SLVUAX8B November 2016 – August 2021 TPS54824
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Test Setup and Results
- 2.1 Input/Output Connections
- 2.2 Efficiency
- 2.3 Output Voltage Load Regulation
- 2.4 Output Voltage Line Regulation
- 2.5 Load Transients
- 2.6 Loop Characteristics
- 2.7 Output Voltage Ripple
- 2.8 Input Voltage Ripple
- 2.9 Powering Up
- 2.10 Powering Down
- 2.11 Start-Up Into Pre-Bias
- 2.12 Hiccup Mode Current Limit
- 3Board Layout
- 4Schematic and Bill of Materials
- 5Revision History
2.9 Powering Up
Figure 2-12 and Figure 2-13 show the start-up waveforms for the TPS54824EVM-779. In Figure 2-12, the output voltage ramps up as soon as the input voltage reaches the UVLO threshold. In Figure 2-13, the input voltage is initially applied and the output is inhibited by pulling EN to GND using an external function generator. When the EN voltage is increased above the enable-threshold voltage, the start-up sequence begins and the output voltage ramps up to the externally set value of 1.8 V. The input voltage for these plots is 12 V and the load is 1 Ω. Alternatively, a jumper at J3 to tie EN to GND can also be used. When the jumper is removed, EN is released and the start-up sequence will begin.
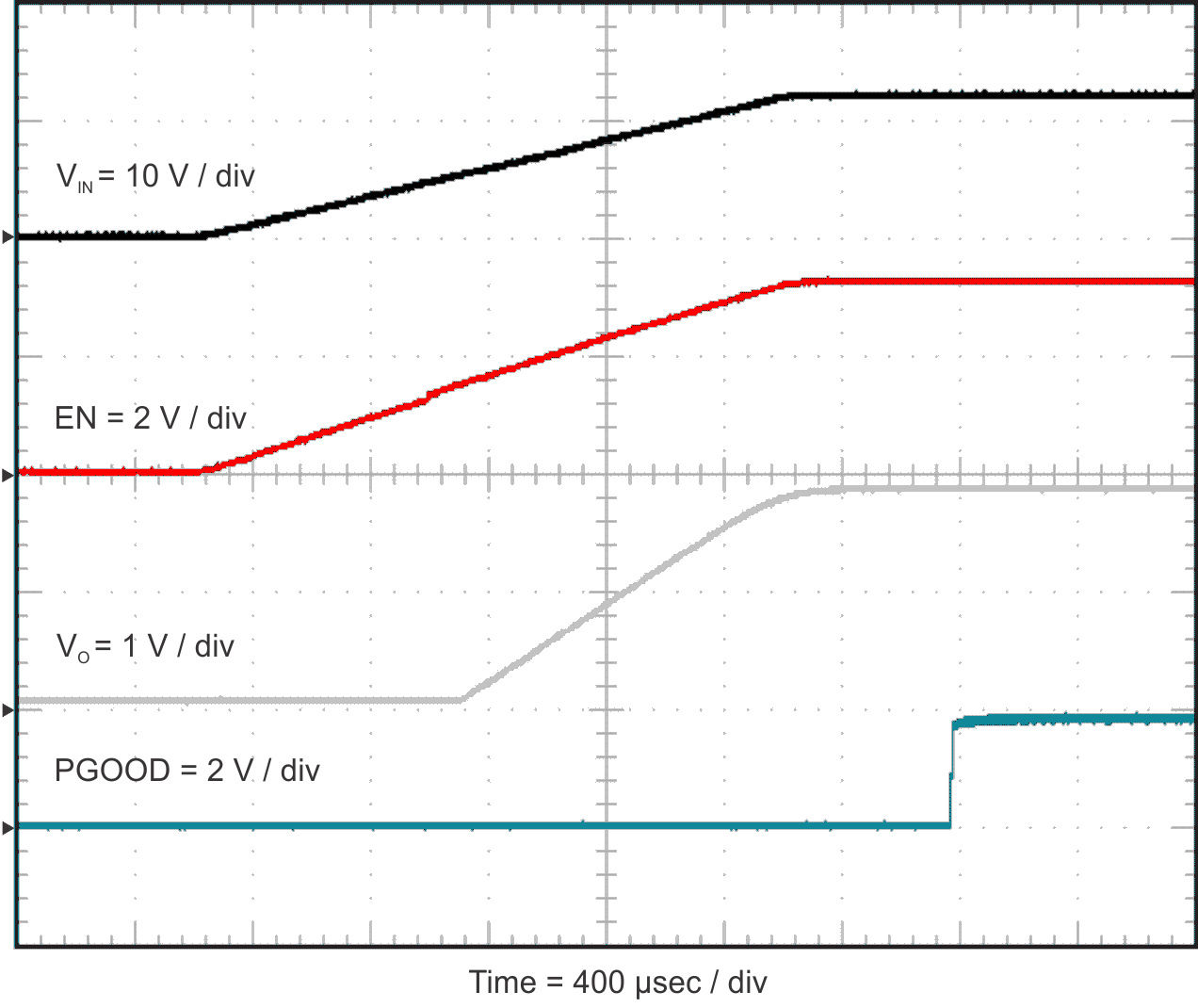 Figure 2-12 TPS54824EVM-779 Start-Up Relative to VIN
Figure 2-12 TPS54824EVM-779 Start-Up Relative to VIN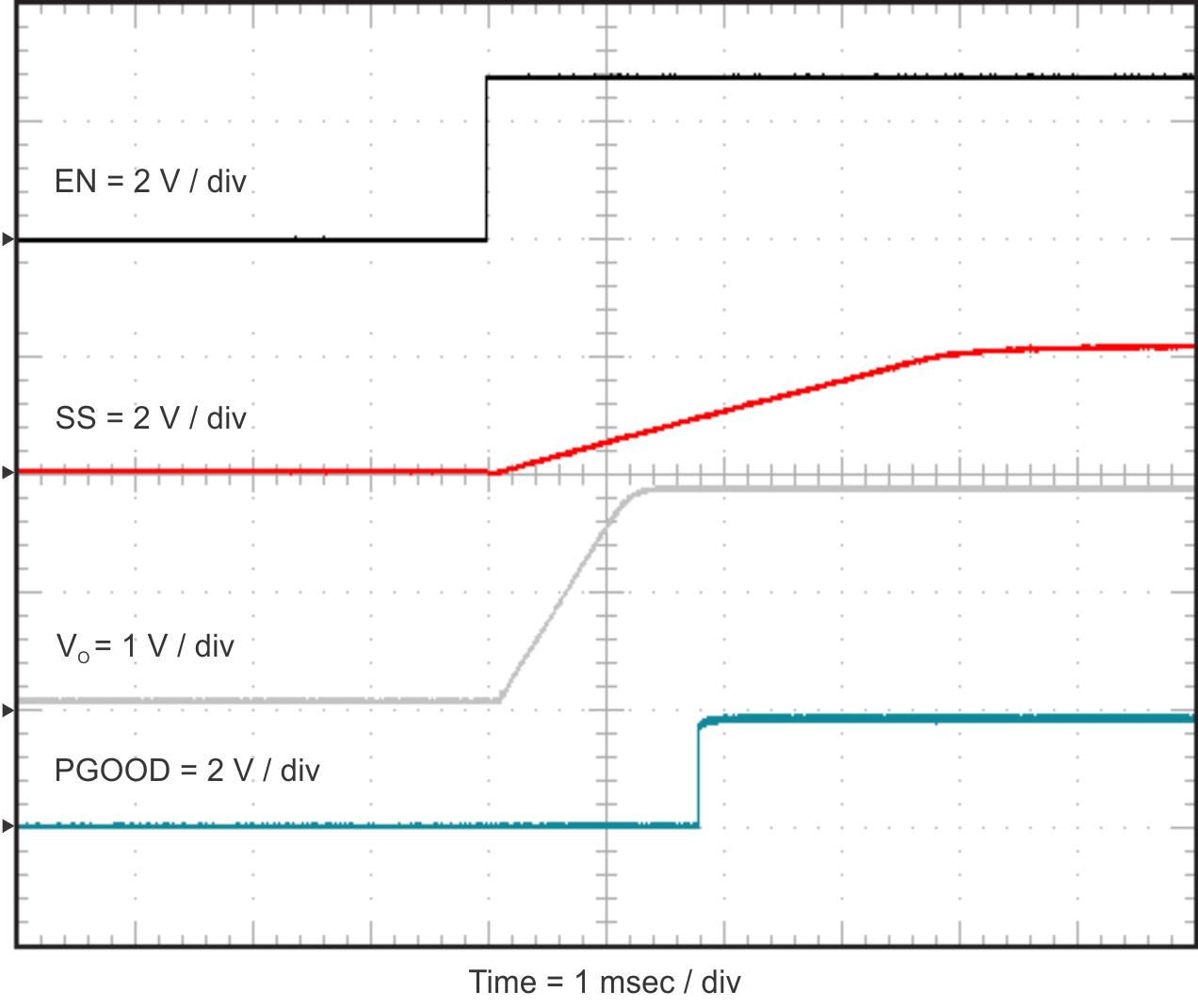 Figure 2-13 TPS54824EVM-779 Start-Up Relative to Enable
Figure 2-13 TPS54824EVM-779 Start-Up Relative to Enable