TIDT346 august 2023
3.4.1 6-V Input Voltage
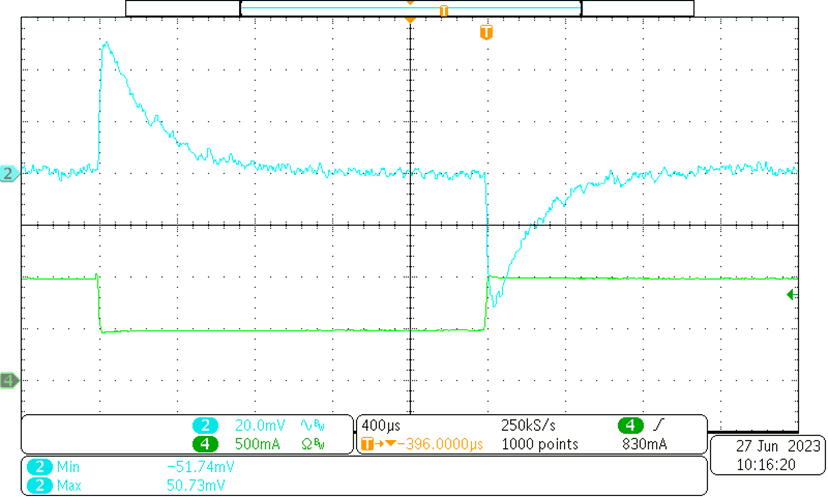 Figure 3-7 Load Step Response at 6-V
Input Voltage
Figure 3-7 Load Step Response at 6-V
Input Voltage- CH2: Output Voltage [scale: 20 mV/div, 400 µs / div, 20-MHz BW, AC coupling]
- CH4: Load transient from 0.5 A to 1 A [scale: 500 mA / div, 400 µs / div]