SBOA431 September 2020 TMP1075 , TMP108 , TMP112 , TMP144 , TMP461 , TMP464 , TMP468
5.2 Using Remote Temperature Sensor
When the CPU or GPU has thermal diode pins available, a remote temperature sensor can be used. Remote temperature sensors apply different currents and read back the change of voltage on the processor pins. The temperature of the junction can be determined through a change in voltage. When using remote temperature sensors, the electrical path to the processor is important because electrical noise on these signal pins can cause temperature errors. Other sources of errors include ideality factor variation, series resistance, and low beta junctions. Some remote temperature sensors have built-in features to limit the temperature error from these error sources. Figure 5-2 shows a typical application schematic of using a remote temperature sensor with a CPU or GPU.
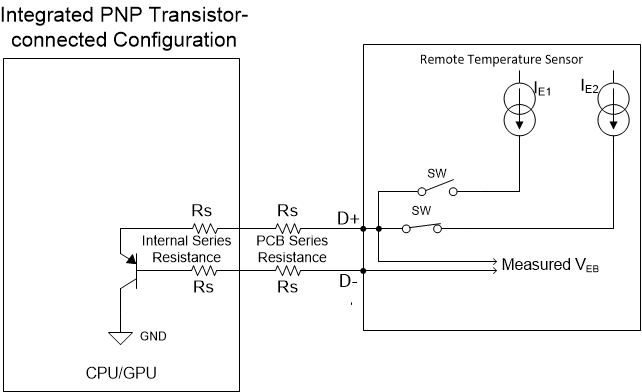 Figure 5-2 Remote Temperature Sensor
Application Schematic
Figure 5-2 Remote Temperature Sensor
Application Schematic