SNIS227C May 2021 – June 2022 TMP126-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Descriptions
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.4.4.2 Comparator Mode
When the INT_COMP bit in the Configuration register is set to 0, the device is in comparator mode. Changing the device to Comparator mode from Interrupt mode will immediately clear the Alert_Status register and reset the ALERT pin. The TMP126-Q1 will then behave as described in this section at the next temperature conversion. In this mode, the device compares the temperature result at the end of every conversion with the limit registers. If the flag is enabled to assert the ALERT, the ALERT will reflect the status bit of the limits. For example, if the THigh_Flag alert is enabled and the THigh_Limit is exceeded, the ALERT will assert while the THigh_Status bit is 1. If the THigh_Flag alert is not enabled in the Alert_Enable register, the ALERT will not assert when THigh_Status bit is 1.
After a conversion below the Hysteresis the Status bit will be set to '0' and the ALERT will de-assert. Unlike the interrupt mode, the ALERT behavior is not affected when reading the Alert_Status register. If the Alert flag is disabled in the Alert_Enable register, the ALERT pin will de-assert immediately if the respective bit is causing an alert. If there are two statuses that are affecting the ALERT such as a THigh_Limit and Slew_Rate_Limit and one of the alerts is disabled, the ALERT will remain asserted until the other limit is not exceeded. For example, if the ALERT has asserted due to a high slew rate and a high temperature and the slew rate alert is then disabled, the ALERT will only de-assert when the temperature drops below the hysteresis value. If both alerts were disabled the ALERT would then de-assert.
Thus, this mode effectively makes the device behave like a high-limit threshold detector. This mode can be used in applications where detecting if the temperature has exceeded a desired threshold is necessary. Figure 8-8 shows a timing diagram of this mode.
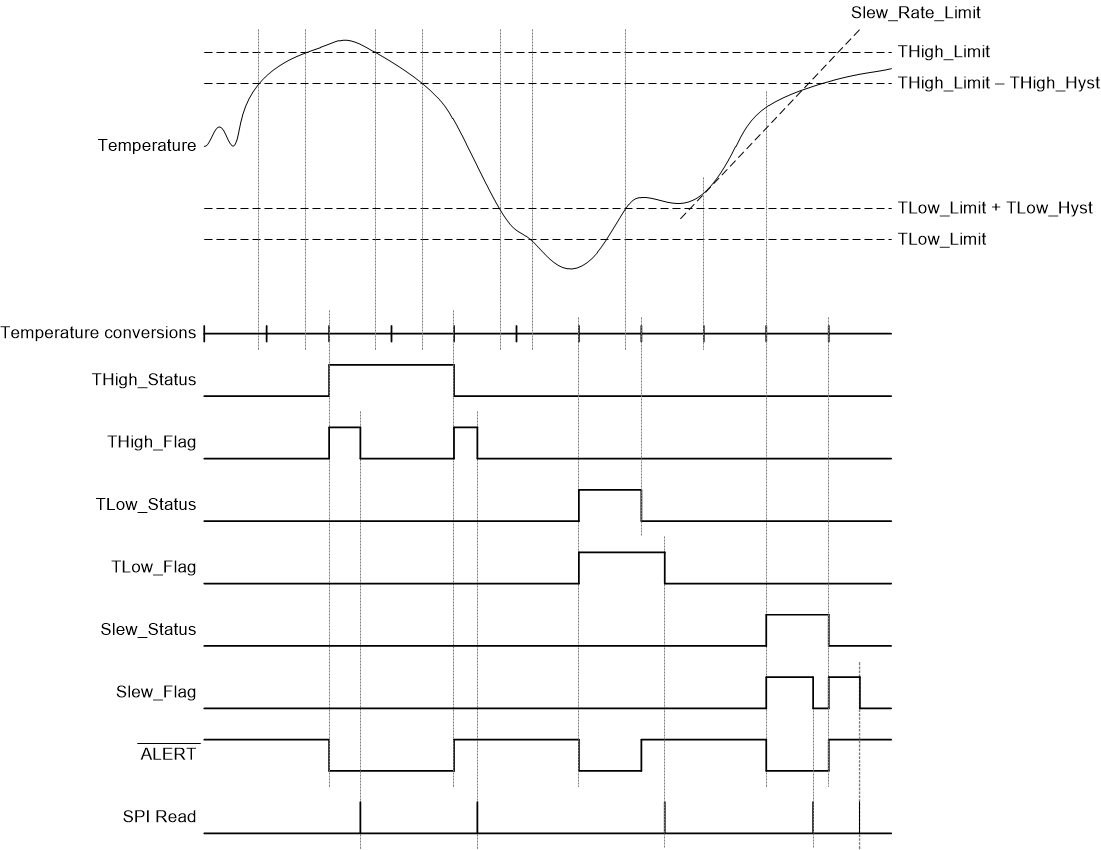 Figure 8-8 Comparator Mode Timing Diagram
Figure 8-8 Comparator Mode Timing Diagram