SSZT716 may 2018 CC2650MODA , CC2652R
Standards like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth low energy have become synonymous with the rise of “smart” devices in our homes that are controlled by digital assistants (such as the Amazon Echo). These standards are popular and well known to consumers. However, as the number of connected devices in our homes, buildings and cities grows, other lesser-known standards, like Thread and Zigbee, are becoming more relevant. The growing number of these technologies has brought the challenges of significant design complexity, including selecting which wireless protocol to use. The choice of which wireless technology to use for a deployment ultimately depends on several factors:
- Whether the device is battery-powered.
- Its form factor.
- The type of application it will support (streaming a high frequency of messages or infrequently sending and receiving commands).
- Integration with existing ecosystems.
Today, many communication technologies enabling device-to-device, device-to-cloud and device-to-mobile communication are at the heart of home and building automation, including Wi-Fi®, Bluetooth® low energy, Sub-1 GHz, Thread and Zigbee®. However, for this blog post, I’ll focus on some of the key advantages and differences of Zigbee and Thread.
What Are Thread and Zigbee?
Thread and Zigbee are low-power, wireless mesh standards that target embedded home and building automation applications. Both protocols leverage the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) 802.15.4 standard, which specifies the lower layers of the Thread and Zigbee protocols (the physical layer [PHY] and media access control [MAC] layers).
Since the upper-level layers are implemented in software rather than hardware (shown in Figure 1), Thread and Zigbee can be deployed as different software variants on top of common hardware, like the SimpleLink™ multi-standard CC2652R wireless microcontroller (MCU).
 Figure 1 Zigbee and Thread Protocol Layering.
Figure 1 Zigbee and Thread Protocol Layering.Both Thread and Zigbee are driven by industry-level alliances that push the protocol development forward and certify products out in the market.
Thread vs. Zigbee
One of the key differences between Thread and Zigbee is that Thread leverages Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), which enables a natural connection between Thread networks and existing IPv6-based networks like Wi-Fi. Zigbee, however, was built from the ground up, and each node in the network gets a 16-bit address that must be translated into IP using an application layer gateway.
Another key difference between the two standards is that Thread does not define specific application layers, while Zigbee defines all layers in the OSI model. This makes Thread a more flexible choice in terms of application layer selection. On the other hand, since Zigbee specifies application layer, a greater interoperability on application layer is guaranteed.
There are also some differences in authentication process between the two protocols. Thread authentication and commissioning is smartphone-based, while with Zigbee, authentication is centralized through a trust center with proximity-based commissioning.
The last key difference between the two protocols is longevity. Thread was first released in 2015, but Zigbee has been around since 2005. Today, Zigbee has much greater market penetration and a larger industry forum. Thread is still relatively new and still in the “adoption” phase. Details of the differences between Zigbee and Thread are highlighted in Figure 2.
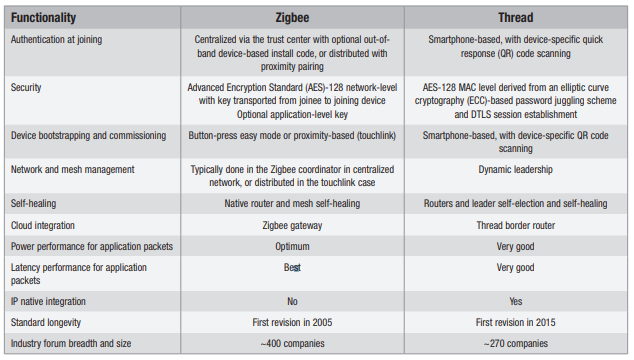 Figure 2 Zigbee and Thread Comparison
Figure 2 Zigbee and Thread ComparisonThe good news is that with TI’s SimpleLink MCU platform, you don’t have to choose between Thread and Zigbee when deciding on hardware. The SimpleLink multi-standard CC2652R wireless MCU supports both standards, and with the SimpleLink CC26X2 software development kit (SDK), application code is portable between the two standards.
Be sure to read the white paper, “Thread and Zigbee for home and building automation,” for a deeper dive into the advantages and differences of these two standards.