SLVSEL7B April 2019 – October 2019 TPS61390
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirement
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Rectifier Diode
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Inductor
- 8.2.2.3 Selecting Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Selecting Filter Resistor and Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Setting the Output Voltage
- 8.2.2.6 Selecting Sample Window
- 8.2.2.7 Selecting Capacitor for CAP pin
- 8.2.2.8 Selecting Capacitor for AVCC pin
- 8.2.2.9 Selecting Capacitor for APD pin
- 8.2.2.10 Selecting the Resistors of MON1 or MON2
- 8.2.2.11 Selecting the Capacitors of MON1 or MON2
- 8.2.2.12 Selecting the Resistor of Gain pin
- 8.2.2.13 Selecting the Short Current Limit
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Selecting the Inductor
It is suggested that the TPS61390 device works in the DCM operation; otherwise the output voltage would not be delivered for low input voltage to high output voltage.
With the device working in DCM operation, the maximum inductor could be calculated by equation Equation 3 and Equation 4:
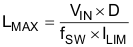
where
- VIN is input voltage
- D is duty cycle
- fSW is switching frequency
- ILIM is current limit
For instance, if VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 60 V, fSW = 600 kHz, ILIM = 0.8 A, the LMAX = 6.5 µH
However, there is minimum inductance is determined by the power delivered to the output side at given input condition.
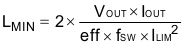
where
- VOUT is output voltage
- IOUT is output current
- eff is the efficiency
- fSW is switching frequency
- ILIM is current limit
For instance, if IOUT = 8 mA, VOUT = 60 V, fSW = 600 kHz, ILIM = 0.8 A, eff = 0.6, the LMIN = 4.2 µH
With the calculation aforementioned, the operating inductor is recommended between the LMIN and LMAX.
The 4.7 µH inductance is optimum value for using the TPS61390 in application.