SWRA680 November 2020 CC3100 , CC3120 , CC3135 , CC3200 , CC3220R , CC3220S , CC3220SF , CC3235S , CC3235SF
2.7.1 Crystal Specifications
When selecting a crystal, keep in mind the respective specifications mentioned in the device's data sheets. Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 show the slow and fast clock respective specifications for only 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi.
| Characteristics | Test Conditions | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal frequency | 32.768 | kHz | |||
| Frequency accuracy | Initial + temperature + aging | ±150 | ppm | ||
| Crystal ESR | 32.768 kHz | 70 | kΩ |
Note that low-frequency tuning fork crystals have a resonance frequency that changes with temperature with a parabolic coefficient of (–0.04 × 10e6) / °C2 typically. Figure 2-1 shows an example of this, where it can be seen that a 40-ppm accuracy is maintained only from –10°C to 50°C.
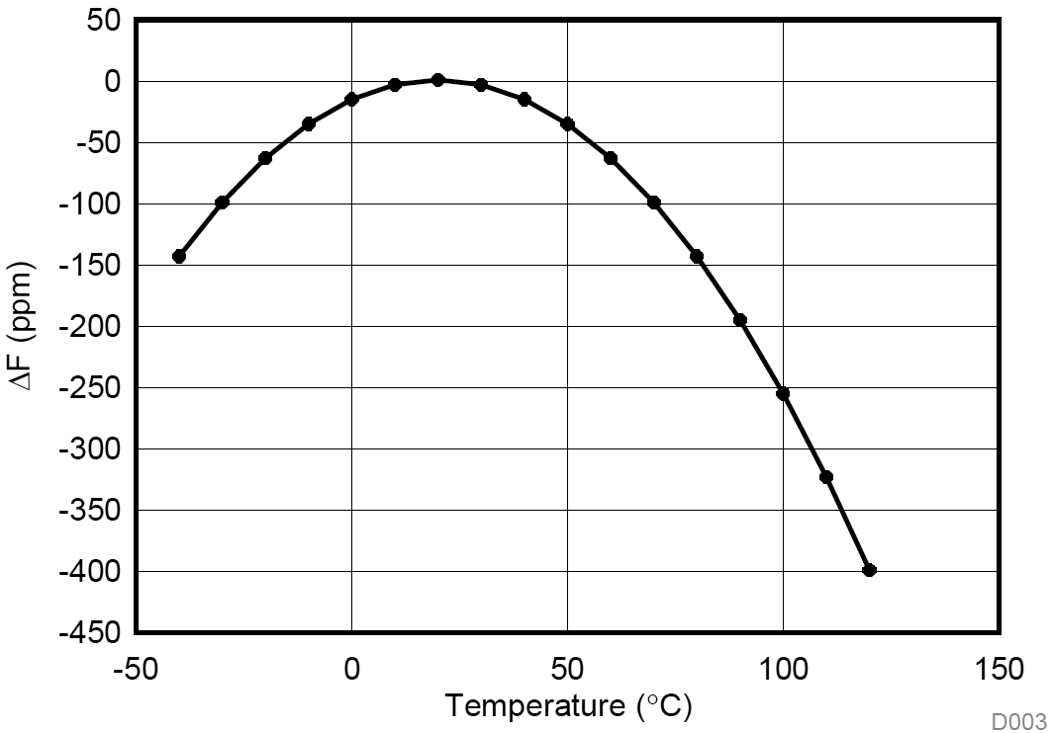 Figure 2-1 Frequency vs Temperature Curve for
a 32.768-kHz Tuning Fork Crystal
Figure 2-1 Frequency vs Temperature Curve for
a 32.768-kHz Tuning Fork Crystal| Characteristics | Test Conditions | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal frequency | 40 | MHz | |||
| Production Tolerance (Intial Torance) | ±10 | ppm | |||
| Load Capacitance (CL) | 8 | pF | |||
| Temperature Stability | ±10 | ppm | |||
| Aging | Assuming 5-year life | ±5 | ppm | ||
| Frequency accuracy | Initial + temperature + aging | ±25 | ppm | ||
| Crystal ESR | 40 MHz | 40 | 50 | 60 | Ω |
Table 2-3 shows the fast clock specifications for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
| Characteristics | Test Conditions | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal frequency | 40 | MHz | |||
| Production Tolerance | ±5 | ppm | |||
| Load Capacitance (CL) | 8 | pF | |||
| Temperature Stability | ±15 | ppm | |||
| Aging | Assuming 5-year life | ±3 | ppm | ||
| Frequency accuracy | Initial + temperature + aging | ±20 | ppm | ||
| Crystal ESR | 40 MHz | 40 | Ω |