JAJSI32 October 2019 ADS1235-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Conversion Control
- 9.4.2 Chop Mode
- 9.4.3 AC-Bridge Excitation Mode
- 9.4.4 ADC Clock Mode
- 9.4.5 Power-Down Mode
- 9.4.6 Reset
- 9.4.7 Calibration
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 Device Identification (ID) Register (address = 00h) [reset = Cxh]
- 9.6.2 Device Status (STATUS) Register (address = 01h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.3 Mode 0 (MODE0) Register (address = 02h) [reset = 24h]
- 9.6.4 Mode 1 (MODE1) Register (address = 03h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.5 Mode 2 (MODE2) Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.6 Mode 3 (MODE3) Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.7 Reference Configuration (REF) Register (address = 06h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration (OFCALx) Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCALx) Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.10 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.11 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 PGA Configuration (PGA) Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.14 Input Multiplexer (INPMUX) Register (address = 11h) [reset = FFh]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.3.7.1.1 Sinc Filter Frequency Response
The overall frequency response of the sinc filter is low pass. The filter reduces signal and noise beginning at the -3-dB bandwidth. Changing the data rate and filter order changes the filter bandwidth together with the rate of frequency roll-off. See the Filter Bandwidth section for the bandwidth of the filter settings.
Figure 49 shows the frequency response of the sinc filter at 2400 SPS for various orders of the sinc filter. The peaks and nulls are characteristic of the sinc filter response. The frequency response nulls occur at f (Hz) = N · fDATA, where N = 1, 2, 3 and so on. At the null frequencies, the filter has zero gain. The response nulls are superimposed with the larger nulls beginning at 14400 Hz. The larger nulls are produced by the first stage. The frequency response is similar to that of data rates 2.5 SPS through 7200 SPS. Figure 50 shows the frequency response nulls for 10 SPS.
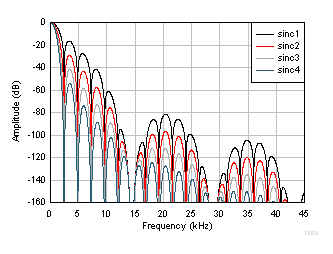 Figure 49. Sinc Frequency Response (2400 SPS)
Figure 49. Sinc Frequency Response (2400 SPS) 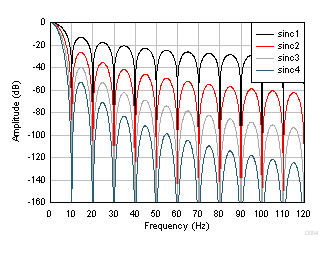 Figure 50. Sinc Frequency Response (10 SPS)
Figure 50. Sinc Frequency Response (10 SPS) Figure 51 and Figure 52 show the frequency response of data rates 50 SPS and 60 SPS, respectively. Increase the attenuation at 50 Hz or 60 Hz and harmonics by increasing the order of the sinc filter, as shown in the figures.
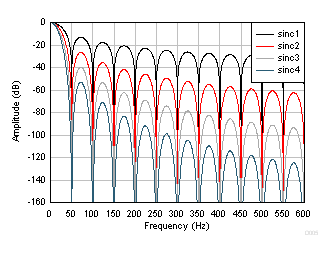 Figure 51. Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS)
Figure 51. Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS) 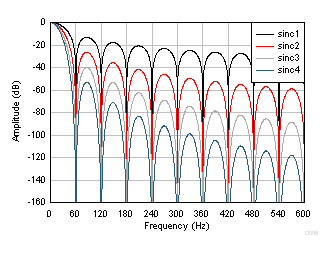 Figure 52. Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)
Figure 52. Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS) Figure 53 and Figure 54 show the detailed frequency response at 50 SPS and 60 SPS, respectively.
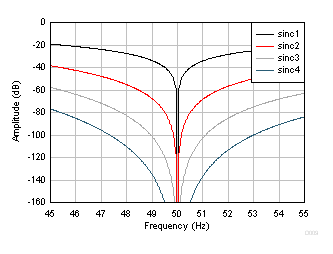 Figure 53. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS)
Figure 53. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS) 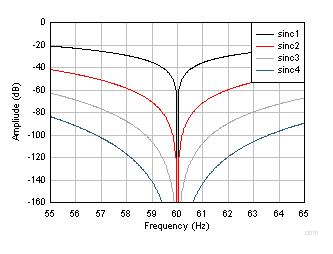 Figure 54. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)
Figure 54. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)