SPNS226E June 2013 – November 2016 TMS570LS0714
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Device Overview
- 2 Revision History
- 3 Device Comparison
-
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagrams
- 4.2
Signal Descriptions
- 4.2.1
PGE Package Terminal Functions
- 4.2.1.1 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADCs)
- 4.2.1.2 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- 4.2.1.3 Enhanced Capture Modules (eCAP)
- 4.2.1.4 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Modules (eQEP)
- 4.2.1.5 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulator Modules (ePWM)
- 4.2.1.6 General-Purpose Input/Output (GIO)
- 4.2.1.7 Controller Area Network Controllers (DCAN)
- 4.2.1.8 Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
- 4.2.1.9 Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 4.2.1.10 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
- 4.2.1.11 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.2.1.12 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
- 4.2.1.13 System Module Interface
- 4.2.1.14 Clock Inputs and Outputs
- 4.2.1.15 Test and Debug Modules Interface
- 4.2.1.16 Flash Supply and Test Pads
- 4.2.1.17 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2V nominal
- 4.2.1.18 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3V nominal
- 4.2.1.19 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
- 4.2.2
PZ Package Terminal Functions
- 4.2.2.1 High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- 4.2.2.2 Enhanced Capture Modules (eCAP)
- 4.2.2.3 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Modules (eQEP)
- 4.2.2.4 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulator Modules (ePWM)
- 4.2.2.5 General-Purpose Input/Output (GIO)
- 4.2.2.6 Controller Area Network Interface Modules (DCAN1, DCAN2)
- 4.2.2.7 Standard Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPI2 and SPI4)
- 4.2.2.8 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI1 and MibSPI3)
- 4.2.2.9 Local Interconnect Network Controller (LIN)
- 4.2.2.10 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converter (MibADC)
- 4.2.2.11 System Module Interface
- 4.2.2.12 Clock Inputs and Outputs
- 4.2.2.13 Test and Debug Modules Interface
- 4.2.2.14 Flash Supply and Test Pads
- 4.2.2.15 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
- 4.2.2.16 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
- 4.2.2.17 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
- 4.2.1
PGE Package Terminal Functions
- 4.3 Pin Multiplexing
- 4.4 Buffer Type
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Input/Output Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.6 Power Consumption Over Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.8 Timing and Switching Characteristics
-
6 System Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Device Power Domains
- 6.2 Voltage Monitor Characteristics
- 6.3 Power Sequencing and Power-On Reset
- 6.4 Warm Reset (nRST)
- 6.5 ARM Cortex-R4F CPU Information
- 6.6 Clocks
- 6.7 Clock Monitoring
- 6.8 Glitch Filters
- 6.9 Device Memory Map
- 6.10 Flash Memory
- 6.11 Tightly Coupled RAM Interface Module
- 6.12 Parity Protection for Accesses to Peripheral RAMs
- 6.13 On-Chip SRAM Initialization and Testing
- 6.14 Vectored Interrupt Manager
- 6.15 DMA Controller
- 6.16 Real-Time Interrupt Module
- 6.17 Error Signaling Module
- 6.18 Reset/Abort/Error Sources
- 6.19 Digital Windowed Watchdog
- 6.20 Debug Subsystem
-
7 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 7.1 I/O Timings
- 7.2
Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM)
- 7.2.1 ePWM Clocking and Reset
- 7.2.2 Synchronization of ePWMx Time-Base Counters
- 7.2.3 Synchronizing all ePWM Modules to the N2HET1 Module Time Base
- 7.2.4 Phase-Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 7.2.5 ePWM Synchronization with External Devices
- 7.2.6 ePWM Trip Zones
- 7.2.7 Triggering of ADC Start of Conversion Using ePWMx SOCA and SOCB Outputs
- 7.2.8 Enhanced Translator-Pulse Width Modulator (ePWMx) Timings
- 7.3 Enhanced Capture Modules (eCAP)
- 7.4 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP)
- 7.5 12-Bit Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converter (MibADC)
- 7.6 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 7.7 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET)
- 7.8 Controller Area Network (DCAN)
- 7.9 Local Interconnect Network Interface (LIN)
- 7.10 Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 7.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module
- 7.12 Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface
- 8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PZ|100
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Specifications
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
Over Operating Free-Air Temperature Range| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage range: | VCC(2) | –0.3 | 1.43 | V | |
| VCCIO, VCCP(2) | –0.3 | 4.6 | |||
| VCCAD(2) | –0.3 | 6.25 | |||
| Input voltage | All input pins, with exception of ADC pins | –0.3 | 4.6 | V | |
| ADC input pins | –0.3 | 6.25 | |||
| Output voltage | All output pins | –0.3 | 4.6 | V | |
| Input clamp current | IIK (VI < 0 or VI > VCCIO) All pins, except AD1IN[23:0] or AD2IN[15:0] |
–20 | 20 | mA | |
| IIK (VI < 0 or VI > VCCAD) AD1IN[23:0] or AD2IN[15:0] |
–10 | 10 | |||
| Total | –40 | 40 | |||
| Output clamp current | IOK (VO < 0 or VO > VCCIO) All pins, except AWM1_EXT_x |
–20 | 20 | mA | |
| Total | –40 | 40 | |||
| Operating free-air temperature (TA) | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Operating junction temperature (TJ) | –40 | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature (Tstg) | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
5.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) performance: | Human Body Model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±2 | kV | |
| Charged Device Model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 |
All pins | ±500 | V | ||
| 100-pin PZ corner pins (1, 25, 26, 50, 51, 75, 76, 100) | ±750 | V | |||
| 144-pin PGE corner pins (1, 36, 37, 72, 73, 108, 109, 144) | ±750 | V | |||
5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)(1)(2)
| NOMINAL CVDD VOLTAGE (V) | JUNCTION TEMPERATURE (Tj) |
LIFETIME POH |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 105ºC | 100K |
5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions(1)
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Digital logic supply voltage (Core) | 1.14 | 1.2 | 1.32 | V | |||
| VCCIO | Digital logic supply voltage (I/O) | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V | |||
| VCCAD | MibADC supply voltage | 3 | 5.25 | V | ||||
| VCCP | Flash pump supply voltage | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V | |||
| VSS | Digital logic supply ground | 0 | V | |||||
| VSSAD | MibADC supply ground | –0.1 | 0.1 | V | ||||
| VADREFHI | Analog-to-digital high-voltage reference source | VSSAD | VCCAD | V | ||||
| VADREFLO | Analog-to-digital low-voltage reference source | VSSAD | VCCAD | V | ||||
| VSLEW | Maximum positive slew rate for VCCIO, VCCAD and VCPP supplies | 1 | V/μs | |||||
| Vhys | Input hysteresis | All inputs | 180 | mV | ||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | All inputs | –0.3 | 0.8 | V | |||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | All inputs | 2 | VCCIO + 0.3 | V | |||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature(2) | –40 | 150 | °C | ||||
5.5 Input/Output Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions(1)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = IOLmax | 0.2VCCIO | V | ||||
| IOL = 50 µA, standard output mode | 0.2 | |||||||
| IOL = 50 µA, low-EMI output mode (see Section 7.1.2.1) |
0.2VCCIO | |||||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = IOHmax | 0.8VCCIO | V | ||||
| IOH = 50 µA, standard output mode | VCCIO - 0.3 | |||||||
| IOH = 50 µA, low-EMI output mode (see Section 7.1.2.1) |
0.8VCCIO | |||||||
| IIC | Input clamp current (I/O pins) | VI < VSSIO - 0.3 or VI > VCCIO + 0.3 |
–3.5 | 3.5 | mA | |||
| II | Input current (I/O pins) | IIH Pulldown 20 µA | VI = VCCIO | 5 | 40 | µA | ||
| IIH Pulldown 100 µA | VI = VCCIO | 40 | 195 | |||||
| IIL Pullup 20 µA | VI = VSS | –40 | –5 | |||||
| IIL Pullup 100 µA | VI = VSS | –195 | –40 | |||||
| All other pins | No pullup or pulldown | –1 | 1 | |||||
| CI | Input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||||
| CO | Output capacitance | 3 | pF | |||||
5.6 Power Consumption Over Recommended Operating Conditions
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | VCC digital supply current (operating mode) fVCLK = fHCLK/2; Flash in pipelined mode; VCCmax |
fHCLK = 100 MHz | 130 (3) | 270 (1) | mA | ||
| fHCLK = 160 MHz | 160 (3) | 300 (1) | |||||
| VCC digital supply current (LBIST/PBIST mode) | LBIST/PBIST clock frequency = 50 MHz | 150(3) | 290(2)(4) | mA | |||
| LBIST/PBIST clock frequency = 80 MHz | 215(3) | 360 (2)(4) | |||||
| LBIST/PBIST clock frequency = 90 MHz | 240(3) | 390 (2)(4) | |||||
| ICCIO | VCCIO digital supply current (operating mode) | No DC load, VCCmax | 15 | mA | |||
| ICCAD | VCCAD supply current (operating mode) | Single ADC operational, VCCADmax | 15 | mA | |||
| Both ADCs operational, VCCADmax | 30 | ||||||
| ICCREFHI | ADREFHI supply current (operating mode) | Single ADC operational, ADREFHImax | 3 | mA | |||
| Both ADCs operational, ADREFHImax | 6 | ||||||
| ICCP | VCCP supply current | Read from 1 bank and program another bank, VCCPmax | 55 | mA | |||
- linearly with voltage
- by 0.85 mA/MHz for lower operating frequency when fHCLK= 2 * fVCLK
- for lower junction temperature by the equation below where TJK is the junction temperature in Kelvin and the result is in milliamperes.
126 - 0.005 e0.024 TJK
- linearly with voltage
- by 0.85 mA/MHz for lower operating frequency
- for lower junction temperature by the equation below where TJK is the junction temperature in Kelvin and the result is in milliamperes.
126 - 0.005 e0.024 TJK
5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
Table 5-1 shows the thermal resistance characteristics for the QFP - PGE mechanical package.
Table 5-2 shows the thermal resistance characteristics for the QFP - PZ mechanical package.
5.8 Timing and Switching Characteristics
5.8.1 SYSCLK (Frequencies)
5.8.1.1 Switching Characteristics over Recommended Operating Conditions for Clock Domains
Table 5-3 Clock Domain Timing Specifications
5.8.1.2 Wait States Required - PGE and PZ Packages
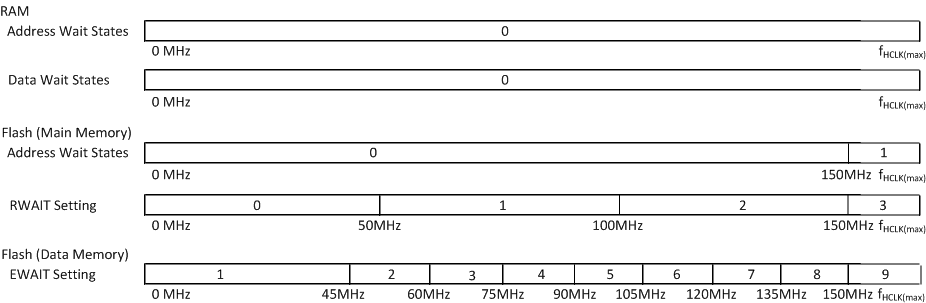 Figure 5-1 Wait States Scheme — PGE, 160 MHz
Figure 5-1 Wait States Scheme — PGE, 160 MHz
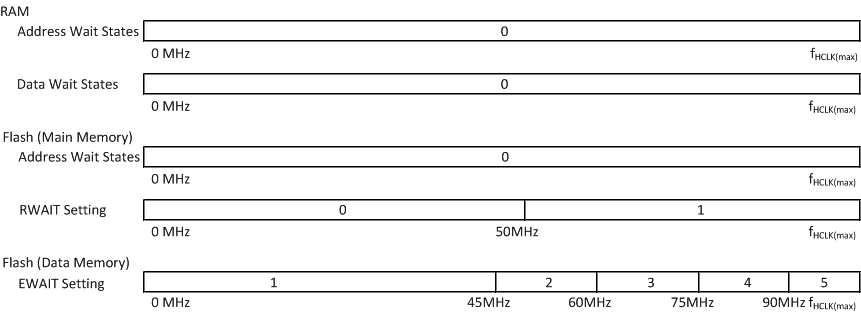 Figure 5-2 Wait States Scheme — PZ, 100 MHz
Figure 5-2 Wait States Scheme — PZ, 100 MHz
As shown in Figure 5-1 and Figure 5-2, the TCM RAM can support program and data fetches at full CPU speed without any address or data wait states required.
The TCM flash can support zero address and data wait states up to a CPU speed of 50 MHz in nonpipelined mode. The flash supports a maximum CPU clock speed of 160 MHz in pipelined mode for the PGE Package, and 100 MHz for the PZ package.
The flash wrapper defaults to nonpipelined mode with zero address wait state and one random-read data wait state.