SLES092E April 2003 – July 2019 PCM1753 , PCM1754 , PCM1755
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Mode Control Registers (PCM1753/55)
- 8.6.1.1 User-Programmable Mode Controls
- 8.6.1.2
Register Definitions
- 8.6.1.2.1 ATx[7:0]: Digital Attenuation Level Setting
- 8.6.1.2.2 MUTx: Soft Mute Control
- 8.6.1.2.3 OVER: Oversampling Rate Control
- 8.6.1.2.4 SRST: Reset
- 8.6.1.2.5 DACx: DAC Operation Control
- 8.6.1.2.6 DM12: Digital De-Emphasis Function Control
- 8.6.1.2.7 DMF[1:0]: Sampling Frequency Selection for the De-Emphasis Function
- 8.6.1.2.8 FMT[2:0]: Audio Interface Data Format
- 8.6.1.2.9 FLT: Digital Filter Rolloff Control
- 8.6.1.2.10 DREV: Output Phase Select
- 8.6.1.2.11 ZREV: Zero Flag Polarity Select
- 8.6.1.2.12 AZRO: Zero Flag Function Select
- 8.6.1
Mode Control Registers (PCM1753/55)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBQ|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.5.1.1 Register Write Operation
All write operations for the serial control port use 16-bit data words. Figure 26 lists the control data word format. The most significant bit must be a 0. There are seven bits, labeled IDX[6:0], that set the register index (or address) for the write operation. The least significant eight bits, D[7:0], contain the data to be written to the register specified by IDX[6:0].
Figure 27 lists the functional timing diagram for writing to the serial control port. ML is held at a logic 1 state until a register needs to be written. To start the register write cycle, ML is set to logic 0. Sixteen clocks are then provided on MC, corresponding to the 16 bits of the control data word on MD. After the sixteenth clock cycle has completed, ML is set to logic 1 to latch the data into the indexed mode control register.
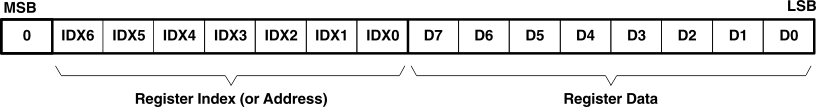 Figure 26. Control Data Word Format for MD
Figure 26. Control Data Word Format for MD 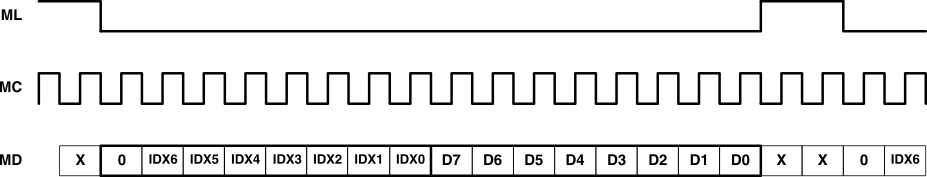 Figure 27. Register Write Operation
Figure 27. Register Write Operation