SPRUJA2 November 2023
- 1
- Description
- Get Started
- Features
- 5
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 Additional Images
- 2.2 Key Features
- 2.3 Interface Mapping
- 2.4 Power ON/OFF Procedure
- 2.5 Clocking
- 2.6 Reset
- 2.7 CSI Interface
- 2.8 OLDI Interface
- 2.9 DSI Interface
- 2.10 Audio Codec Interface
- 2.11 HDMI Display Interface
- 2.12 JTAG Interface
- 2.13 Test Automation Header
- 2.14 UART Interface
- 2.15 USB Interface
- 2.16 Memory Interfaces
- 2.17 Ethernet Interface
- 2.18 GPIO Port Expander
- 2.19 GPIO Mapping
- 2.20 Power
- 2.21 EVM User Setup/Configuration
- 2.22 Expansion Headers
- 2.23 Interrupt
- 2.24 I2C Address Mapping
- 3Hardware Design Files
- 4Compliance Information
- 5Additional Information
2.13 Test Automation Header
AM62P SK EVM has an optional 40-pin test automation header (FH12A-40S-0.5SH) to allow any external controller to manipulate some basic operations like Power Down, POR, Warm Reset, and Boot Mode control.
The Test Automation Circuit is powered by the 3.3V supply generated by an Always On regulator Mfr. Part# LM5141QRGETQ1. The SOC’s I2C1 instance is connected to the test automation header. Another I2C instance (BOOTMODE_I2C) from the Test Automation Header is connected to the 24-bit I2C boot mode IO Expander of Mfr. Part# TCA6424ARGJR to allow control of the boot modes for the AM62P SOC.
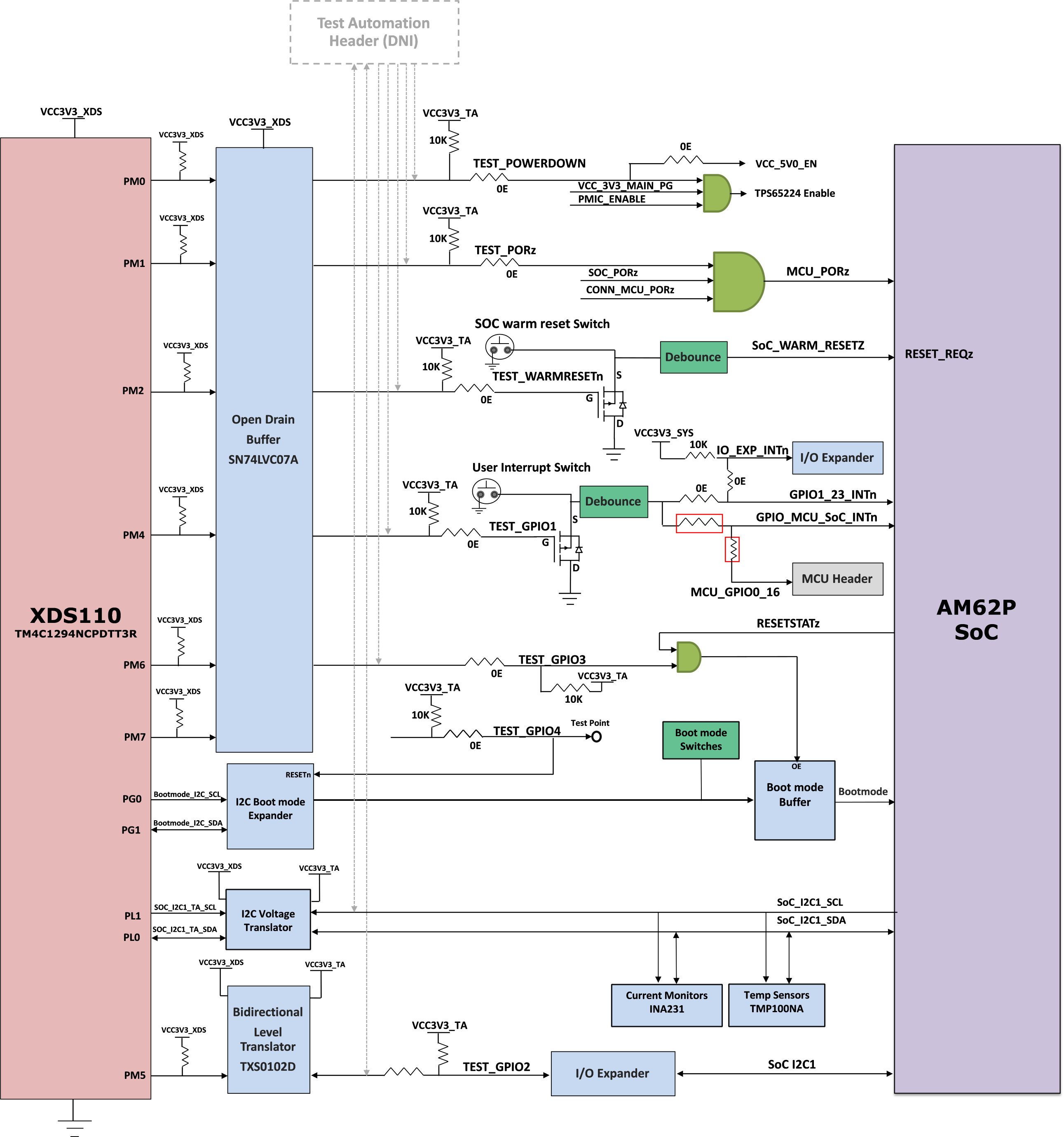 Figure 2-13 Test Automation
Interface
Figure 2-13 Test Automation
InterfaceThe test automation has voltage translation circuits so that the controller is isolated from the I/O voltages used by the AM62P. Boot mode for the AM62P can be user controlled by either using DIP Switches or the test automation header through the I2C I/O Expander. Boot Mode Buffers are used to isolate the Boot Mode controls driven through DIP Switches or I2C I/O Expander. The boot mode can also be set using two 8-bit DIP switches on the board, which connects a pull-up resistor to the output of a buffer when the switch is set to the ON position and to a weaker pull-down resistor when set to OFF position. The outputs of the buffer are connected to the boot mode pins on the AM62P SOC and the output is only enabled when the boot mode is needed during a reset cycle.
When boot mode is to be set through Test Automation header, the required switch values are set at the I2C I/O expander output, which overwrites the DIP switch values to give the desired boot values to the SOC. The pins used for boot mode also have other functions which are automatically isolated by disabling the boot mode buffer during normal operation.
The power down signal from the Test automation header instructs the SK EVM to power down all the rails except for dedicated power supplies on the board. Similarly, PORZn signal provides a hard reset to the SOC and WARM_RESETn for a warm reset to the SOC.
| Pin no. | Signal | IO Direction | Pin no. | Signal | IO Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC3V3_TA | Power | 21 | NC | NA |
| 2 | VCC3V3_TA | Power | 22 | NC | NA |
| 3 | VCC3V3_TA | Power | 23 | NC | NA |
| 4 | NC | NA | 24 | NC | NA |
| 5 | NC | NA | 25 | DGND | Power |
| 6 | NC | NA | 26 | TEST_POWERDOWN | Input |
| 7 | DGND | Power | 27 | TEST_PORZn | Input |
| 8 | NC | NA | 28 | TEST_WARMRESETn | Input |
| 9 | NC | NA | 29 | NC | NA |
| 10 | NC | NA | 30 | TEST_GPIO1 | Input |
| 11 | NC | NA | 31 | TEST_GPIO2 | Bidirectional |
| 12 | NC | NA | 32 | TEST_GPIO3 | Input |
| 13 | NC | NA | 33 | TEST_GPIO4 | Input |
| 14 | NC | NA | 34 | DGND | Power |
| 15 | NC | NA | 35 | NC | NA |
| 16 | DGND | Power | 36 | SoC_I2C1_TA_SCL | Bidirectional |
| 17 | NC | NA | 37 | BOOTMODE_I2C_SCL | Bidirectional |
| 18 | NC | NA | 38 | SoC_I2C1_TA_SDA | Bidirectional |
| 19 | NC | NA | 39 | BOOTMODE_I2C_SDA | Bidirectional |
| 20 | NC | NA | 40 | DGND | Power |