SLVAES3C May 2020 – October 2020 TPS61378-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS61378-Q1, TPS613781-Q1, TPS613782-Q1, TPS613783-Q1, TPS613784-Q1, TPS613785-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the TPS61378-Q1, TPS613781-Q1, TPS613782-Q1, TPS613783-Q1, TPS613784-Q1, TPS613785-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the 'Pin Configuration and Functions' section in the TPS61378-Q1 datasheet.
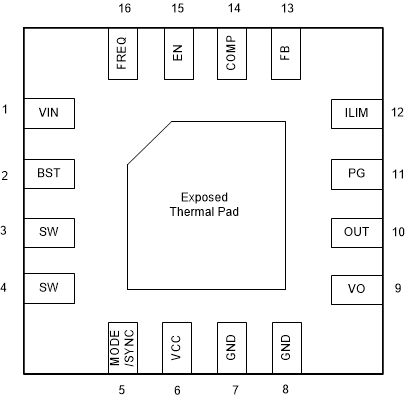 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- Device used within the 'Recommended Operating Conditions' and the 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' found in the TPS61378-Q1 data sheet.
- Configuration as shown in the 'Application and Implementation' found in the TPS61378-Q1 data sheet.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Device will not operate. Power supply is short. | B |
| BST | 2 | Possibe device damage. | A |
| SW | 3 | Potential damage to inductor and pin. | A |
| SW | 4 | Potential damage to inductor and pin. | A |
| MODE/SYNC | 5 | For TPS61378-Q1, TPS613781-Q1, TPS613782-Q1, device will remain in auto PFM mode. Loss of forced PWM mode, spread spectrum functionality and frequency synchronization functionality. | C |
| For TPS613783-Q1, TPS613784-Q1, TPS613785-Q1, device will remain in auto PFM mode. Loss of forced PWM mode and frequency synchronization funtionality. | |||
| VCC | 6 | Output voltage out of regulation. | B |
| GND | 7 | No effect. | D |
| GND | 8 | No effect. | D |
| VO | 9 | Device will reamin in hiccup output short circuit protection mode. | B |
| OUT | 10 | Potential damage to device. | A |
| PG | 11 | Correct output voltage. Loss of PG functionality. | C |
| ILIM | 12 | Correct output voltage. Peak switch current limit is maximum and can't be configured. | C |
| FB | 13 | For TPS61378-Q1, TPS613783-Q1, Vout = 5 V. | B |
| For TPS613781-Q1, TPS613784-Q1, Vout = 5.7 V. | |||
| For TPS613782-Q1, TPS613785-Q1, Vout = 9 V. | |||
| COMP | 14 | No output voltage. | B |
| EN | 15 | Loss of ENABLE functionality. Device will remain in shut-down mode. | B |
| FREQ | 16 | Switching frequency is 2MHz typically. | C |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | Device doesn’t work. Vout = 0 V. | B |
| BST | 2 | Device damaged. | A |
| SW | 3 | Possible device damage. | A |
| SW | 4 | Possible device damage. | A |
| MODE/SYNC | 5 | For TPS61378-Q1, TPS613781-Q1, TPS613782-Q1, device will remain in auto PFM mode. Loss of forced PWM mode, spread spectrum functionality and frequency synchronization functionality. | C |
| For TPS613783-Q1, TPS613784-Q1, TPS613785-Q1, device will remain in auto PFM mode. Loss of forced PWM mode and frequency synchronization functionality. | |||
| VCC | 6 | High ripple on VCC pin. Effeiciency is lower. | C |
| GND | 7 | Possible device damage. | A |
| GND | 8 | Possible device damage. | A |
| VO | 9 | No output voltage. | B |
| OUT | 10 | Possible device damage. | A |
| PG | 11 | Correct output voltage. Loss of PG functionality. | C |
| ILIM | 12 | Output current capability decreases. | B |
| FB | 13 | Output voltage is out of regulation. | B |
| COMP | 14 | Output voltage is out of regulation. | B |
| EN | 15 | Loss of ENABLE functionality. Device will remain in shut-down mode. | B |
| FREQ | 16 | No output voltage. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effects(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | BST | Possible device damage. | A |
| BST | 2 | SW | Output voltage out of regulation. | B |
| SW | 3 | SW | No effect. | D |
| SW | 4 | MODE/SYNC | Possible device damage. | A |
| MODE/SYNC | 5 | VCC | Device will remain in forced PWM mode. Loss of auto PFM mode and frequency synchronization functionality. | C |
| VCC | 6 | GND | Device doesn't work. Vout = 0 V. | B |
| GND | 7 | GND | No effect. | D |
| GND | 8 | VO | Device will reamin in hiccup output short circuit protection mode. | B |
| VO | 9 | OUT | Loss of down mode functionality and hiccup output short circuit protection. | B |
| OUT | 10 | PG | Possible device damage. | A |
| PG | 11 | ILIM | Potential device damage if PG is pulled up to higher than 6 V. | A |
| ILIM | 12 | FB | OVP is triggered. | B |
| FB | 13 | COMP | No output voltage. | B |
| COMP | 14 | EN | OVP is triggered. | B |
| EN | 15 | FREQ | No output voltage. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | 1 | No effect. | D |
| BST | 2 | Possible device damage. | A |
| SW | 3 | Damage to internal power FETs. | A |
| SW | 4 | Damage to internal power FETs. | A |
| MODE/SYNC | 5 | MODE/SYNC pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| VCC | 6 | VCC pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| GND | 7 | Possible device damage due to large current. | A |
| GND | 8 | Possible device damage due to large current. | A |
| VO | 9 | Vo = Vin. | B |
| OUT | 10 | Device ramain in hiccup mode. No output voltage. | B |
| PG | 11 | Possible device damage. | A |
| ILIM | 12 | ILIM pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| FB | 13 | FB pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| COMP | 14 | COMP pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| EN | 15 | EN pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |
| FREQ | 16 | FREQ pin damaged if supply voltage is higher than 6 V. | A |