JAJSHI4 May 2019 DRV8340-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1
Three Phase Smart Gate Drivers
- 8.3.1.1
PWM Control Modes
- 8.3.1.1.1 6x PWM Mode (PWM_MODE = 000b or MODE Pin Tied to AGND)
- 8.3.1.1.2 3x PWM Mode (PWM_MODE = 001b or MODE Pin = 18 kΩ to AGND)
- 8.3.1.1.3 1x PWM Mode (PWM_MODE = 010b or MODE Pin = 75 kΩ to AGND)
- 8.3.1.1.4 Independent Half-Bridge PWM Mode (PWM_MODE = 011b or MODE Pin is > 1.5 MΩ to AGND or Hi-Z)
- 8.3.1.1.5 Phases A and B are Independent Half-Bridges, Phase C is Independent FET (MODE = 100b)
- 8.3.1.1.6 Phases B and C are Independent Half-Bridges, Phase A is Independent FET (MODE = 101b or MODE Pin is 75 kΩ to DVDD)
- 8.3.1.1.7 Phases A is Independent Half-Bridge, Phases B and C are Independent FET (MODE = 110b or MODE Pin is 18 kΩ to DVDD)
- 8.3.1.1.8 Independent MOSFET Drive Mode (PWM_MODE = 111b or MODE Pin = 0.47 kΩ to DVDD)
- 8.3.1.2 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.1.3 Gate Driver Voltage Supplies
- 8.3.1.4 Smart Gate Drive Architecture
- 8.3.1.1
PWM Control Modes
- 8.3.2 DVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.3 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.4
Gate Driver Protective Circuits
- 8.3.4.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.4.2 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.4.3 MOSFET VDS Overcurrent Protection (VDS_OCP)
- 8.3.4.4 Gate Driver Fault (GDF)
- 8.3.4.5 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.4.6 Thermal Shutdown (OTSD)
- 8.3.4.7 Open Load Detection (OLD)
- 8.3.4.8 Offline Shorts Diagnostics
- 8.3.4.9 Reverse Supply Protection
- 8.3.1
Three Phase Smart Gate Drivers
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Status Registers
- 8.6.2
Control Registers
- 8.6.2.1 IC1 Control Register (Address = 0x04) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.2.2 IC2 Control Register (address = 0x05) [reset = 0x40]
- 8.6.2.3 IC3 Control Register (Address = 0x06) [reset = 0xFF]
- 8.6.2.4 IC4 Control Register (Address = 0x07) [reset = 0xFF]
- 8.6.2.5 IC5 Control Register (Address = 0x08) [reset = 0xFF]
- 8.6.2.6 IC6 Control Register (Address = 0x09) [reset = 0x99]
- 8.6.2.7 IC7 Control Register (Address = 0x0A) [reset = 0x99]
- 8.6.2.8 IC8 Control Register (Address = 0x0B) [reset = 0x99]
- 8.6.2.9 IC9 Control Register (Address = 0x0C) [reset = 0x2F]
- 8.6.2.10 IC10 Control Register (Address = 0x0D) [reset = 0x61]
- 8.6.2.11 IC11 Control Register (Address = 0x0E) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.2.12 IC12 Control Register (Address = 0x0F) [reset = 0x2A]
- 8.6.2.13 IC13 Control Register (Address = 0x10) [reset = 0x7F]
- 8.6.2.14 IC14 Control Register (Address = 0x10) [reset = 0x00]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PHP|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PHP|48
発注情報
8.3.1.1.8 Independent MOSFET Drive Mode (PWM_MODE = 111b or MODE Pin = 0.47 kΩ to DVDD)
In independent MOSFET drive mode, the INHx and INLx pins control the outputs, GHx and GLx, respectively. This control mode lets the DRV8340-Q1 device drive separate high-side and low-side loads with each half-bridge. These types of loads include unidirectional brushed DC motors, solenoids, and low-side and high-side switches. In this mode, turning on both the high-side and low-side MOSFETs at the same time in a given half-bridge gate driver is possible to use the device as a high-side or low-side driver. The dead time (tDEAD) is bypassed in the mode and must be inserted by the external MCU.
Table 9. Independent PWM Mode Truth Table
| INLx | INHx | GLx | GHx |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | L | L |
| 0 | 1 | L | H |
| 1 | 0 | H | L |
| 1 | 1 | H | H |
Figure 12 shows how the DRV8340-Q1 device can be used to connect a high-side load and a low-side load at the same time with one half-bridge and drive the loads independently. In this mode, the VDS monitors are active for both the MOSFETs to protect from an overcurrent condition.
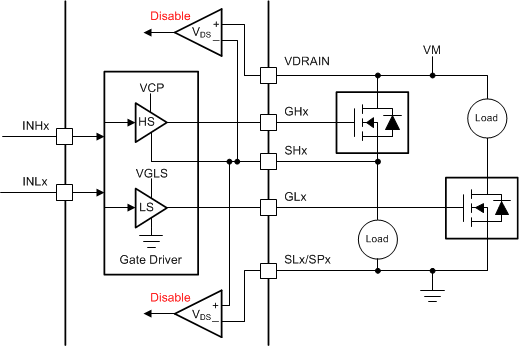 Figure 12. Independent PWM High-Side and Low-Side Drivers
Figure 12. Independent PWM High-Side and Low-Side Drivers If the half-bridge is used to implement only a high-side or low-side driver, using the VDS monitors to help protect from an overcurrent condition is possible as shown in Figure 13 or Figure 14. The unused gate driver can stay disconnected.
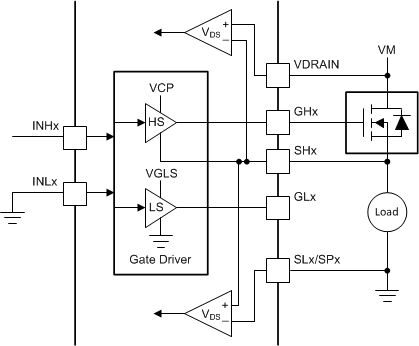 Figure 13. One High-Side Driver
Figure 13. One High-Side Driver 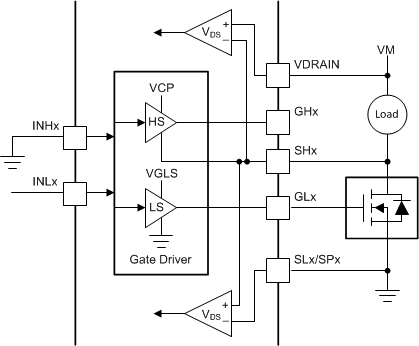 Figure 14. One Low-Side Driver
Figure 14. One Low-Side Driver Figure 15 shows how the DRV8340-Q1 device can be used to connect a solenoid load where both the high-side and low-side MOSFETs can be turned on at the same time to drive the load without causing shoot-through. TI recommends having the external diodes for current recirculation. If a half-bridge is not used, the gate pins (GHx and GLx) can stay unconnected and the sense pins (SHx and DLx) can be tied directly or with a resistor to GND.
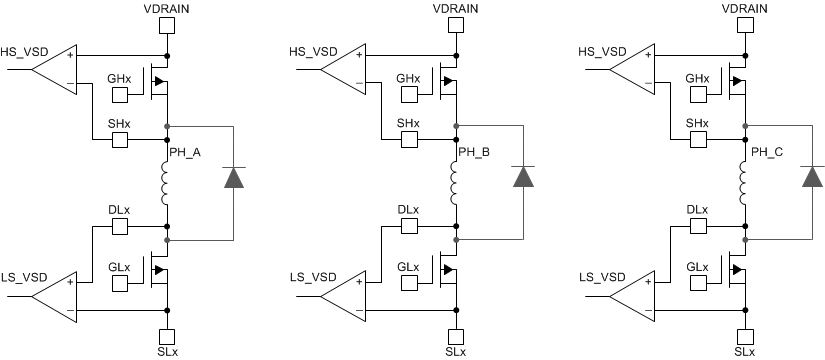 Figure 15. Solenoid Drive Configuration
Figure 15. Solenoid Drive Configuration