SLVAEF0 September 2020 – MONTH TPS92630-Q1 , TPS92638-Q1
2 Supply Line Transients In Automotive Rear Lamp Applications
In automotive equipments, the electric systems or components may be subjected to different supply line transients such as momentary drop in supply voltage, cold cranking, load dump, which can cause supply voltage deviations from the nominal values. Multiple tests, as specified in international standards such as ISO 7637-2 or ISO 16750-2, or specified by the the vehicle manufacturers, should be performed to evaluate the immunity of a device against these power supply transients.
In some transient scenarios, there is big voltage drop in power supply voltages. The V(supply) voltage seen at the power supply pins of TPS92630/8-Q1 may have different conditions, depending on the transient waveforms and the external circuits connected at the power supply pins.
According to the minimum value V(supply) decreases to, the device behavior can be divided into three different conditions, as shown in Figure 2-1. When V(supply) is always higher than 5 V and the device is enabled during the transient, the device keeps working in the normal state. When V(supply) decreases below 1.2 V or the device is disabled, the device will enter power-on-reset state where it will be reset. If V(supply) is between the two voltage levels and the device is enabled, the device behavior is undefined. The fault detection circuits may not be able to keep normal operation. Fault might be falsely detected and reported. If the device detects certain faults it falls into the protection mode and requires a power-on-reset to regain full functionality. So this condition should be avoided.
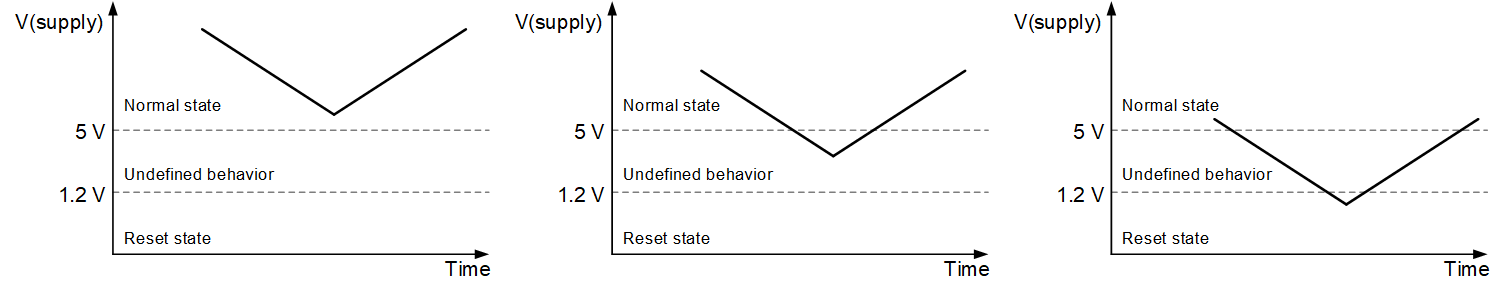 Figure 2-1 Supply Voltage Conditions
Figure 2-1 Supply Voltage ConditionsIf a V(supply) > 5 V cannot be guaranteed by the design and no other means of reset after faults (e.g. an MCU) are implemented, the following circuitry described in Section 3 can be used to ensure that the device is disabled when V(supply) is lower than 5 V, so that there will be no unwanted behavior triggered.