SLVSCH9E December 2014 – March 2022 TPS62406-Q1 , TPS62407-Q1 , TPS62422-Q1 , TPS62423-Q1 , TPS62424-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.4.1.3 100% Duty-Cycle Low-Dropout Operation
The converters offer a low input-to-output voltage difference while still maintaining operation with the use of the 100% duty-cycle mode. In this mode, the P-channel switch is constantly on. This is particularly useful in battery-powered applications to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole battery-voltage range. The minimum input voltage to maintain regulation depends on the load current and output voltage, which one can calculate as:
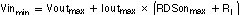
with
- IOUTxmax = maximum output current plus inductor ripple current
- rDS(on)max = maximum P-channel switch rDS(on)
- RL = dc resistance of the inductor
- VOUTxmax = nominal output voltage plus maximum output-voltage tolerance
With decreasing load current, the device automatically switches into pulse-skipping operation, in which the power stage operates intermittently based on load demand. Running cycles periodically minimizes the switching losses, and the device runs with a minimum quiescent current, maintaining high efficiency.