SBVS392A june 2022 – august 2023 TPS7B4255-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.5 Current Limit
The device has an internal current limit circuit to protect the device during overcurrent or shorting conditions. The current limit circuit, as shown in Figure 7-4, is a brick-wall scheme. When the device is in current limit, the device sources ICL and the output voltage is not regulated. In this scenario, the output voltage depends on the load impedance.
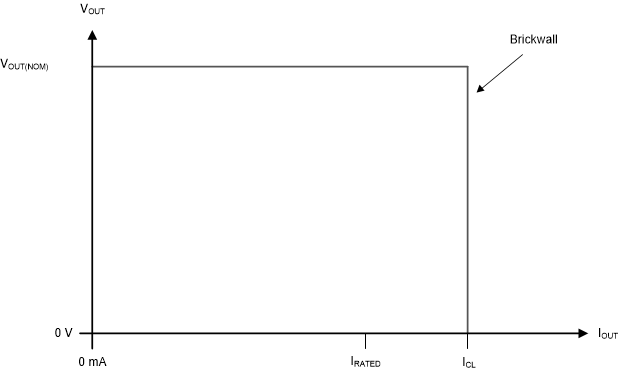 Figure 7-4 Current Limit: Brick-Wall
Scheme
Figure 7-4 Current Limit: Brick-Wall
SchemeDuring a current limit event, the potential for high power dissipation exists because of the elevated current level and the increased input-to-output differential voltage (VIN – VOUT). If the device heats enough, the device can enter thermal shutdown. If the current-limit condition is not removed when the device turns back on after cooling, the device can enter thermal shutdown again and continue this cycle until the current limit condition is removed. The device survives this fault, but repeatedly operating in this mode degrades long-term reliability.