SBOS762B November 2016 – June 2017 TMP468
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 7.6.1.1 Pointer Register
- 7.6.1.2 Local and Remote Temperature Value Registers
- 7.6.1.3 Software Reset Register
- 7.6.1.4 THERM Status Register
- 7.6.1.5 THERM2 Status Register
- 7.6.1.6 Remote Channel Open Status Register
- 7.6.1.7 Configuration Register
- 7.6.1.8 η-Factor Correction Register
- 7.6.1.9 Remote Temperature Offset Register
- 7.6.1.10 THERM Hysteresis Register
- 7.6.1.11 Local and Remote THERM and THERM2 Limit Registers
- 7.6.1.12 Block Read - Auto Increment Pointer
- 7.6.1.13 Lock Register
- 7.6.1.14 Manufacturer and Device Identification Plus Revision Registers
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power supply | V+ | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| Input voltage | THERM, THERM2, SDA, SCL, and ADD only | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| D1+ through D8+ | –0.3 | ((V+) + 0.3) and ≤ 6 | ||
| D– only | –0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| Input current | SDA sink | –25 | mA | |
| All other pins | –10 | 10 | ||
| Operating temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Junction temperature (TJ, maximum) | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –60 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±750 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V+ | Supply voltage | 1.7 | 3.6 | V | |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| TD | Remote junction temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TMP468 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGT (VQFN) | YFF (DSBGA) | |||
| 16 PINS | 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 46 | 76 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 43 | 0.7 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 17 | 13 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.8 | 0.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 5 | 13 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
at TA = –40°C to +125°C and V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT | |||||||
| TLOCAL | Local temperature sensor accuracy | TA = 20°C to 30°C, V+ = 1.7 V to 2 V (DSBGA) | –0.35 | ±0.125 | 0.35 | °C | |
| TA = –40°C to 125°C, V+ = 1.7 V to 2 V (DSBGA) | –0.75 | ±0.125 | 0.75 | °C | |||
| TA = –40°C to 100°C, V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V (VQFN) | |||||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C, V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V | –1 | ±0.5 | 1 | °C | |||
| TREMOTE | Remote temperature sensor accuracy | (DSBGA): TA = –10°C to 50°C, TD = –55°C to 150°C V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V |
–0.75 | ±0.125 | 0.75 | °C | |
| (VQFN): TA = –10°C to 85°C, TD = –55°C to 150°C V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V |
|||||||
| TA = –40°C to 125°C, TD = –55°C to 150°C V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V |
–1 | ±0.5 | 1 | ||||
| Local temperature error supply sensitivity | V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V | –0.15 | ±0.05 | 0.15 | °C/V | ||
| Remote temperature error supply sensitivity | V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V | –0.25 | ±0.1 | 0.25 | °C/V | ||
| Temperature resolution (local and remote) |
0.0625 | °C | |||||
| ADC conversion time | One-shot mode, per channel (local or remote) | 16 | 17 | ms | |||
| ADC resolution | 13 | Bits | |||||
| Remote sensor source current | High | Series resistance 1 kΩ (maximum) | 120 | µA | |||
| Medium | 45 | ||||||
| Low | 7.5 | ||||||
| η | Remote transistor ideality factor | 1.008 | |||||
| SERIAL INTERFACE (SCL, SDA) | |||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × (V+) | V | ||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.3 × (V+) | V | ||||
| Hysteresis | 200 | mV | |||||
| SDA output-low sink current | 20 | mA | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IO = –20 mA, V+ ≥ 2 V | 0.15 | 0.4 | V | ||
| IO = –15 mA, V+ < 2 V | 0.2 × V+ | V | |||||
| Serial bus input leakage current | 0 V ≤ VIN ≤ 3.6 V | –1 | 1 | μA | |||
| Serial bus input capacitance | 4 | pF | |||||
| DIGITAL INPUTS (ADD) | |||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × (V+) | V | ||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.3 | 0.3 × (V+) | V | |||
| Input leakage current | 0 V ≤ VIN ≤ 3.6 V | –1 | 1 | μA | |||
| Input capacitance | 4 | pF | |||||
| DIGITAL OUTPUTS (THERM, THERM2) | |||||||
| Output-low sink current | VOL = 0.4 V | 6 | mA | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IO = –6 mA | 0.15 | 0.4 | V | ||
| IOH | High-level output leakage current | VO = V+ | 1 | μA | |||
| POWER SUPPLY | |||||||
| V+ | Specified supply voltage range | 1.7 | 3.6 | V | |||
| IQ | Quiescent current | Active conversion, local sensor | 240 | 375 | µA | ||
| Active conversion, remote sensors | 400 | 600 | |||||
| Standby mode (between conversions) | 15 | 21 | |||||
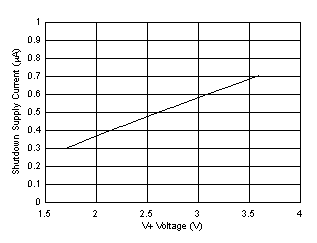
| Shutdown mode, serial bus inactive | 0.3 | 4 | |||||
| Shutdown mode, serial bus active, fS = 400 kHz | 120 | µA | |||||
| Shutdown mode, serial bus active, fS = 2.56 MHz | 300 | µA | |||||
| POR | Power-on-reset threshold | Rising edge | 1.5 | 1.65 | V | ||
| Falling edge | 1 | 1.2 | 1.35 | ||||
| POH | Power-on-reset hysteresis | 0.2 | V | ||||
6.6 Two-Wire Timing Requirements
at TA = –40°C to +125°C and V+ = 1.7 V to 3.6 V (unless otherwise noted)The master and the slave have the same V+ value. Values are based on statistical analysis of samples tested during initial release.
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fSCL | SCL operating frequency | Fast mode | 0.001 | 0.4 | MHz | |
| High-speed mode | 0.001 | 2.56 | ||||
| tBUF | Bus free time between stop and start condition | Fast mode | 1300 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 160 | |||||
| tHD;STA | Hold time after repeated start condition. After this period, the first clock is generated. |
Fast mode | 600 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 160 | |||||
| tSU;STA | Repeated start condition setup time | Fast mode | 600 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 160 | |||||
| tSU;STO | Stop condition setup time | Fast mode | 600 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 160 | |||||
| tHD;DAT | Data hold time when SDA | Fast mode | 0 | (1) | ns | |
| High-speed mode | 0 | 130 | ||||
| tVD;DAT | Data valid time(2) | Fast mode | 0 | 900 | ns | |
| High-speed mode | — | — | ||||
| tSU;DAT | Data setup time | Fast mode | 100 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 20 | |||||
| tLOW | SCL clock low period | Fast mode | 1300 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 250 | |||||
| tHIGH | SCL clock high period | Fast mode | 600 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 60 | |||||
| tF – SDA | Data fall time | Fast mode | 20 × (V+ / 5.5) | 300 | ns | |
| High-speed mode | 100 | |||||
| tF, tR – SCL | Clock fall and rise time | Fast mode | 300 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | 40 | |||||
| tR | Rise time for SCL ≤ 100 kHz | Fast mode | 1000 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode | ||||||
| Serial bus timeout | Fast mode | 15 | 20 | ms | ||
| High-speed mode | 15 | 20 | ||||
(1) The maximum tHD;DAT can be 0.9 µs for fast mode, and is less than the maximum tVD;DAT by a transition time.
(2) tVD;DAT = time for data signal from SCL LOW to SDA output (HIGH to LOW, depending on which is worse).
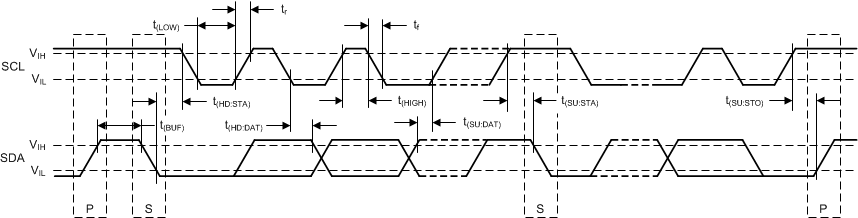 Figure 1. Two-Wire Timing Diagram
Figure 1. Two-Wire Timing Diagram
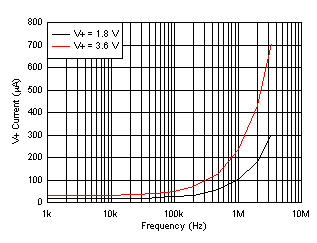
6.7 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C and V+ = 3.6 V (unless otherwise noted)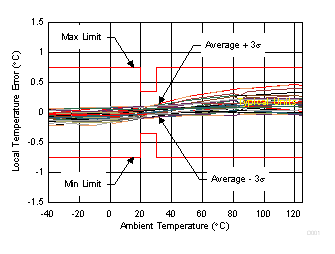
| Typical behavior of 95 DSBGA devices over temperature at V+ = 1.8 V |
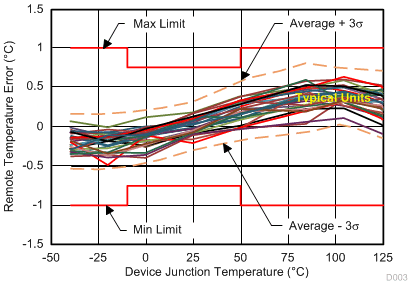
| Typical behavior of 30 DSBGA devices over temperature at V+ = 1.8 V with the remote diode junction at 150°C. |
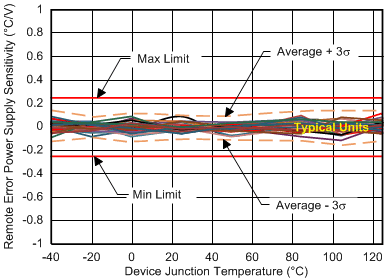
| Typical behavior of 30 devices over temperature with V+ from 1.8 V to 3.6 V |
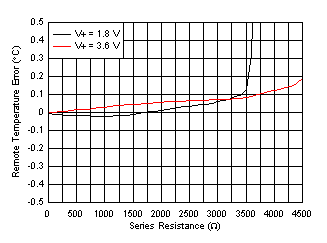
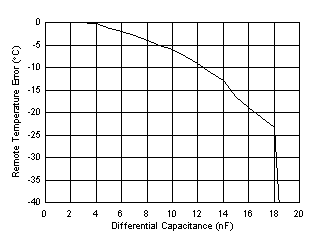
| No physical capacitance during measurement |
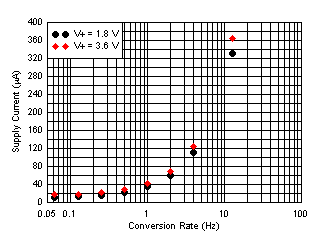
(at Default Conversion Rate of 16 Conversions Per Second)
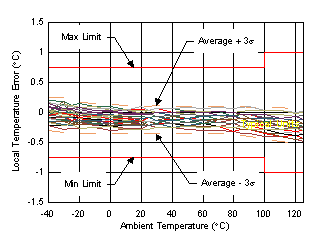
| Typical behavior of 75 VQFN devices over temperature at V+ = 1.8 V |
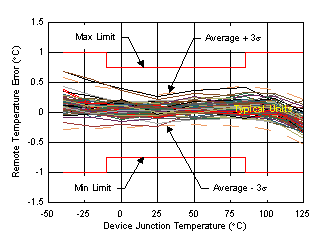
| Typical behavior of 75 VQFN devices over temperature at V+ = 1.8 V with the remote diode junction at 150°C. |
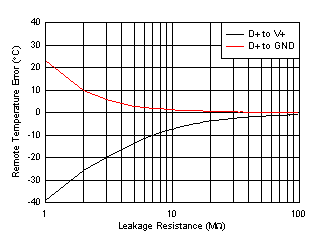
| No physical series resistance on D+, D– pins during measurement |
Differential Capacitance
| 16 samples per second (default mode) |
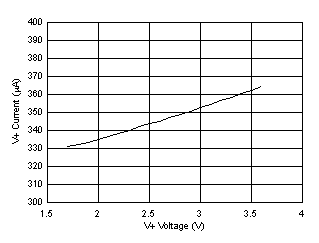
vs SCL Clock Frequency