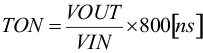SLVSDR8B April 2018 – February 2023 TPS62147 , TPS62148
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
- 9.4.2 Power Save Mode Operation (PWM/PFM)
- 9.4.3 100% Duty-Cycle Operation
- 9.4.4 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (for TPS62148)
- 9.4.5 HICCUP Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (for TPS62147)
- 9.4.6 Soft Start / Tracking (SS/TR)
- 9.4.7 Output Discharge Function (TPS62148 only)
- 9.4.8 Starting into a Pre-Biased Load
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGX|11
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
TPS62147, TPS62148 have two operating modes: Forced PWM mode discussed in this section and PWM/PFM as discussed in Power Save Mode Operation (PWM/PFM).
With the MODE pin set to high, the TPS62147, TPS62148 operate with pulse width modulation in continuous conduction mode (CCM) with a nominal switching frequency of 2.5 MHz for FSEL = high and 1.25 MHz for FSEL = low. The frequency variation in PWM is controlled and depends on VIN, VOUT and the inductance. The on-time (TON) in forced PWM mode depends on the setting of FSEL.
For FSEL = high (2.5 MHz):
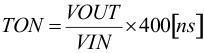
For FSEL = low (1.25 MHz):