SFFS465 May 2022 TPS62901-Q1 , TPS62902-Q1 , TPS62903-Q1
3 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS629xx-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 3-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 3-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 3-4)
- Pin short-circuited to VIN (see Table 3-5)
Table 3-2 through Table 3-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 3-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 3-1 shows the TPS629xx-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the 'Pin Configuration and Functions' section in the TPS629xx-Q1 datasheet.
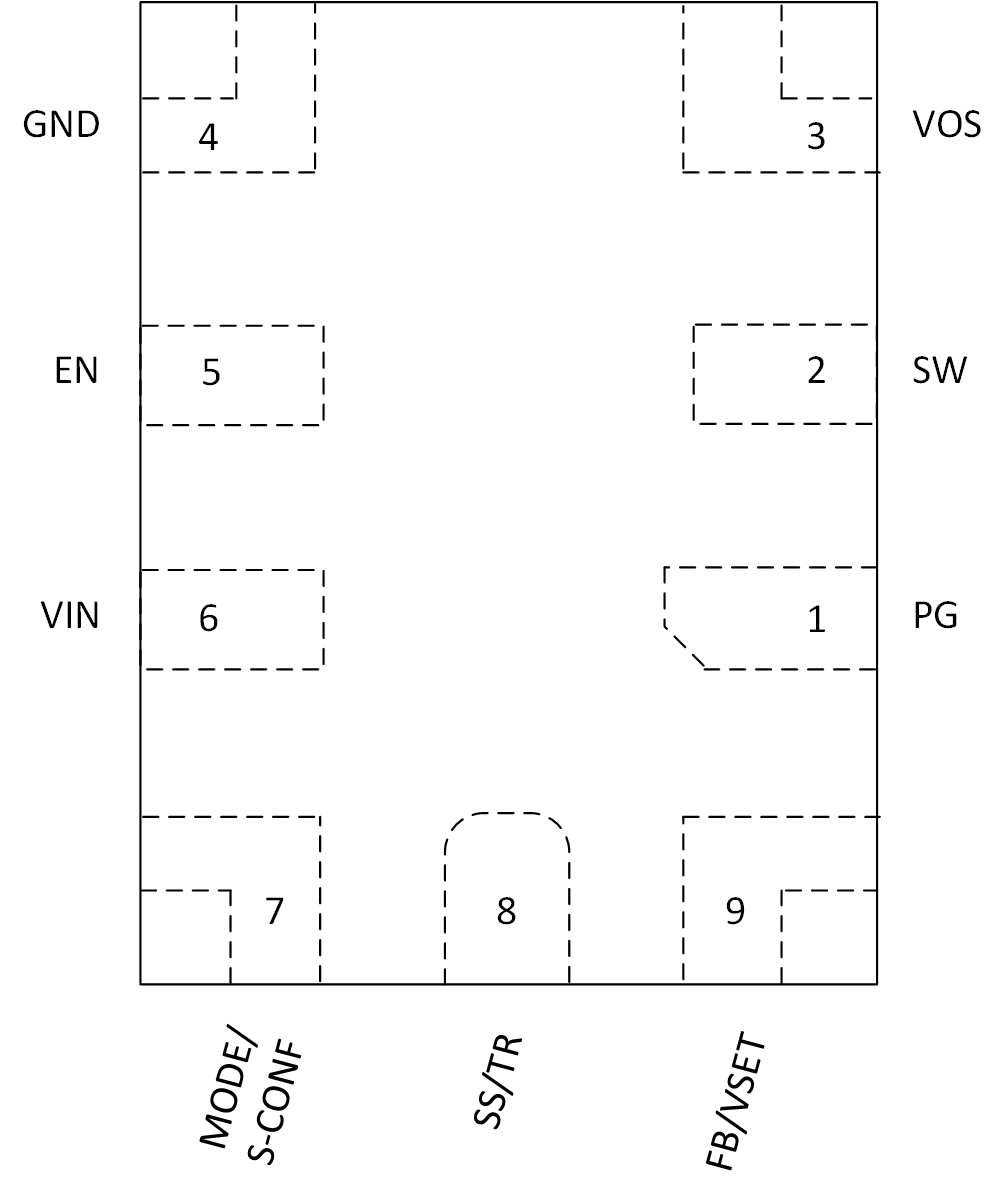
Figure 3-1 PIin Diagram
Following are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- The device is operating in one of the two typical application configurations show in Figure 3-2 or Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-2 Adjustable VO Operation Schematic
Figure 3-3 Selectable VO Operation Schematic
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Application Configuration | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG |
1 | Loss of PG functionality | C | |
| SW |
2 |
Possible device damage | A | |
| VOS |
3 | Loss of output voltage | B | |
| GND |
4 | Intended pin connection | D | |
| EN |
5 |
The device does not power on. | B | |
| VIN |
6 | The device does not power on. | B | |
| MODE/S-CONF |
7 | External FB(3) | The device runs in 2.5M-Hz APFM with AEE mode.(5) | C(5) |
| Internal FB(4) | Loss of output voltage
regulation. Output voltage goes to VIN.(5) Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A(5) | ||
| SS/TR |
8 |
The device does not power on. | B | |
| FB/VSET |
9 |
External FB(3) | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Output voltage goes to VIN. Possible device damage. (2)Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. |
A |
| Internal FB(4) | The device regulates output voltage to 1.2 V. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Application Configuration | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG |
1 | Loss of PG functionality | C | |
| SW |
2 |
Loss of output voltage regulation | B | |
| VOS |
3 | External FB(3) | Open loop operation. Undetermined output voltage behavior |
B |
| Internal FB(4) | Loss of output voltage
regulation. Output voltage may go to VIN. Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A | ||
| GND |
4 | Potential device damage | A | |
| EN |
5 | The device does not power on. | B | |
| VIN |
6 |
The device does not power on. | B | |
| MODE/S-CONF |
7 | External FB(3) | The device runs in 2.5-MHz APFM with AEE mode(5). Output voltage is not set based on the external resistor divider ratio. Instead, VOUT is set according to the internal FB (VSET) table based on external feedback resistance values. | B(5) |
| Internal FB(4) | The device runs in 2.5-MHz APFM with AEE mode.(5) | C(5) | ||
| SS/TR |
8 |
Allowable pin condition. Soft-start time is minimized. | D | |
| FB/VSET |
9 |
External FB(3) | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Output voltage may go to VIN. Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. |
A |
| Internal FB(4) | The device regulates output voltage to 3.3 V. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Application Configuration | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG | 1 | SW | Loss of output voltage regulation and possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded if PG is connected to VOS through a resistor. | A | |
| SW | 2 | VOS | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. |
A | |
| VOS | 3 | GND | Loss of output voltage | B | |
| GND | 4 | EN | The device does not power on. | B | |
| EN | 5 | VIN | The device cannot be disabled. | B | |
| VIN | 6 | MODE/S_CONF | External FB(3) | The device runs in 2.5-MHz FPFM mode. | C |
| Internal FB(4) | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Output voltage goes to VIN.(5) Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. |
A | |||
| MODE/S_CONF | 7 | SS/TR | External FB(3) | The device operating mode is indeterminate. (5) | B(5) |
| Internal FB(4) | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. |
A | |||
| SS/TR | 8 | FB/VSET | Output voltage is regulated below the target value. | B | |
| FB/VSET | 9 | PG | Loss of
output voltage regulation. Possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded if PG is connected to VIN through a resistor. |
A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Application Configuration | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG |
1 | Potential device damage. Absolute maximum current rating for the pin. | A | |
| SW |
2 |
Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A | |
| VOS |
3 | Possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A | |
| GND |
4 | The device is not functional. | B | |
| EN |
5 | The device cannot be disabled. | B | |
| VIN |
6 |
Intended pin connection | D | |
| MODE/S-CONF |
7 | External FB(3) | The device runs in 2.5-MHz FPFM mode. (5) | C(5) |
| Internal FB(4) | Loss of output voltage
regulation. Output voltage goes to VIN.(5) Possible device damage. (2) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A(5) | ||
| SS/TR |
8 |
Potential device damage. Absolute maximum current rating for pin | A | |
| FB/VSET |
9 |
Possible device damage.(1) Absolute maximum voltage may be exceeded. | A |