SLLSEP2D August 2015 – May 2017 TUSB320HI , TUSB320LI
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RWB|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
- An extra trace (or stub) is created when connecting between more than two points. A trace connecting pin A6 to pin B6 will create a stub because the trace also has to go to the USB Host. Ensure that:
- A stub created by short on pin A6 (DP) and pin B6 (DP) at Type-C receptacle does not exceed 3.5 mm.
- A stub created by short on pin A7 (DM) and pin B7 (DM) at Type-C receptacle does not exceed 3.5 mm.
- A 100-nF capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the TUSB320 VDD pin.
10.2 Layout Example
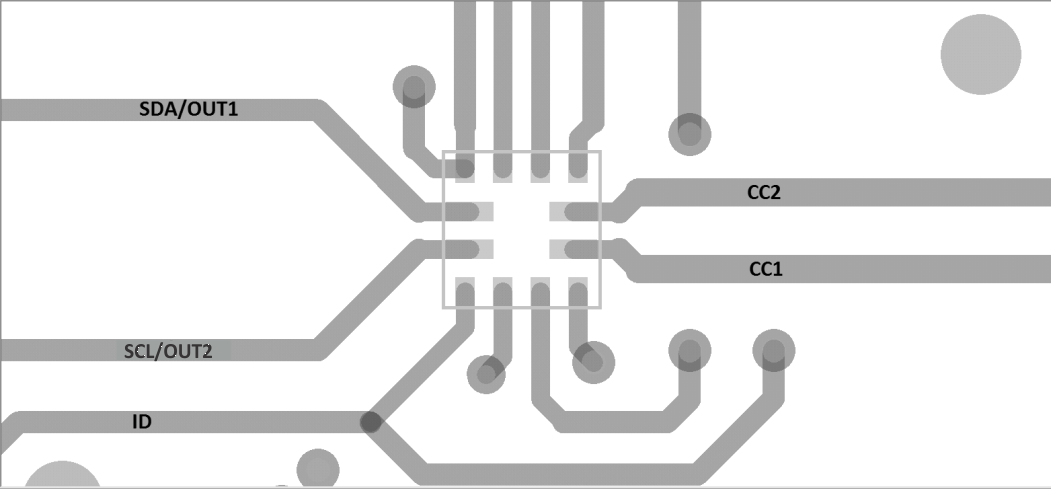 Figure 22. TUSB320 Layout
Figure 22. TUSB320 Layout