active, the controller can broadcast the alert response target address. Following this alert response, any target devices that generated an alert identify themselves by acknowledging the alert response and sending respective I2C address on the bus. The alert response can activate several different target devices simultaneously. If more than one target attempts to respond, bus arbitration rules apply. The device with the lowest address wins the arbitration. If the OPT4060 loses the arbitration, the device does not acknowledge the I2C transaction and the INT pin remains in an active state, prompting the I2C controller processor to issue a subsequent SMBus alert response. When the OPT4060 wins the arbitration, the device acknowledges the transaction and sets the INT pin to inactive. The controller can issue that same command again, as many times as necessary to clear the INT pin. See Interrupt Modes of OperationInterrupt Modes of Operation for additional details of how the flags and INT pin are controlled. The controller can obtain information about the source of the OPT4060 interrupt from the address broadcast in the above process. The FLAG_H value is sent as the final LSB of the address to provide the controller additional information about the cause of the OPT4060 interrupt. If the controller requires additional information, the result register or the configuration register can be queried. The FLAG_H and FLAG_L registers are not cleared upon an SMBus alert response.