SLVS821E May 2008 – May 2019 TPS61087
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Rectifier Diode Selection
To achieve high efficiency a Schottky type should be used for the rectifier diode. The reverse voltage rating should be higher than the maximum output voltage of the converter. The averaged rectified forward current Iavg, the Schottky diode needs to be rated for, is equal to the output current Iout:
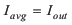
Usually a Schottky diode with 2-A maximum average rectified forward current rating is sufficient for most applications. The Schottky rectifier can be selected with lower forward current capability depending on the output current Iout but has to be able to dissipate the power. The dissipated power, PD, is the average rectified forward current times the diode forward voltage, Vforward.
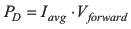
Typically, the diode should be able to dissipate around 500 mW depending on the load current and forward voltage.
Table 4. Rectifier Diode Selection
| CURRENT RATING Iavg | Vr | Vforward/Iavg | SUPPLIER | COMPONENT CODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 A | 20 V | 0.44 V / 2 A | Vishay Semiconductor | SL22 |
| 2 A | 20 V | 0.5 V / 2 A | Fairchild Semiconductor | SS22 |