SLLSF70C September 2018 – February 2022 TCAN1046V-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
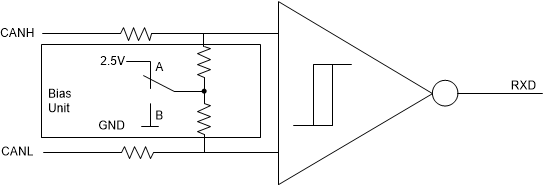
8.3.2 CAN Bus States
The CAN bus has two logical states during operation: recessive and dominant. See Figure 8-2 and Figure 8-3.
A dominant bus state occurs when the bus is driven differentially and corresponds to a logic low on the TXD1, TXD2, RXD1 and RXD2 pins. A recessive bus state occurs when the bus is biased to VCC/2 via the high-resistance internal input resistors RIN) of the receiver and corresponds to a logic high on the TXD1, TXD2, RXD1 and RXD2 pins.
A dominant state overwrites the recessive state during arbitration. Multiple CAN nodes may be transmitting a dominant bit at the same time during arbitration, and in this case the differential voltage of the bus is greater than the differential voltage of a single driver.
The TCAN1046V-Q1 transceiver implements a low-power standby (STB) mode which enables a third bus state where the bus pins are weakly biased to ground via the high resistance internal resistors of the receiver. See Figure 8-2 and Figure 8-3.
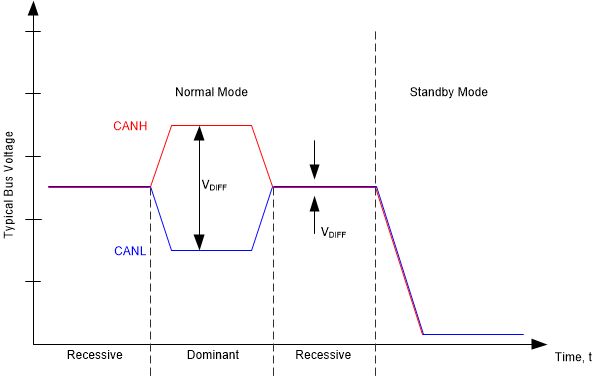 Figure 8-2 Bus States
Figure 8-2 Bus States