SLVAET3 October 2021 TPS8802
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2System Architecture
- 3Current Consumption
- 4System Power Calculation and Measurements
- 5Summary
- 6References
2.4 Photoelectric Smoke Sensor LED Supply
The photoelectric smoke sensor LED can be powered by the battery, PLDO, or LEDLDO. For maximum power savings, the LED should be supplied directly from the battery if the voltage supports it. If direct battery voltage is not supported, use the boost converter with VBST set to the minimum required voltage. Before selecting how to power the LED, the minimum LED supply voltage VLED(min) must be calculated using Equation 1. VF is the LED forward voltage, VDINA(drop) is the LED driver dropout voltage (300 mV at 150 mA and 500 mV at 500 mA), VCSA is the voltage at the CSA current sense pin, and ΔVLED is the voltage drop caused by the capacitive voltage supply on the LED. Using a higher capacitance on the LED supply decreases the supply voltage drop when pulsing the LED as shown in Equation 2.

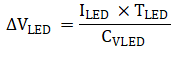
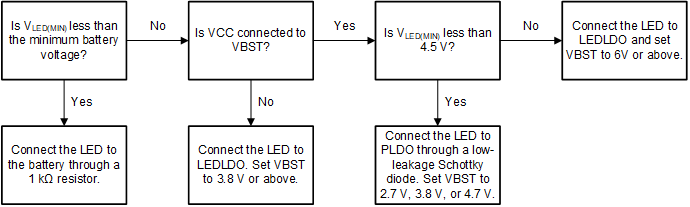 Figure 2-4 LED Supply Selection Guide
Figure 2-4 LED Supply Selection Guide