SNLA360 October 2020 DP83TD510E
Overview of SPE
Standard Ethernet uses simplex communication with independent cables for transmitting and receiving data, as Standard Ethernet Interface for 10/100 Mbps shows.
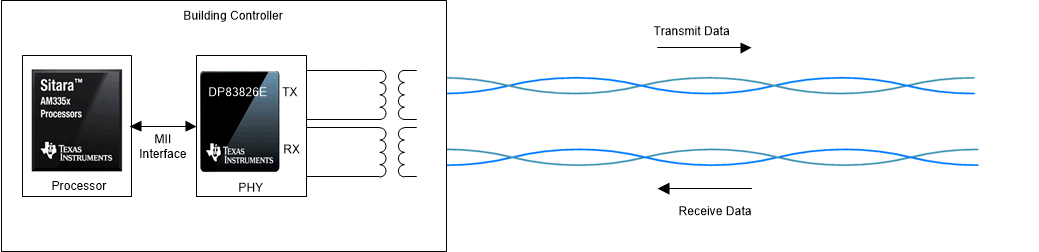 Standard Ethernet Interface for 10/100 Mbps.
Standard Ethernet Interface for 10/100 Mbps. SPE is broadly classified into three categories:
IEEE 802.3.cg (10 Mbps)
IEEE 802.3.bw (100 Mbps)
IEEE 802.3.bp (1,000 Mbps)
IEEE 802.3cg has two more classifications:
Long and short cable lengths reach over a single balanced pair of either shielded or unshielded wire. 10BASE-T1L: IEEE 802.3 Physical Layer specification for a 10 Mb/s Ethernet local area network over a single balanced pair of conductors up to at least 1000 m reach (long reach using 18 AWG wire for point to point connection).
10BASE-T1S: IEEE 802.3 Physical Layer specification for a 10 Mb/s Ethernet local area network over a single balanced pair of conductors up to at least 15 m reach (short reach using 24–26 AWG wire with multidrop connection).
This article covers use cases for 10BASE-T1L, which offers up to 10 Mbps data rate over 1,000-m distances in building automation systems.
The 10BASE-T1L physical layer (PHY) operates using full-duplex communications over a single balanced pair of conductors with an effective data rate of 10 Mbps simultaneously in each direction. A 10BASE-T1L PHY, such as the DP83TD510E, uses three-level pulse amplitude modulation (PAM3), transmitted at 7.5 megabaud on the link segment. A 33-bit scrambler can help improve electromagnetic compatibility. MII transmit data (TXD<3:0>) are encoded together using four-binary three-ternary (4B3T) encoding, which keeps the running average (DC baseline) of the transmitted PAM3 symbols within bounds. Using the management data input/output interface to set the transmitter output voltage of the 10BASE-T1L PHY to 1.0 Vpp or 2.4 Vpp differentials will help achieve a longer communication distance over different cables.
As SPE Interface for 10 Mbps Using the DP83TD510E shows, SPE uses echo cancellation to achieve full duplex communication, along with multilevel signaling and equalization to improve signal quality and achieve the required data rate over a single-pair cable. There is no difference in the interface between the processor and the PHY; however, within the PHY, the transmit and receive sections of the Medium Dependent Interface require modification as outlined above to enable single-pair operation.
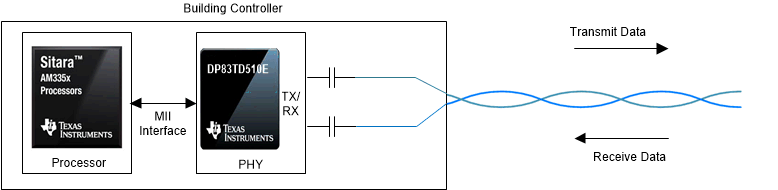 SPE Interface for 10 Mbps Using the DP83TD510E.
SPE Interface for 10 Mbps Using the DP83TD510E. SPE also enables sending power over data lines (PoDL) along the same single-pair cable through a low-pass filter like the one shown in PoDL Example.
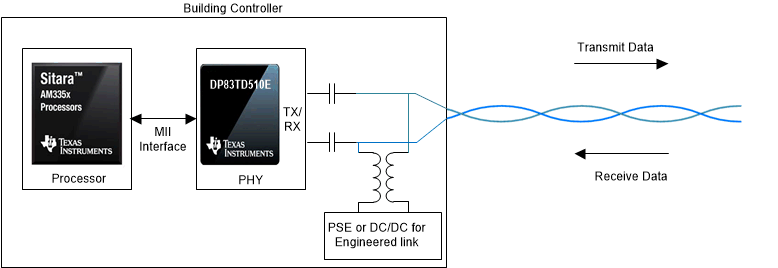 PoDL Example.
PoDL Example. The table in the following image lists the various power classes supported by the IEEE 802.3.cg standard. The maximum power deliverable to the load is 52 W and is defined under Class 15. Power classes below 10 are covered by IEEE 802.3.bu.
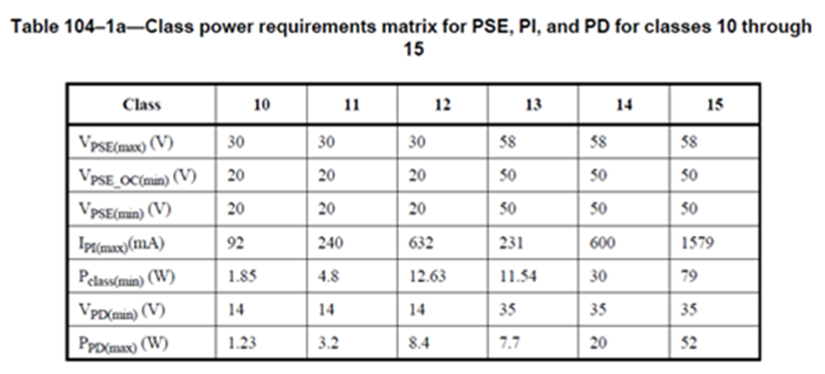 Power Classes Supported by the IEEE 802.3.cg Standard.
Power Classes Supported by the IEEE 802.3.cg Standard.