SLVS931B November 2009 – December 2016 TPS2556 , TPS2557
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Current-Limiting Power-Distribution Switch
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Orderable Information
9 Detailed Description
9.1 Overview
The TPS2556 and TPS2557 are current-limited, power-distribution switches using N-channel MOSFETs for applications where short circuits or heavy capacitive loads are encountered. These devices allow the user to program the current-limit threshold from 500 mA to 5 A (typical) through an external resistor. These devices incorporate an internal charge pump and the gate drive circuitry necessary to drive the N-channel MOSFET. The charge pump supplies power to the driver circuit and provides the necessary voltage to pull the gate of the MOSFET above the source. The charge pump operates from input voltages as low as 2.5 V and requires little supply current. The driver controls the gate voltage of the power switch. The driver incorporates circuitry that controls the rise and fall times of the output voltage to limit large current and voltage surges and provides built-in soft-start functionality. The TPS255x family limits the output current to the programmed current-limit threshold (IOS) during an overcurrent or short-circuit event by reducing the charge pump voltage driving the N-channel MOSFET and operating it in the linear range of operation. The result of limiting the output current to IOS reduces the output voltage at OUT because N-channel MOSFET is no longer fully enhanced.
9.2 Functional Block Diagram
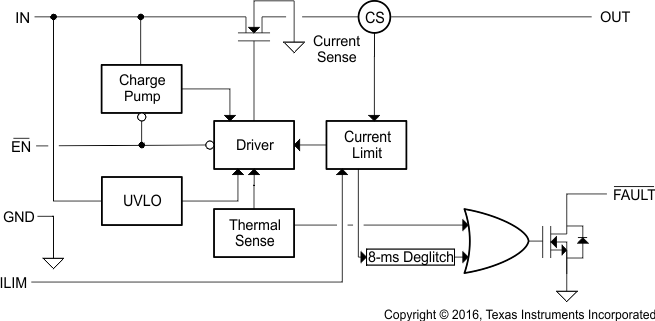
9.3 Feature Description
9.3.1 Overcurrent Conditions
The TPS255x responds to overcurrent conditions by limiting their output current to IOS. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and the output voltage reduces accordingly. Two possible overload conditions can occur.
The first condition is when a short circuit or partial short circuit is present when the device is powered up or enabled. The output voltage is held near zero potential with respect to ground and the TPS255x ramps the output current to IOS. The TPS255x limits the current to IOS until the overload condition is removed or the device begins to thermal cycle.
The second condition is when a short circuit, partial short circuit, or transient overload occurs while the device is enabled and powered on. The device responds to the overcurrent condition within time tIOS (see Figure 16). The current-sense amplifier is overdriven during this time and momentarily disables the internal N-channel MOSFET. The current-sense amplifier recovers and ramps the output current to IOS. Similar to the previous case, the TPS255x limits the current to IOS until the overload condition is removed or the device begins to thermal cycle.
The TPS255s thermal cycles if an overload condition is present long enough to activate thermal limiting in any of the above cases. The device turns off when the junction temperature exceeds 135°C (minimum) while in current limit. The device remains off until the junction temperature cools 20°C (typical) and then restarts. The TPS255x cycles on and off until the overload is removed (see Figure 5) .
9.3.2 FAULT Response
The FAULT open-drain output is asserted (active low) during an overcurrent or overtemperature condition. The TPS255s asserts the FAULT signal until the fault condition is removed and the device resumes normal operation. The TPS255s is designed to eliminate false FAULT reporting by using an internal delay deglitch circuit for overcurrent (9-ms typical) conditions without the need for external circuitry. This ensures that FAULT is not accidentally asserted due to normal operation such as starting into a heavy capacitive load. The deglitch circuitry delays entering and leaving current-limit induced fault conditions. The FAULTsignal is not deglitched when the MOSFET is disabled due to an overtemperature condition but is deglitched after the device has cooled and begins to turn on. This unidirectional deglitch prevents FAULT oscillation during an overtemperature event.
9.3.3 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
The undervoltage lockout (UVLO) circuit disables the power switch until the input voltage reaches the UVLO turnon threshold. Built-in hysteresis prevents unwanted on and off cycling due to input voltage droop during turnon.
9.3.4 Enable (EN OR EN)
The logic enable controls the power switch and device supply current. The supply current is reduced to less than 2-µA when a logic high is present on EN or when a logic low is present on EN. A logic low input on EN or a logic high input on EN enables the driver, control circuits, and power switch. The enable input is compatible with both TTL and CMOS logic levels.
9.3.5 Thermal Sense
The TPS255x self-protects by using two independent thermal sensing circuits that monitor the operating temperature of the power switch and disable operation if the temperature exceeds recommended operating conditions. The TPS255x operates in constant-current mode during an overcurrent conditions, which increases the voltage drop across power switch. The power dissipation in the package is proportional to the voltage drop across the power switch, which increases the junction temperature during an overcurrent condition. The first thermal sensor (OTSD) turns off the power switch when the die temperature exceeds 135°C (minimum) and the part is in current limit. Hysteresis is built into the thermal sensor, and the switch turns on after the device has cooled approximately 20°C.
The TPS255x also has a second ambient thermal sensor (OTSD2). The ambient thermal sensor turns off the power switch when the die temperature exceeds 155°C (minimum) regardless of whether the power switch is in current limit and turns on the power switch after the device has cooled approximately 20°C. The TPS255x continues to cycle off and on until the fault is removed.
9.4 Device Functional Modes
There are no other functional modes.