SNOAA67A May 2021 – June 2022 TMP116 , TMP117 , TMP1826 , TMP61 , TMP63 , TMP64
2.1 TMP116 and TMP117
The TMP116 has significantly better accuracy than the Class B RTD. In addition, when compared to the Class A RTD, the TMP116 accuracy is better over most of the –55°C to +125°C operating temperature range. This improvement in accuracy is in addition to lower cost and simplified designs when compared with RTDs.
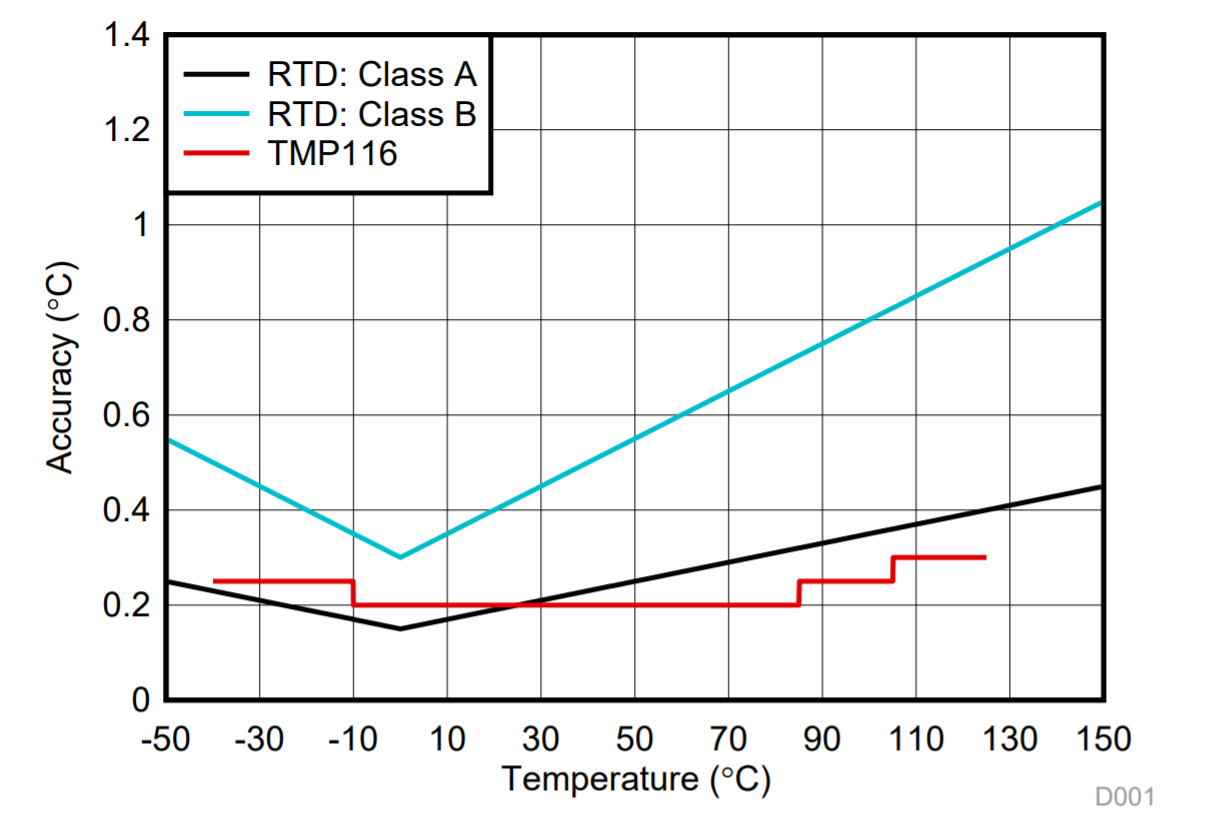 Figure 2-1 Comparing the Accuracy of an RTD to the TMP116
Figure 2-1 Comparing the Accuracy of an RTD to the TMP116The TMP117 is another semiconductor temperature sensor that can replace RTDs. It is a high-precision digital temperature sensor which provides a 16-bit result with a resolution of 0.0078°C and an accuracy of up to ±0.1°C across the –20°C to +50°C temperature range with no calibration. The TMP117 is I2C- and SMBus™ interface-compatible, has a programmable alert function, and can allow up to four devices on a single bus. Table 2-1 shows the overall accuracy of the TMP117 across its operating range.
| Temperature Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| –20°C to +50°C | ±0.1°C |
| –40°C to +100°C | ±0.2°C |
| –55°C to +150°C | ±0.3°C |
Figure 2-2 shows the accuracy of the TMP117 versus an RTD across the operating temperature range of –55°C to +150°C. It is evident looking at Figure 2-2 that the TMP117 with no calibration has the same or better accuracy as an RTD Class-AA sensor. Note that this is the raw accuracy of the two devices and that the final system layout has a minor effect on the TMP117 and a major effect on the accuracy of an RTD sensor due to a number of parameters such as the choice of ADC, layout of signal traces, and component tolerances.
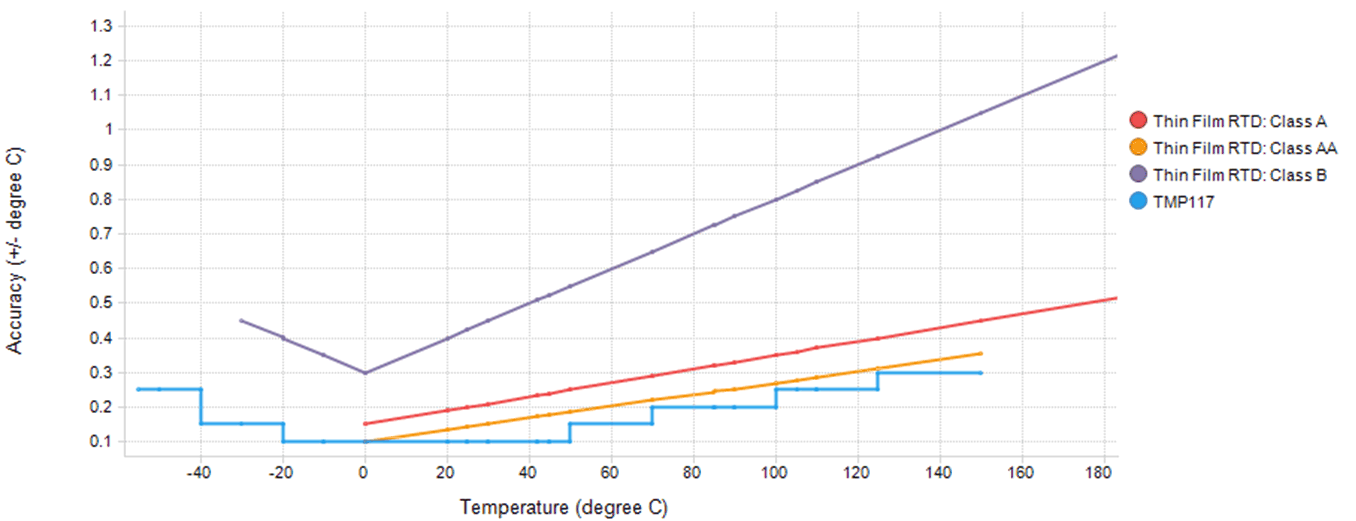 Figure 2-2 Accuracy Chart for TMP117 and RTD
Figure 2-2 Accuracy Chart for TMP117 and RTDThe TMP117 is comparable in accuracy to the Class AA thin-film RTD and consumes a fraction of the power of a PT100 RTD. The systems using the TMP117 require less components, such as delta-sigma ADCs, programmable gain amplifiers, and RC filters, than the systems using RTD elements.