SLLA585 April 2022 THVD2410 , THVD2450
2.2 Wide Input Common Mode Range
In several systems especially for long-distance communication, the ground potential of different locations can vary greatly. This ground potential becomes the common-mode shift with respect to the differential signal of the bus. For example, in a long-distance point-to-point communication, the output signal of the A and B pins toggle from 1-V to 3-V at node 1. If node 2 has a -7 V ground potential shift relative to node 1, the bus signal is alternating between 8-V to 10-V with respect to the local ground of node 2. Larger input common mode range of RS-485 devices allow for the system to work in wider ground shift scenarios. The following lab measurement demonstrates THVD24x0 devices work with ±25-V input common-mode range.
In the tests, two the half-duplex EVMs are populated with THVD2410 and 120-Ω termination resistor (Figure 2-1). The two boards are connected with two 10-ft (3-m) cables. Ground potential is created between two boards and the ground potential difference is modulated to vary from time to time. As one board is configured as the transmitter and the other one as the receiver, the communication data being sent is a 1-MHz clock signal.
In Figure 2-2, the signal is measured at the bus pins (pin 6 and 7 – channel 4 in plot) and the R pin (pin 8 – channel 1 in plot) of the receiving node with respect to the board’s local ground (GND2). The input signal shifts from 11-V to 25-V peak to peak at a 50-kHz rate. While the differential bus signal varies about 12-V common-mode wise, the receiver output generates the correct signal. Similarly, if the ground potential difference is positive, the received bus signal has a negative common-mode shift (Figure 2-3). In this test, the device works well with -11-V to -25-V peak to peak differential signal. The two measurements show that THVD24x0 devices not only work with extended common-mode range but also relatively frequently varying common-mode voltage.
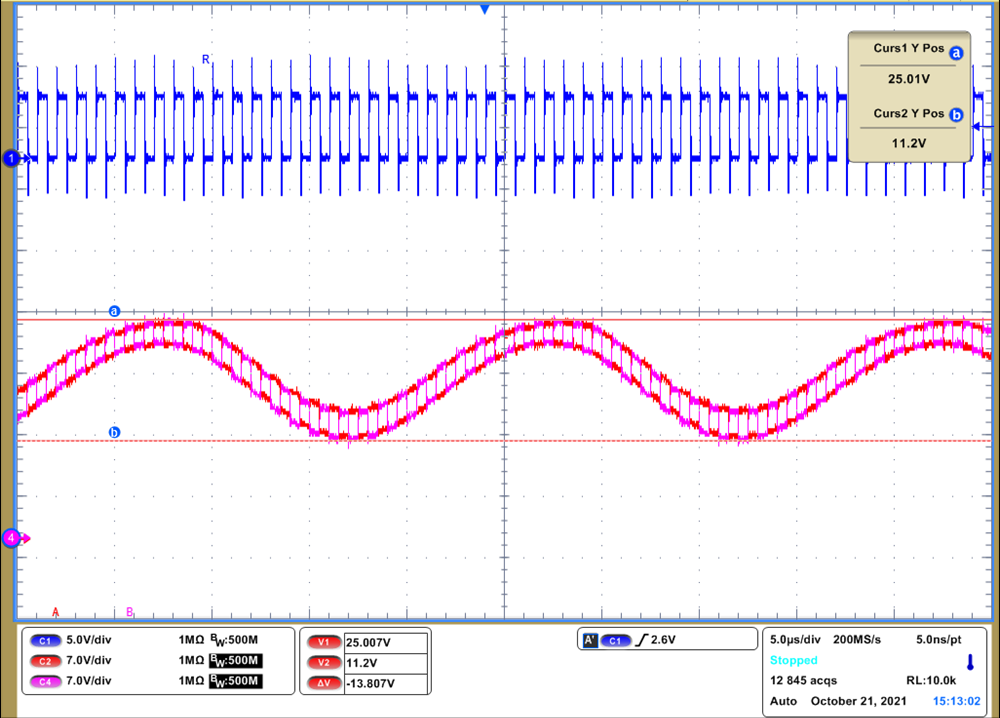 Figure 2-2 THVD2410 Working with +25 V
Common Mode Signal
Figure 2-2 THVD2410 Working with +25 V
Common Mode Signal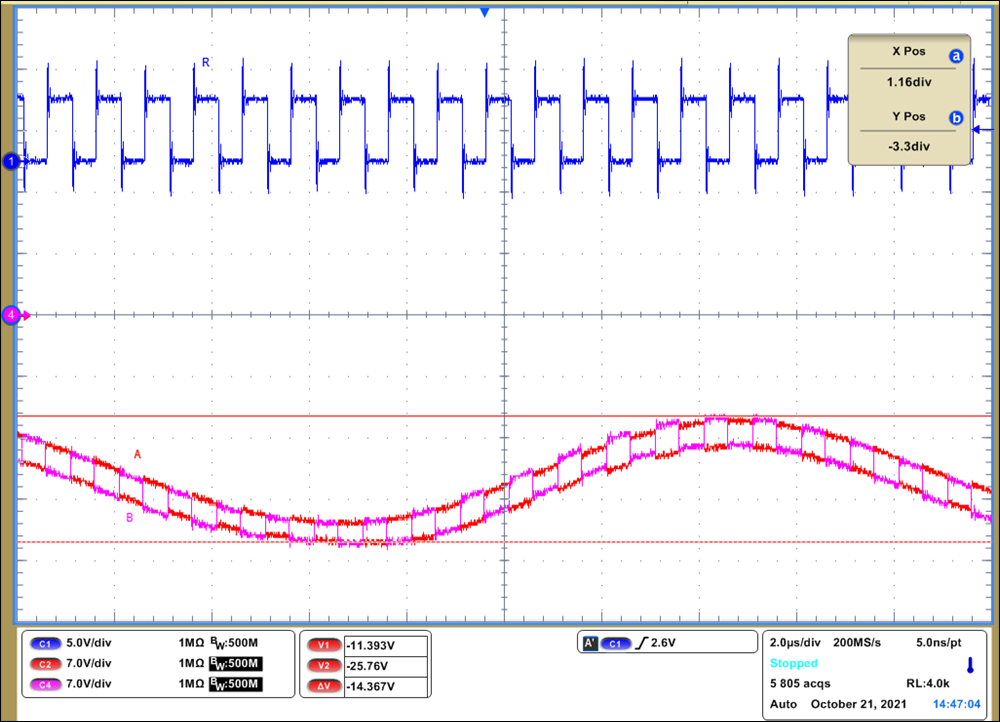 Figure 2-3 THVD2410 Working with -25 V
Common Mode Signal
Figure 2-3 THVD2410 Working with -25 V
Common Mode Signal