SFFS844 April 2024 CD74HCT4051-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the CD74HCT4051-Q1 (SOIC package). The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
- Pin short-circuited to VEE (see Table 4-6)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-6 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the CD74HCT4051-Q1 pin diagram for the SOIC package. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the CD74HCT4051-Q1data sheet.
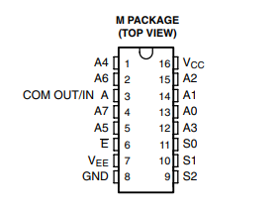 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOIC) Package
Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram (SOIC) Package| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | 1 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A6 | 2 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| COM OUT/IN A | 3 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the Ax pins. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A7 | 4 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A5 | 5 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| E | 6 | E stuck low. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| VEE | 7 | There is no effect; this is normal operation, if the switch path signal voltages are positive. Possible damage to the device if the switch path signal voltages are negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| GND | 8 | There is no effect; this is normal operation. | D |
| S2 | 9 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S1 | 10 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S0 | 11 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| A3 | 12 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A0 | 13 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A1 | 14 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| A2 | 15 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, device damage is possible. | A |
| VCC | 16 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | 1 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| A6 | 2 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| COM OUT/IN A | 3 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the Ax pins. | B |
| A7 | 4 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| A5 | 5 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| E | 6 | Loss of control of E pin. Cannot disable switch. Defaults to switches enabled. | B |
| VEE | 7 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| GND | 8 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. | B |
| S2 | 9 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S1 | 10 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| S0 | 11 | Control of the address pin is lost. Cannot control switch. | B |
| A3 | 12 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| A0 | 13 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| A1 | 14 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| A2 | 15 | Corruption of analog signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. | B |
| VCC | 16 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted To | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | 1 | A6 | Possible corruption of analog signal passed onto Ax and COM pin. | B |
| A6 | 2 | COM OUT/IN A | Possible corruption of analog signal passed onto Ax and COM pin. | B |
| COM OUT/IN A | 3 | A7 | Possible corruption of analog signal passed onto Ax and COM pin. | B |
| A7 | A5 | Possible corruption of analog signal passed onto Ax and COM pin. | B | |
| A5 | 5 | E | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the COM pin. Switch state will be undefined. | B |
| E | 6 | VEE |
Possible damage to device if the signal voltage is negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. |
A |
| VEE | 7 |
GND |
Possible damage to device if the signal voltage is negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| GND | 8 | S2 | Not considered; corner pin. | D |
| S2 | 9 | S1 | Control of the switch state is lost. | B |
| S1 | 10 | S0 | Control of the switch state is lost. | B |
| S0 | 11 | A3 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax and COM pin. Control of the switch state is lost. | B |
| A3 | 12 | A0 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax and COM pin. | B |
| A0 | 13 | A1 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax and COM pin. | B |
| A1 | 14 | A2 | Possible corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax and COM pin. | B |
| A2 | 15 | VCC | Corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VCC | 16 | A4 | Not considered, corner pin. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | 1 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A6 | 2 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| COM OUT/IN A | 3 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax pins. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A7 | 4 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A5 | 5 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| E | 6 | E stuck high. Can no longer enable the device. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| VEE | 7 | Device is unpowered. Device is not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| GND | 8 | Device is unpowered. Device is not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| S2 | 9 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| S1 | 10 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| S0 | 11 | Address stuck high. Cannot control switch states. | B |
| A3 | 12 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A0 | 13 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A1 | 14 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A2 | 15 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VCC | 16 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | 1 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A6 | 2 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| COM OUT/IN A | 3 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the Ax pins. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A7 | 4 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A5 | 5 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| E | 6 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| VEE | 7 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| GND | 8 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| S2 | 9 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Cannot control switch states. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| S1 | 10 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Cannot control switch states. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| S0 | 11 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Cannot control switch states. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |
| A3 | 12 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A0 | 13 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A1 | 14 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| A2 | 15 | Corruption of the signal passed onto the COM OUT/IN A pin. If there is no limiting resistor in the switch path, then device damage is possible. | A |
| VCC | 16 | Possible damage to the device if signal voltage is negative. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage is possible. | A |