DLPU102B December 2020 – July 2022
- Read This First
- 1DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 EVM Overview
- 2Quick Start
-
3Operating the DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 EVM
- 3.1 DLP LightCrafter Dual DLPC900 Control Software
- 3.2 PC Software
- 3.3 System Common Controls
- 3.4 System Settings
- 3.5 Video Mode
- 3.6
Pattern Modes
- 3.6.1 Menu Bar
- 3.6.2 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Pattern On-The-Fly Mode
- 3.6.3 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Pre-Stored Pattern Mode
- 3.6.4 Reordering a Pattern Sequence using the Edit LUT Feature
- 3.6.5 Creating a Pattern Sequence in Video Pattern Mode
- 3.6.6 Creating a Pattern Sequence With DMD Block Load
- 3.6.7 Pattern Settings
- 3.7 Batch Files
- 3.8 Peripherals
- 3.9 Firmware
- 3.10 Flash Device Parameters
- 3.11 JTAG Flash Programming
- 3.12 Intel (Altera) FPGA Programming
- 4Connectors
- 5Power Supply Requirements
- 6Safety
- 7Revision History
3.5 Video Mode
Click the Video Mode button at the top of the GUI to display the Video Mode panel. Within this panel, there are two tabs:
- The Source Settings Tab is shown in Video Mode Panel - Source Settings Tab.
- The Display Settings Tab is shown in Video Mode Panel - Display Settings Tab.
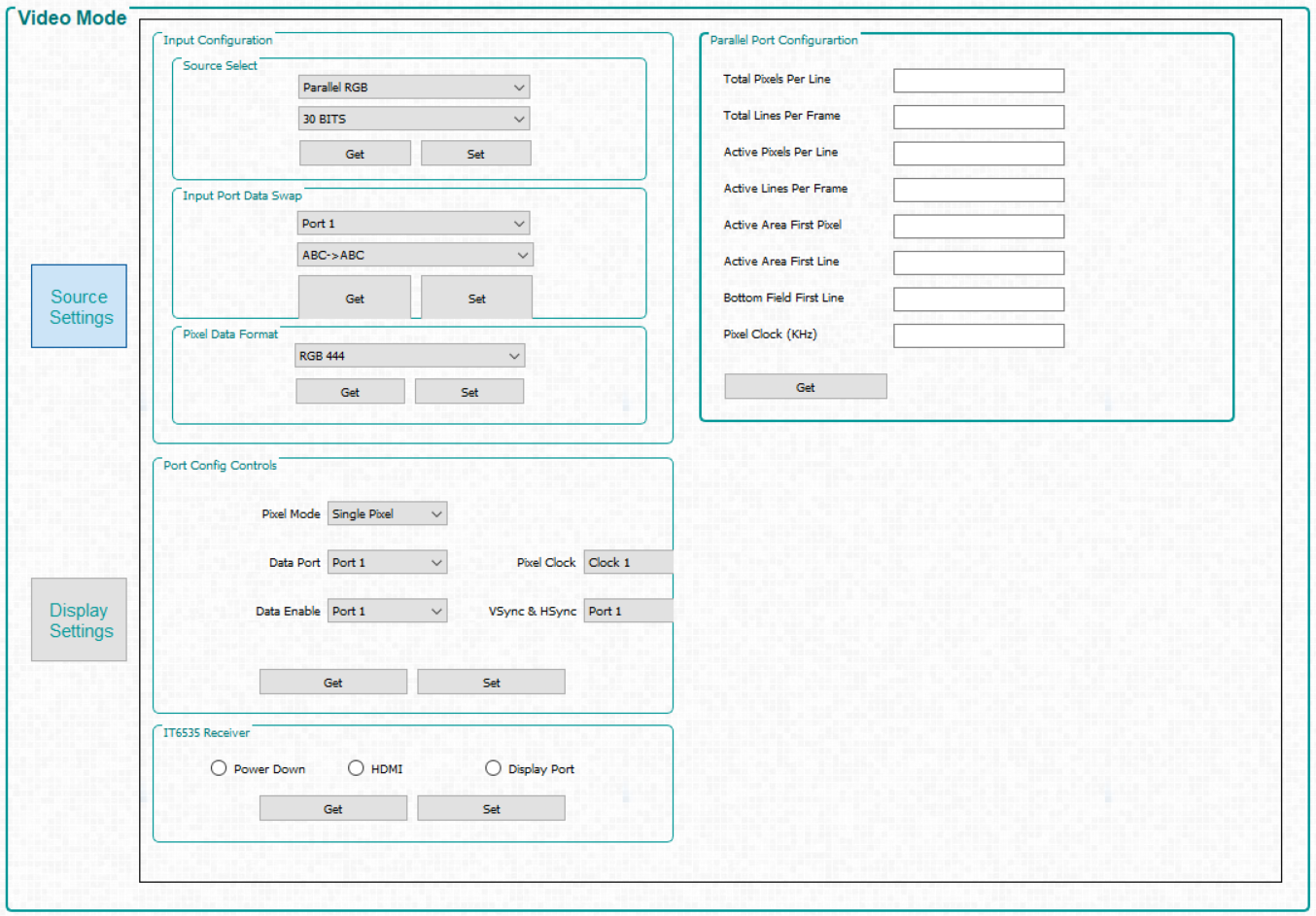 Figure 3-4 Video
Mode Panel - Source Settings Tab
Figure 3-4 Video
Mode Panel - Source Settings Tab - Input Configuration.
- Source Select –
Allows the user to select:
- Parallel RGB interface
- Internal test pattern generator
- Pattern images from flash memory
- Solid Curtain– which displays a constant, solid color image (including black or white)
- Input Port Data Swap – Depending on the routing of the parallel RGB data lines, it may be necessary to swap the order of the color channels. The DLP LightCrafter Single DLPC900 EVM require ABC->BAC setting. ABC corresponded to RGB; therefore, the settings mentioned previously means that channels RG are swapped. The user can also select which port to apply the settings to.
- Pixel Data Format – Allows the user to select the video format of the input source.
- Source Select –
Allows the user to select:
- Port Config Controls – Depending on which input signals were chosen during board design, it may be necessary to select the appropriate signals so that the DLPC900 can properly detect the incoming video source. If incorrect settings are chosen, the curtain may be displayed or the image may be incorrect. Pixel Mode can also be set to Single Pixel or Dual Pixel. Dual Pixel allows for higher data rates by loading two pixels per clock instead of one pixel per clock.
- IT6535 Receiver – This control allows selection between the HDMI or the DisplayPort input connectors of the IT6535 digital receiver. The digital receiver can also be powered-down, which tri-states all the output signals of the IT6535 to allow another device to share the input ports and syncs of the DLPC900.
- Pixel Port Configuration - Allows readback of the current parallel port configuration parameters determined by the EDID or user Display Dimensions
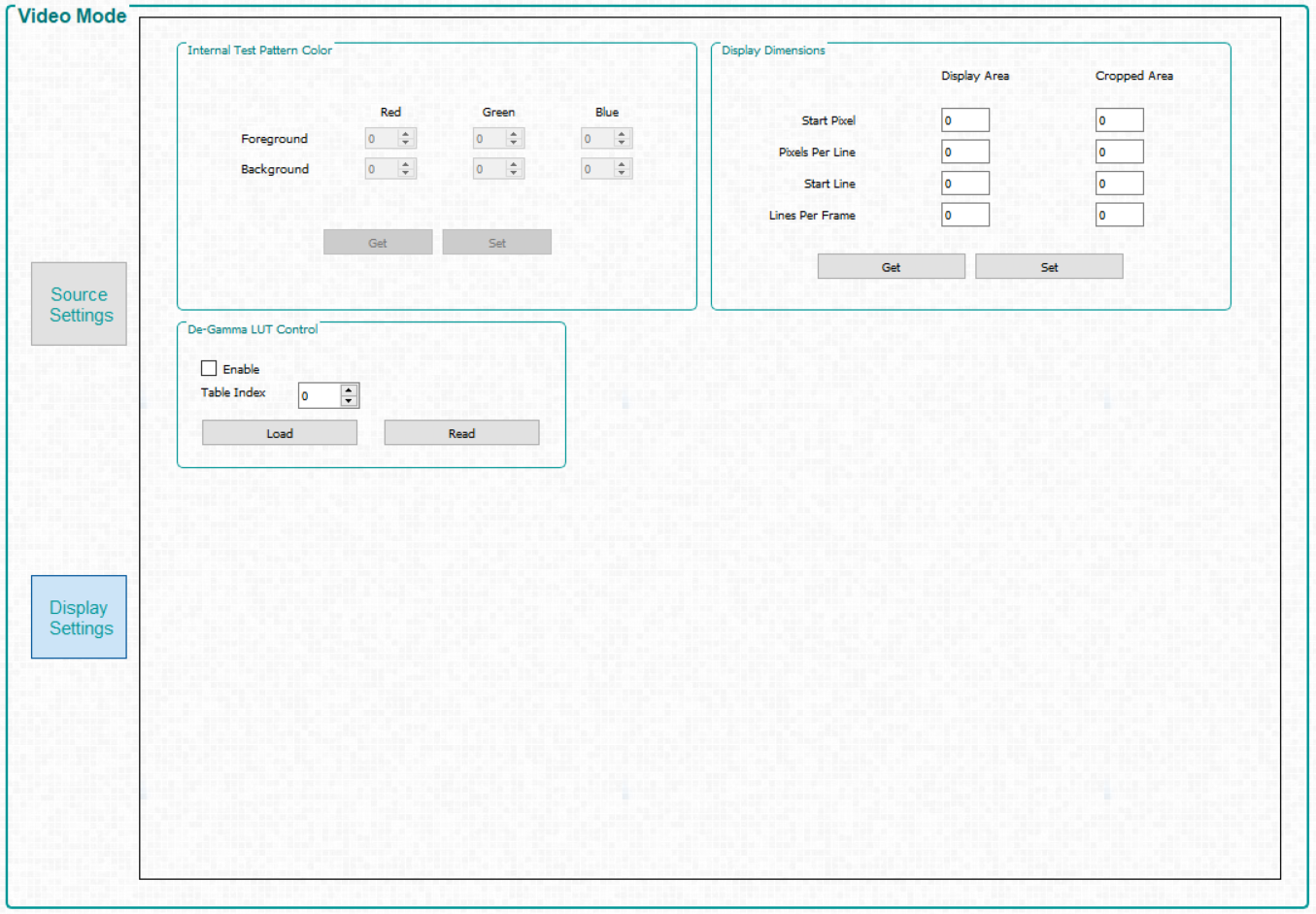 Figure 3-5 Video
Mode Panel - Display Settings Tab
Figure 3-5 Video
Mode Panel - Display Settings Tab - Internal Test Pattern Color – When the internal test pattern is selected as the input source, the foreground and background colors can be changed.
- Display Dimensions – Allows the user to scale or crop the image of the incoming video source.
- De-Gamma LUT Control – De-Gamma controls:
- De-Gamma LUT Control –
De-Gamma controls:
- Enable/Disable - Command enables or disables De-Gamma
- Sets the level of De-gamma - See the Gamma Configuration and Enable section of the DLPC900 Programmer's Guide for further information.