SLOA198A September 2014 – December 2021 DRV2665 , DRV2667 , DRV2700 , DRV8662
- Trademarks
- 1 Boost Converter Basics
- 2 DRV8662, DRV2700, DRV2665, and DRV2667 Boost Converter
- 3 Configuring the Boost Converter
- 4 Boost Converter Output Voltage
- 5 Calculating the Load Current
- 6 Selecting an Inductor
- 7 Calculate the Maximum Boost Current
- 8 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9 Input Capacitor Selection
- 10PCB Layout
- 11Examples
- 12Revision History
6.2 Saturation Current Rating
Saturation current is the second-most important parameter of an inductor when using a hysteretic boost converter. Inductor saturation current is typically measured as the peak current that causes the inductance to decrease by 30%. This is the maximum operating current of the inductor.
In Figure 6-1, the saturation current for the 3.3-µH inductor is approximately 400 mA, which is the current that causes the inductance to reduce to 2 µH or by about 30%. A graph like Figure 6-1 can be used to determine and verify the saturation current rating of a specific inductor.
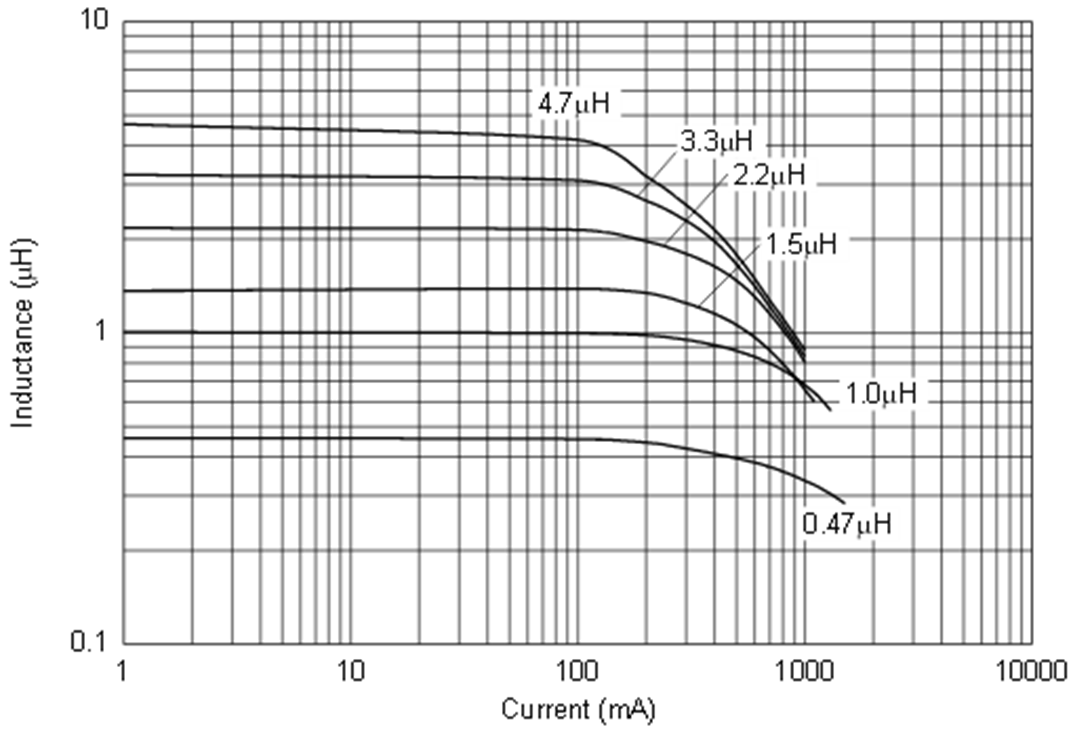 Figure 6-1 Inductance vs DC Current
Figure 6-1 Inductance vs DC CurrentThe inductor saturation current value affects two things in the DRV8662, DRV2700, DRV2665, and DRV2667 boost design:
- The amount of current that can be delivered to the load; the larger the saturation current, the larger amount of current can be delivered to the load.
- The value of the current limit resistor (REXT) for the DRV8662, DRV2665, and DRV2667. It should be set equal to or less than the saturation current of the inductor. Section 6.4 describes how to choose the correct current limit resistor.
Remember that the current limit on the DRV8662, DRV2665, and DRV2667 is not a safety mechanism, but a threshold to signal when the boost switch should open.
| Tip |
| Often the saturation current is listed on the front page of an inductor datasheet; however, it is good practice to verify this value using an “Inductance vs DC Current” graph similar to Figure 6-1. |