SLVS400D August 2001 – January 2015 TPS54611 , TPS54612 , TPS54613 , TPS54614 , TPS54615 , TPS54616
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Lock Out (UVLO)
- 7.3.2 Slow-Start and Enable (SS/ENA)
- 7.3.3 VBIAS Regulator
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Oscillator and PWM Ramp
- 7.3.6 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.7 PWM Control
- 7.3.8 Dead-Time Control and MOSFET Drivers
- 7.3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.11 Powergood (PWRGD)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI | Input voltage | VIN, SS/ENA, FSEL | −0.3 | 7 | V |
| RT | −0.3 | 6 | V | ||
| VSENSE | −0.3 | 4 | V | ||
| BOOT | −0.3 | 17 | V | ||
| VO | Output voltage | VBIAS, PWRGD | −0.3 | 7 | V |
| PH | −0.6 | 10 | V | ||
| IO | Source current | PH | Internally Limited | V | |
| VBIAS | 6 | mA | |||
| IS | Sink current | PH | 12 | A | |
| SS/ENA, PWRGD | 10 | mA | |||
| Voltage differential | AGND to PGND | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| Continuous power dissipation | See | ||||
| TJ | Operating virtual junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | −65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controller Input Voltage, VIN | 3 | 6 | V | ||
| Junction Temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
6.3 Thermal Information(1)
| THERMAL METRIC(2) | TPS5461x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (28 PINS) | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, with solder | 18.2 | °C/W |
| Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, without solder | 40.5 | ||
(1) Test Board Conditions:
- 3 inches × 3 inches, 4 layers, thickness: 0.062 inch
- 1.5 oz. copper traces located on the top of the PCB
- 1.5 oz. copper ground plane on the bottom of the PCB
- 0.5 oz. copper ground planes on the 2 internal layers
- 12 thermal vias. See Figure 19 for more information.
(2) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.4 Dissipation Ratings(1)(2)
| TA = 25°C POWER RATING |
TA = 70 °C POWER RATING |
TA = 85 °C POWER RATING |
UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 Pin PWP with Solder | 5.49 (3) | 3.02 | 2.20 | W |
| 28 Pin PWP without Solder | 2.48 | 1.36 | 0.99 | W |
(1) For more information on the PWP package, refer to TI technical brief, SLMA002
(2) Test Board Conditions:
- 3 inches × 3 inches, 4 layers, thickness: 0.062 inch
- 1.5 oz. copper traces located on the top of the PCB
- 1.5 oz. copper ground plane on the bottom of the PCB
- 0.5 oz. copper ground planes on the 2 internal layers
- 12 thermal vias. See Figure 19 for more information.
(3) Maximum power dissipation may be limited by over-current protection
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = –40°C to 125°C, VI = 3 V to 6 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE, VIN | |||||||
| VIN | Input voltage range | 3.0 | 6.0 | V | |||
| I(Q) | Quiescent current | fs = 350 kHz, FSEL ≤ 0.8 V, RT open, phase pin open | 6.2 | 9.6 | mA | ||
| fs = 550 kHz, FSEL ≤ 2.5 V, RT open, phase pin open | 8.4 | 12.8 | |||||
| Shutdown, SS/ENA = 0 V | 1 | 1.4 | |||||
| UNDERVOLTAGE LOCK OUT | |||||||
| UVLO | Start threshold voltage | 2.95 | 3.0 | V | |||
| Stop threshold voltage | 2.70 | 2.80 | V | ||||
| Hysteresis voltage | 0.14 | 0.16 | V | ||||
| Rising and falling edge deglitch(3) | 2.5 | µs | |||||
| BIAS VOLTAGE | |||||||
| VBIAS | Output voltage | I(VBIAS) = 0 | 2.70 | 2.80 | 2.90 | V | |
| Output current(1) | 100 | µA | |||||
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE | |||||||
| VO | Output voltage | TPS54611 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 0.9 | V | ||
| 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | –2.0% | 2.0% | |||||
| TPS54612 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 1.2 | V | ||||
| 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | –2.0% | 2.0% | |||||
| TPS54613 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 1.5 | V | ||||
| 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | –2.0% | 2.0% | |||||
| TPS54614 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 1.8 | V | ||||
| 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40°C ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | –3.0% | 3.0% | |||||
| TPS54615 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 2.5 | V | ||||
| 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40° ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | –3.0% | 3.0% | |||||
| TPS54616 | TJ = 25°C, VIN = 5 V | 3.3 | V | ||||
| 4 V ≤ VIN ≤ 6 V, 0 ≤ IL ≤ 6 A, −40° ≤ TJ ≤ 125°C | −3.0% | 3.0% | |||||
| REGULATION | |||||||
| Line regulation(3)(2) | IL = 3 A, 350 ≤ fs ≤ 550 kHz, TJ = 85°C | 0.088 | %/V | ||||
| Load regulation(3)(2) | IL = 0 A to 6 A, 350 ≤ fs ≤ 550 kHz, TJ = 85°C | 0.0917 | %/A | ||||
| OSCILLATOR | |||||||
| Internally set – free running frequency | FSEL ≤ 0.8 V, RT open | 280 | 350 | 420 | kHz | ||
| FSEL ≥ 2.5 V, RT open | 440 | 550 | 660 | ||||
| Externally set – free running frequency range | RT = 180 kΩ (1% resistor to AGND)(3) | 252 | 280 | 308 | kHz | ||
| RT = 100 kΩ (1% resistor to AGND) | 460 | 500 | 540 | ||||
| RT = 68 kΩ (1% resistor to AGND)(3) | 663 | 700 | 762 | ||||
| FSEL | High level threshold | 2.5 | V | ||||
| Low level threshold | 0.8 | V | |||||
| Ramp valley(3) | 0.75 | V | |||||
| Ramp amplitude (peak-to-peak)(3) | 1 | V | |||||
| Minimum controllable on time(3) | 200 | ns | |||||
| Maximum duty cycle(3) | 90% | ||||||
| ERROR AMPLIFIER | |||||||
| Error amplifier open loop voltage gain(3) | 26 | dB | |||||
| Error amplifier unity gain bandwidth(3) | 3 | 5 | MHz | ||||
| Error amplifier common mode input voltage range | Powered by internal LDO(3) | 0 | VBIAS | V | |||
| PWM COMPARATOR | |||||||
| PWM comparator propagation delay time, PWM comparator input to PH pin (excluding deadtime) | 10-mV overdrive(3) | 70 | 85 | ns | |||
| SLOW-START/ENABLE | |||||||
| Enable threshold voltage, SS/ENA | 0.82 | 1.20 | 1.40 | V | |||
| Enable hysteresis voltage, SS/ENA(3) | 0.03 | V | |||||
| Falling edge deglitch, SS/ENA(3) | 2.5 | µs | |||||
| Internal slow-start time(3) | TPS54611 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 4.1 | ms | ||
| TPS54612 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 5.4 | ||||
| TPS54613 | 4.4 | 5.6 | 6.7 | ||||
| TPS54614 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 4.1 | ||||
| TPS54615 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 5.6 | ||||
| TPS54616 | 4.7 | 6.1 | 7.6 | ||||
| Charge current, SS/ENA | SS/ENA = 0V | 3 | 5 | 8 | µA | ||
| Discharge current, SS/ENA | SS/ENA = 0.2 V, VI = 2.7 V | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.0 | mA | ||
| POWERGOOD | |||||||
| Powergood threshold voltage | VSENSE falling | 90 | %VO | ||||
| Powergood hysteresis voltage | See (3) | 3 | %VO | ||||
| Powergood falling edge deglitch | See (3) | 35 | µs | ||||
| Output saturation voltage, PWRGD | I(sink) = 2.5 mA | 0.18 | 0.3 | V | |||
| Leakage current, PWRGD | VI = 5.5 V | 1 | µA | ||||
| CURRENT LIMIT | |||||||
| Current limit | VI = 3 V(3) | 7.2 | 10 | A | |||
| VI = 6 V(3) | 10 | 12 | |||||
| Current limit leading edge blanking time(3) | 100 | ns | |||||
| Current limit total response time(3) | 200 | ns | |||||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | |||||||
| Thermal shutdown trip point(3) | 135 | 150 | 165 | °C | |||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis(3) | 10 | ||||||
| OUTPUT POWER MOSFETS | |||||||
| rDS(on) | Power MOSFET switches | IO = 3 A, VI = 6 V(4) | 26 | 47 | mΩ | ||
| IO = 3 A, VI = 3 V(4) | 36 | 65 | |||||
(1) Static resistive loads only
(2) Tested using circuit in Figure 10.
(3) Specified by design
(4) Matched MOSFETs, low-side rDS(on) production tested, high-side rDS(on) specified by design.
6.6 Typical Characteristics
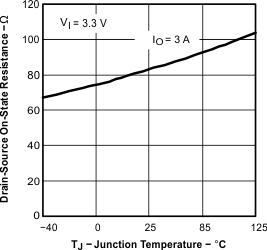
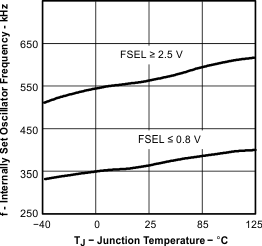
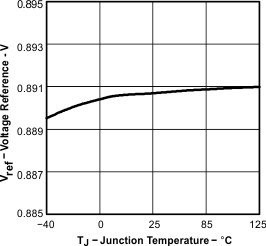
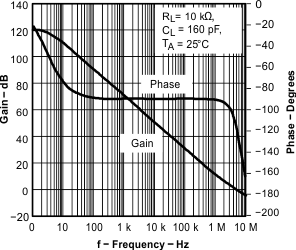

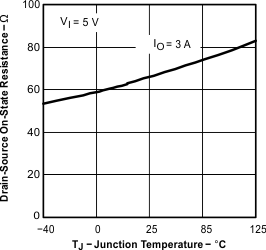
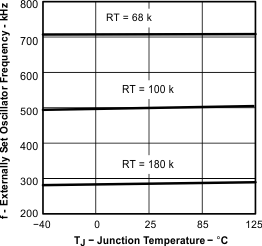
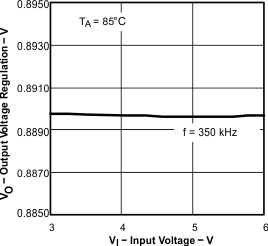
| Tested using TPS54611 | ||
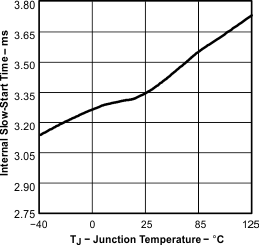
| Tested using TPS54611 | ||