SLVU353A November 2009 – October 2021 TPS54326
1.3.1 Output Voltage Set Point
To change the output voltage of the EVMs, change the value of resistor R1. Changing the value of R1 can change the output voltage above 0.765 V. The value of R1 for a specific output voltage can be calculated using Equation 1 and Equation 2.
For output voltage from 0.76 V to 2.5 V:
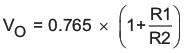
For output voltage over 2.5 V:
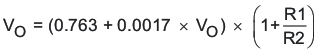
Table 1-3 lists the R1 values for some common output voltages. For higher output voltages, a feedforward capacitor is required. Pads for this component (C2) are provided on the printed circuit board. C2 is used for faster load transient response and is recommended for auto skip mode stability. Note that the values given in Table 1-3 are standard values, and not the exact value calculated using Table 1-3.
| Output Voltage (V) | R1 (kΩ) | R2 (kΩ) | C2 (pF) | L1 (µH) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 6.81 | 22.1 | 1.5 | |
| 1.05 | 8.25 | 22.1 | 1.5 | |
| 1.2 | 12.7 | 22.1 | 1.5 | |
| 1.8 | 30.1 | 22.1 | 10 - 47 | 2.2 |
| 2.5 | 49.9 | 22.1 | 10 - 47 | 2.2 |
| 3.3 | 73.2 | 22.1 | 10 - 47 | 2.2 |
| 5.0 | 121 | 22.1 | 10 - 47 | 3.3 |