SLVS646B September 2006 – November 2018 TPS2376-H
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1 Overview
The following descriptions refer to the schematic of Typical Application Circuit and the Functional Block Diagram.
ILIM: A resistor from this pin to VSS sets the inrush current limit per Equation 1:
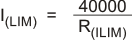
where ILIM is the desired inrush current value, in Amperes, and R(ILIM) is the value of the programming resistor from ILIM to VSS, in ohms. The practical limits on R(ILIM) are 125 kΩ to 1 MΩ. A value of 287 kΩ is recommended for compatibility with legacy power sourcing equipment (PSE).
Inrush current limiting prevents current drawn by the bulk capacitor from causing the line voltage to sag below the lower UVLO threshold. Adjustable inrush current limiting allows the use of arbitrarily large capacitors and also accommodates legacy systems that require low inrush currents.
The ILIM pin must not be left open or shorted to VSS.
CLASS: Classification is implemented by means of an external resistor, R(CLASS), connected between CLASS and VSS. The controller draws current from the input line through R(CLASS) when the input voltage lies between 13 V and 21 V. The classification currents specified in the electrical characteristics table include the bias current flowing into VDD and any RTN leakage current.
A high power system will not meet the standard power CLASS ranges defined in IEEE 802.3af, which are shown for reference in Table 1. An end-to-end high power system may either redefine the CLASS power, or dispense with CLASS entirely.
The CLASS pin must not be shorted to ground.
Table 1. Classification - IEEE 802.3af Values
| CLASS | PD POWER (W) | R(CLASS) (Ω) | 802.3af LIMITS (mA) | NOTE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.44 – 12.95 | 4420 ±1% | 0 - 4 | Default class |
| 1 | 0.44 – 3.84 | 953 ±1% | 9 - 12 | |
| 2 | 3.84 – 6.49 | 549 ±1% | 17 - 20 | |
| 3 | 6.49 – 12.95 | 357 ±1% | 26 - 30 | |
| 4 | - | 255 ±1% | 36 - 44 | Reserved for future use |
DET: R(DET) should be connected between VDD and the DET pin when it is used. R(DET) is connected across the input line when V(VDD) lies between 1.4 V and 11.3 V, and is disconnected when the line voltage exceeds this range to conserve power.
The parallel combination of R(DET) and the UVLO program resistors must equal 24.9 kΩ, ±1%. Minimizing R(DET), and maximizing the UVLO program resistors, improves efficiency during normal operation. Conversely, R(DET) may be eliminated with the UVLO divider providing the 24.9 kΩ signature to reduce component count.
VSS: This is the input supply negative rail that serves as a local ground. The PowerPad must be connected to this pin.
RTN: This pin provides the switched negative power rail used by the downstream circuits. The operational and inrush current limit control current into the pin. The PG circuit monitors the RTN voltage and also uses it as the return for the PG pin pulldown transistor. The internal MOSFET body diode clamps VSS to RTN when voltage is present between VDD and RTN and the Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) input is not present.
PG: This pin goes to a high resistance state when the internal MOSFET that feeds the RTN pin is enabled, and the device is not in inrush current limiting. In all other states except detection, the PG output is pulled to RTN by the internal open-drain transistor. Performance is ensured with at least 4 V between VDD and RTN.
PG is an open-drain output, which may require a pullup resistor or other interface to the dc/dc converter. PG may be left open if not used.
UVLO: The UVLO pin is used with an external resistor divider between VDD and VSS to set the upper and lower UVLO thresholds. The TPS2376-H enables the output when V(UVLO) exceeds the upper UVLO threshold, and turns it off when the input falls below the lower threshold.
The UVLO divider resistance may be used alone to provide the 24.9 kΩ detection signature, or be used in conjunction with R(DET). Eliminating R(DET) reduces the component count at the cost of lower operating efficiency. The Typical Application Circuit demonstrates the elimination of R(DET).
VDD: This is the positive input supply that is also common to downstream load circuits. This pin provides operating power and allows the controller to monitor the line voltage to determine the mode of operation.