SLOS369G July 2002 – October 2015 TPA2005D1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGN|8
- DRB|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
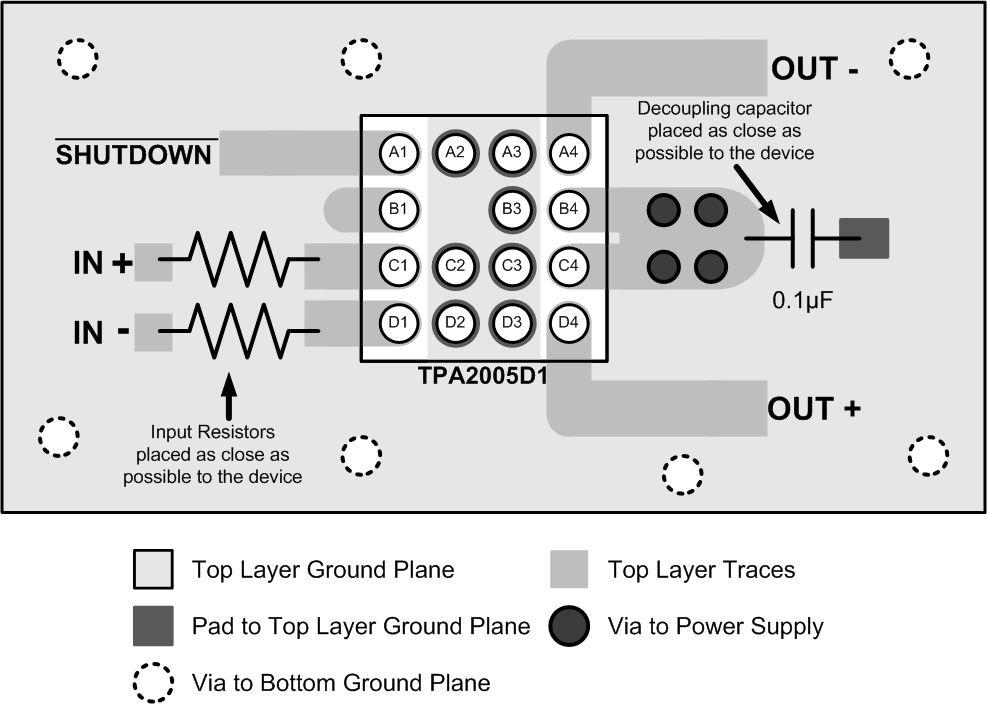
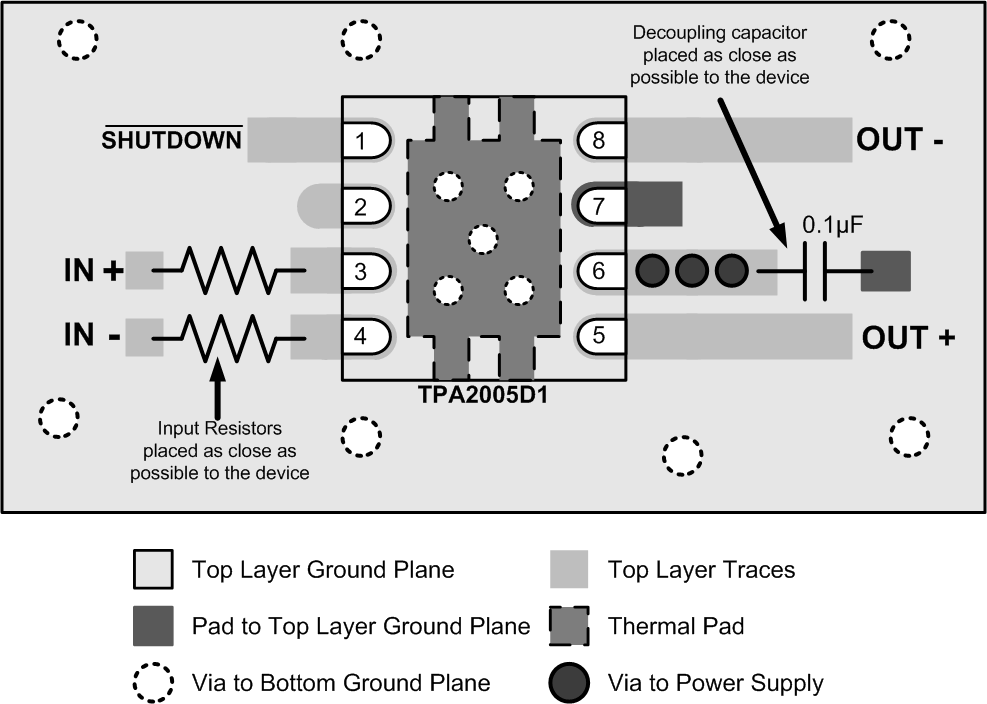
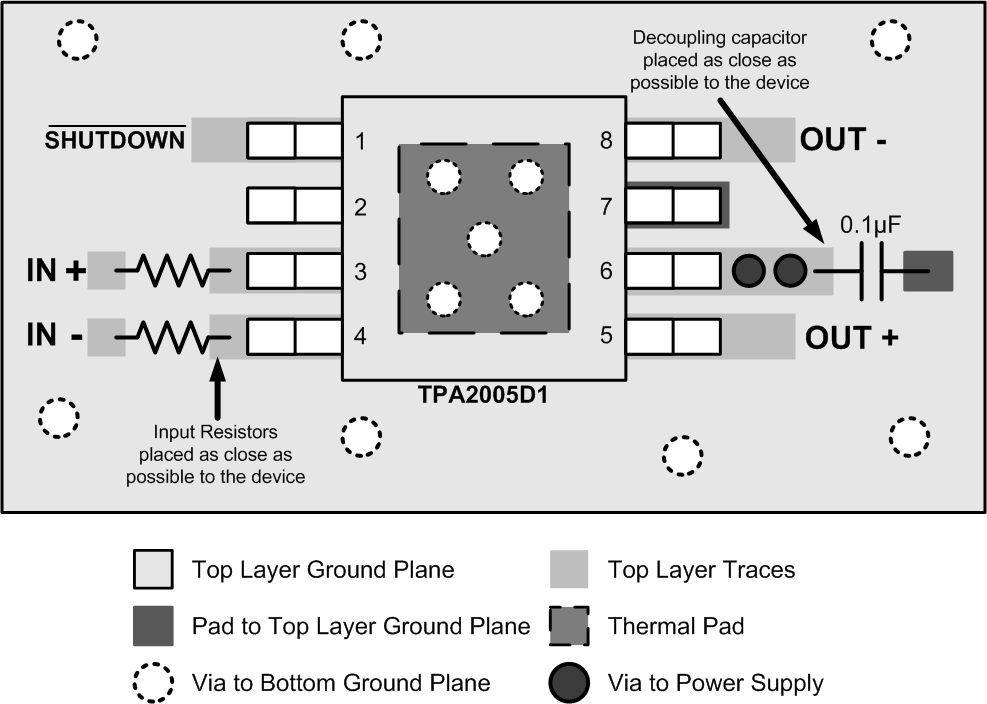
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
12.1.1 Component Location
Place all the external components close to the TPA2005D1. The input resistors need to be close to the TPA2005D1 input pins so noise does not couple on the high impedance nodes between the input resistors and the input amplifier of the TPA2005D1. Placing the decoupling capacitor, CS, close to the TPA2005D1 is important for the efficiency of the class-D amplifier. Any resistance or inductance in the trace between the device and the capacitor can cause a loss in efficiency.
12.1.2 Trace Width
Make the high current traces going to pins VDD, GND, VO+ and VO- of the TPA2005D1 have a minimum width of 0,7 mm. If these traces are too thin, the TPA2005D1's performance and output power will decrease. The input traces do not need to be wide, but do need to run side-by-side to enable common-mode noise cancellation.
12.1.3 MicroStar Junior™ BGA Specifications
Use the following MicroStar Junior BGA ball diameters:
- 0,25 mm diameter solder mask
- 0,28 mm diameter solder paste mask/stencil
- 0,38 mm diameter copper trace
Figure 44 shows how to lay out a board for the TPA2005D1 MicroStar Junior BGA.
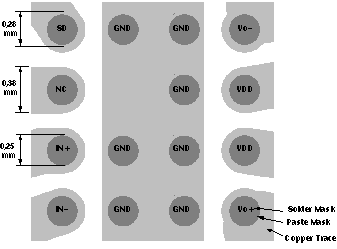 Figure 44. TPA2005D1 MicroStar Junior BGA Board Layout (Top View)
Figure 44. TPA2005D1 MicroStar Junior BGA Board Layout (Top View)