SPRY345B february 2022 – april 2023 DP83TG720R-Q1 , DP83TG720S-Q1 , TCAN1043A-Q1
- At a glance
- Authors
- Introduction
- Overcoming E/E architecture challenges
- Power distribution challenges and solutions
- Decentralization of power distribution
- Replacing melting fuses with semiconductor fuses
- Smart sensor and actuator challenges and solutions
- Zonal modules –new microcontroller requirements
- Smart sensors and actuators
- Data challenges and solutions
- Types of data
- Time sensitivity of data
- Communication security
- Conclusion
Smart sensor and actuator challenges and solutions
The zone E/E architecture significantly affects sensing and actuation functions at the boundary of a vehicle – the so-called edge. In domain architectures, dedicated ECUs that are typically in proximity to the sensors or actuators perform these functions. New features and functions usually result in new ECUs, each with dedicated battery power and networking wires, further increasing harness complexity. The introduction of zonal modules can greatly reduce harness complexity by merging the logical input/output (I/O) functions of multiple ECUs into the zonal module, and by maintaining sensor and actuator locations. This results in separation of physical and logical I/O functionality as shown in Figure 5, which brings new challenges and demands new solutions.
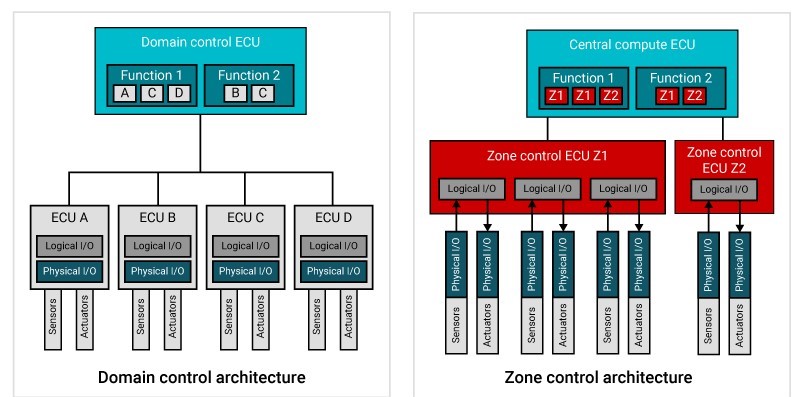 Figure 5 Separation of logical and
physical I/O functionality from a domain architecture to a zone
architecture.
Figure 5 Separation of logical and
physical I/O functionality from a domain architecture to a zone
architecture.