SBAS533E March 2011 – February 2023 ADS4222 , ADS4225 , ADS4226 , ADS4242 , ADS4245 , ADS4246
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADS4246, ADS4245, ADS4242
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADS4226, ADS4225, ADS4222
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 7.8 Digital Characteristics
- 7.9 Timing Requirements: LVDS and CMOS Modes (1)
- 7.10 Serial Interface Timing Characteristics (1)
- 7.11 Reset Timing (Only When Serial Interface Is Used)
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Orderable Information
7.12.1 ADS4246
At TA = 25°C, AVDD = 1.8 V, DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum rated sampling frequency, sine wave input clock, 1.5-VPP differential clock amplitude, 50% clock duty cycle, –1 dBFS differential analog input, High-Performance Mode disabled, 0-dB gain, DDR LVDS output interface, and 32k point FFT, unless otherwise noted.
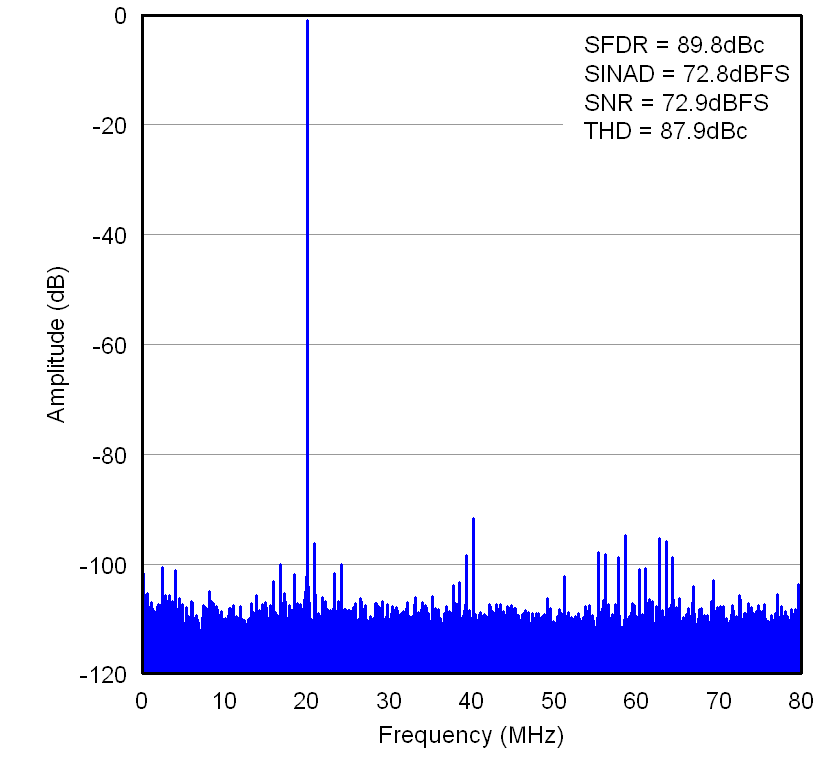 Figure 7-6 FFT
for 20-MHz Input Signal
Figure 7-6 FFT
for 20-MHz Input Signal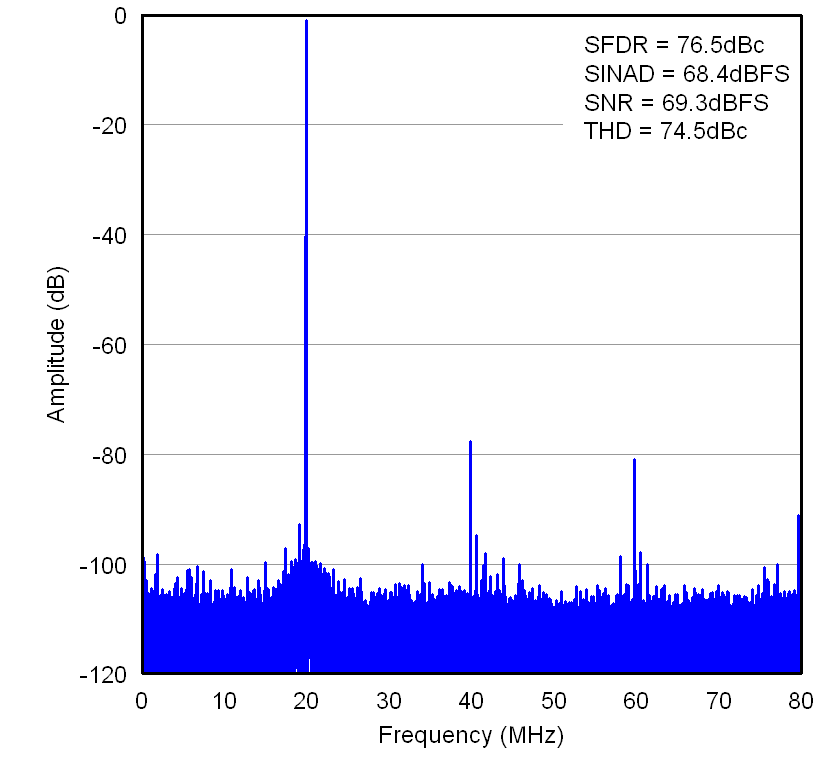 Figure 7-8 FFT
for 300-MHz Input Signal
Figure 7-8 FFT
for 300-MHz Input Signal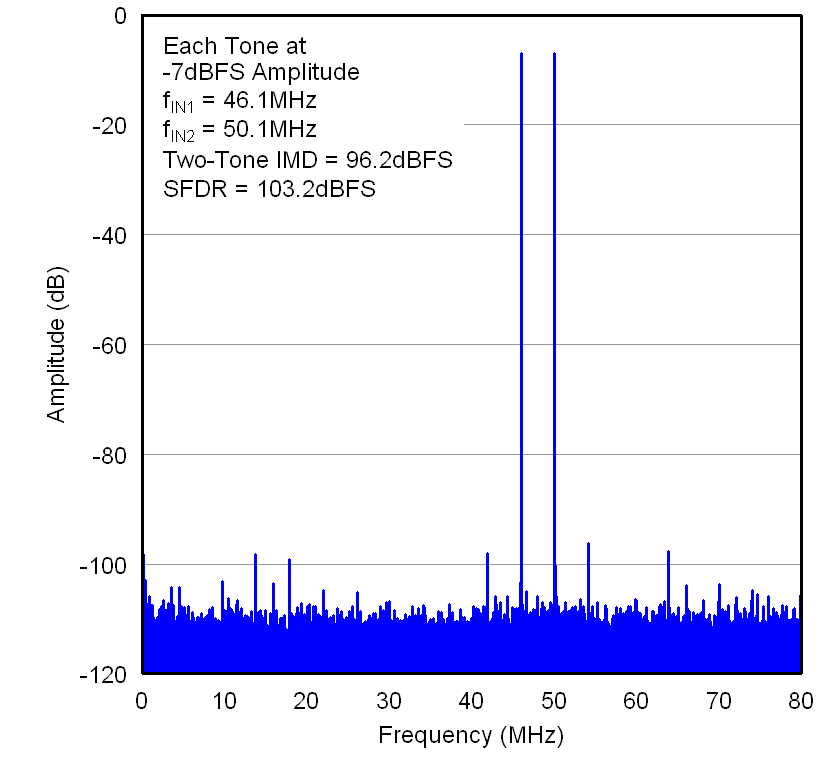 Figure 7-10 FFT
for Two-Tone Input Signal
Figure 7-10 FFT
for Two-Tone Input Signal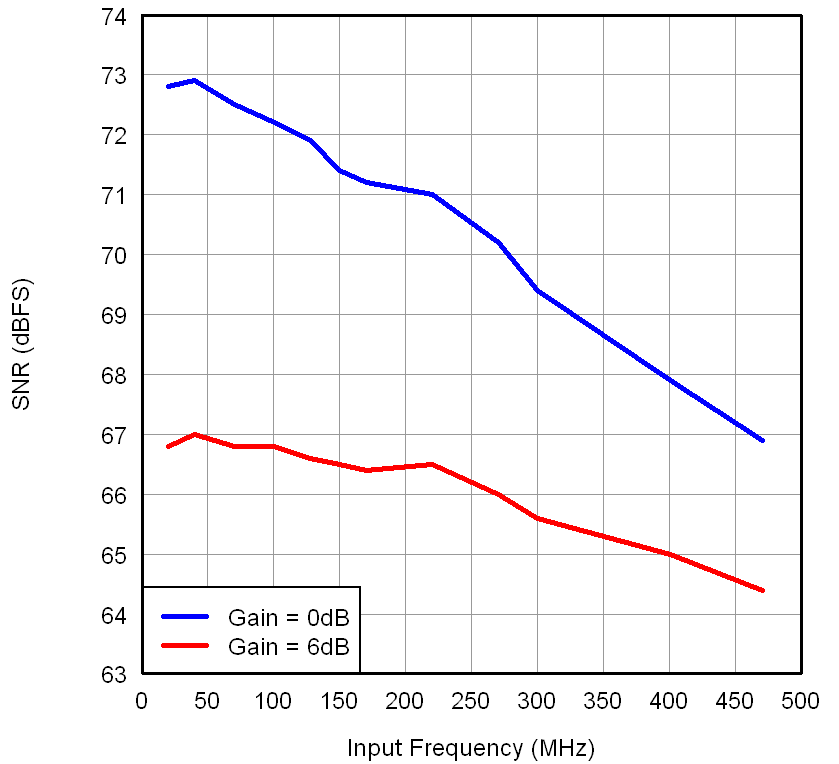 Figure 7-12 SNR
vs Input Frequency
Figure 7-12 SNR
vs Input Frequency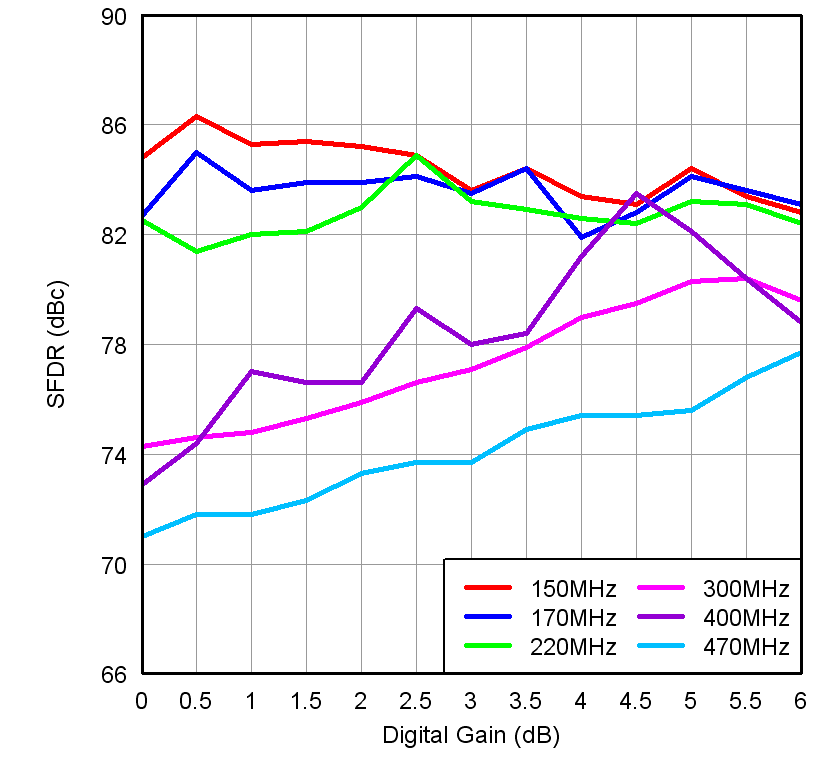 Figure 7-14 SFDR
vs Gain and Input Frequency
Figure 7-14 SFDR
vs Gain and Input Frequency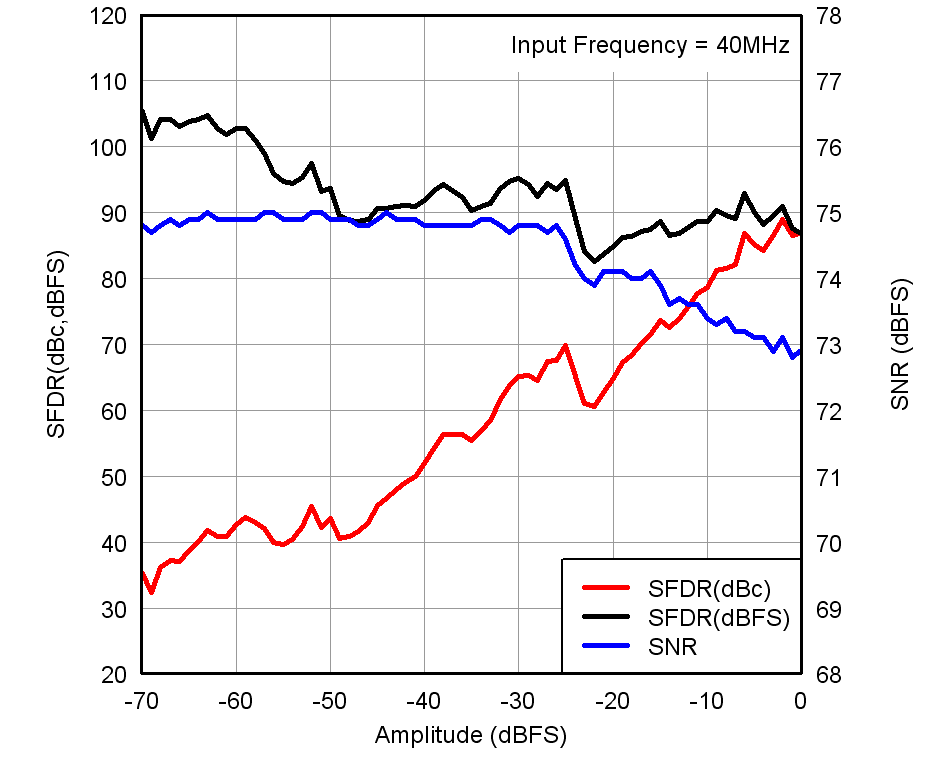 Figure 7-16 Performance vs Input Amplitude
Figure 7-16 Performance vs Input Amplitude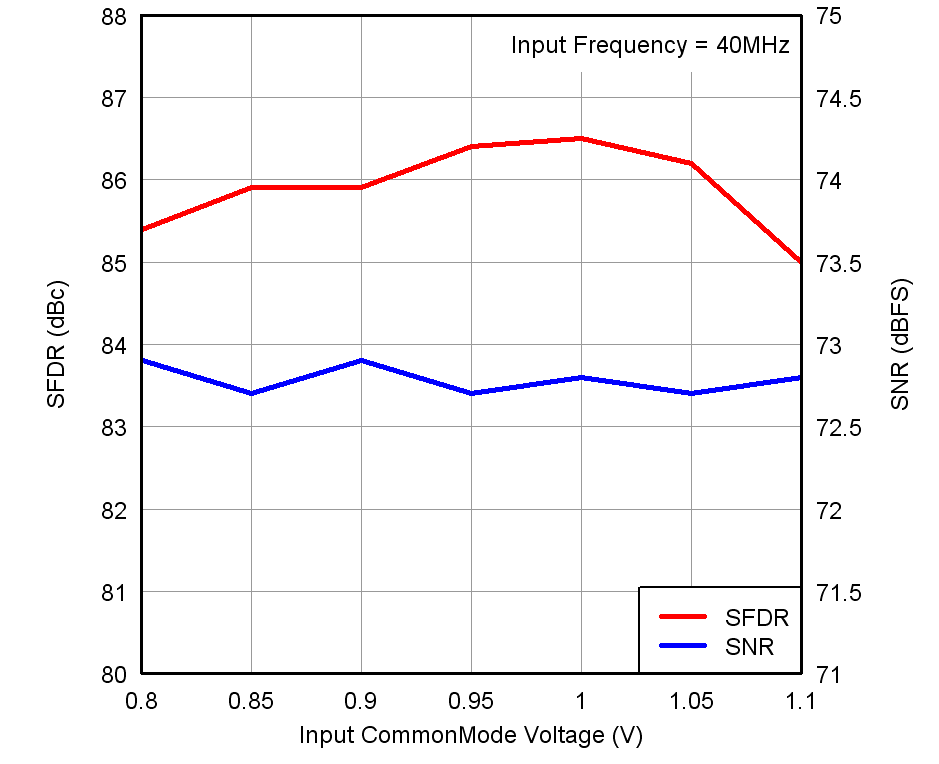 Figure 7-18 Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 7-18 Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage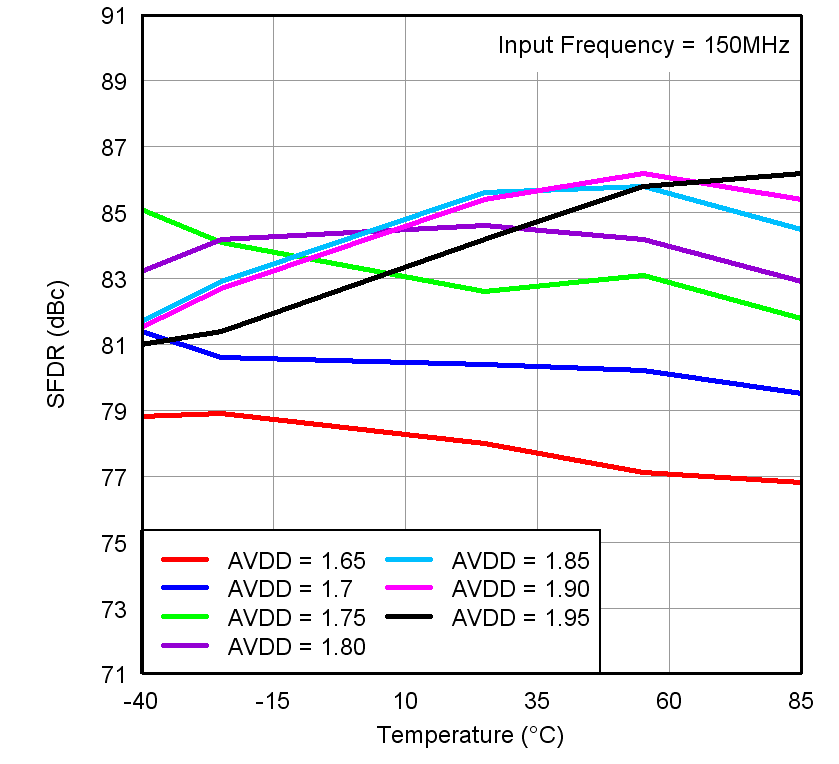 Figure 7-20 SFDR
vs Temperature and AVDD Supply
Figure 7-20 SFDR
vs Temperature and AVDD Supply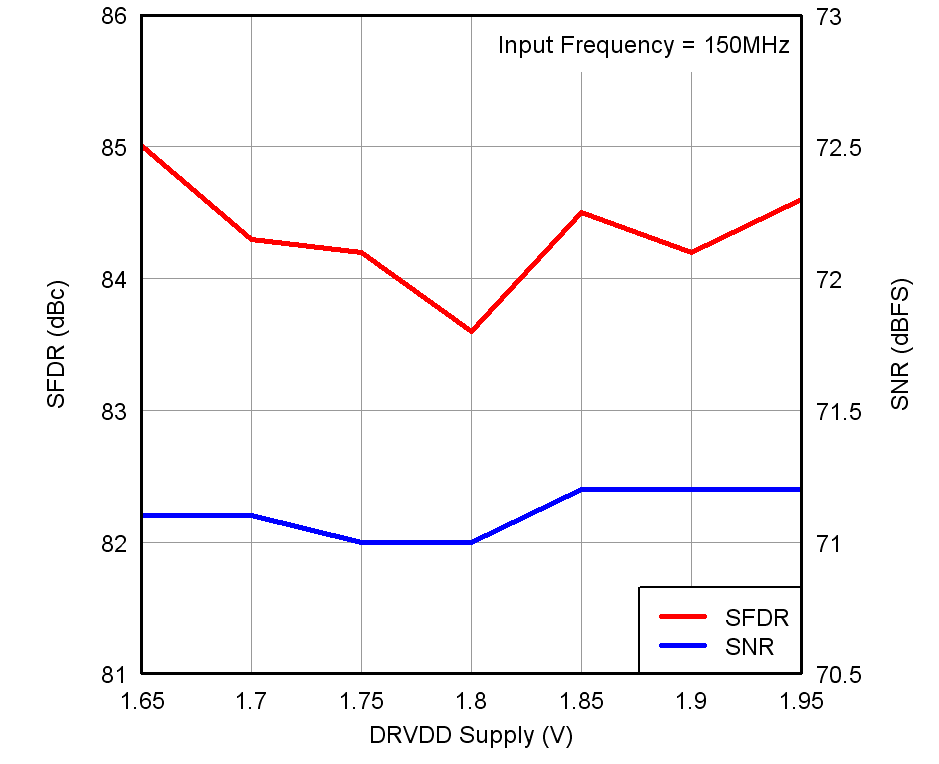 Figure 7-22 Performance vs DRVDD Supply Voltage
Figure 7-22 Performance vs DRVDD Supply Voltage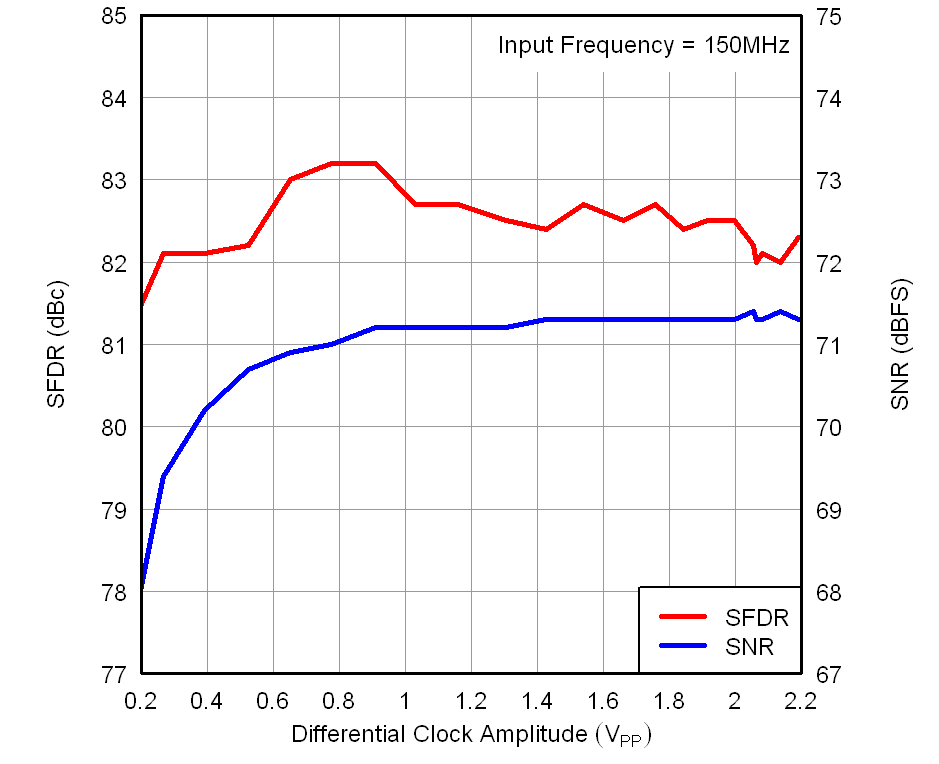 Figure 7-24 Performance vs Input Clock Amplitude
Figure 7-24 Performance vs Input Clock Amplitude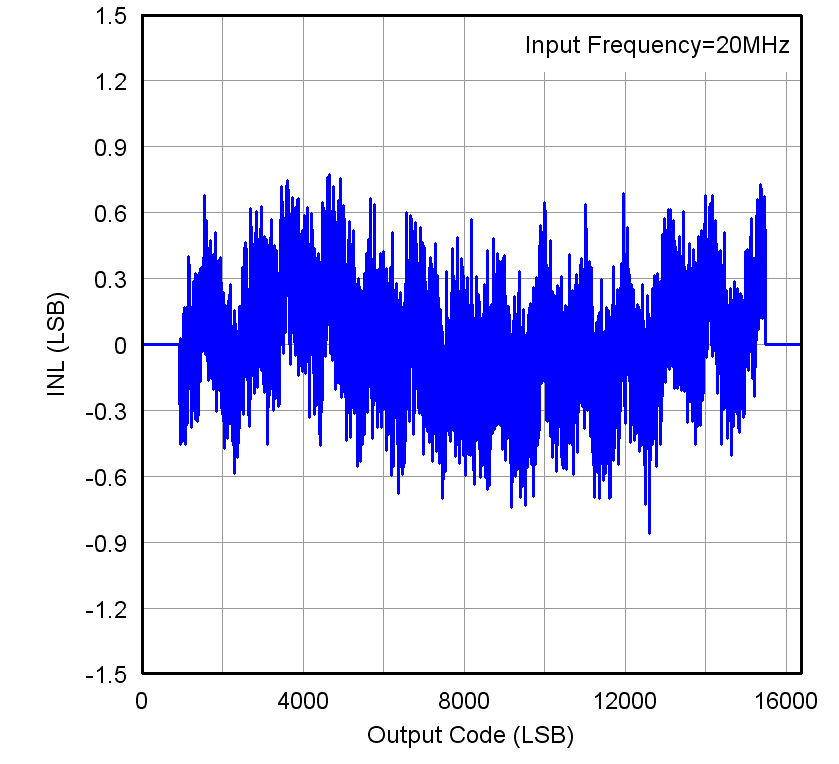 Figure 7-26 Integrated Nonlinearity
Figure 7-26 Integrated Nonlinearity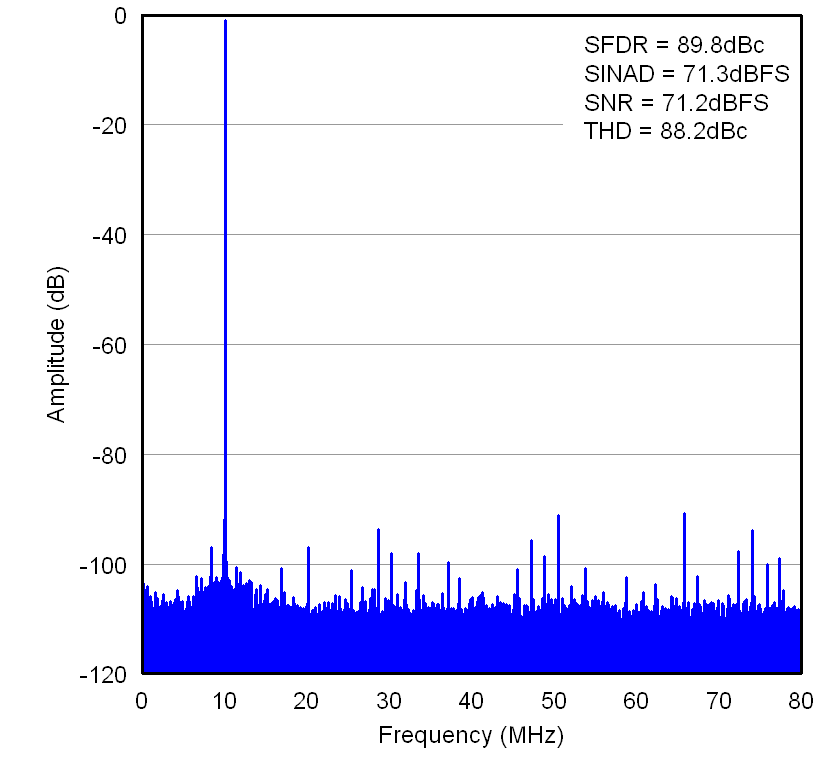 Figure 7-7 FFT
for 170-MHz Input Signal
Figure 7-7 FFT
for 170-MHz Input Signal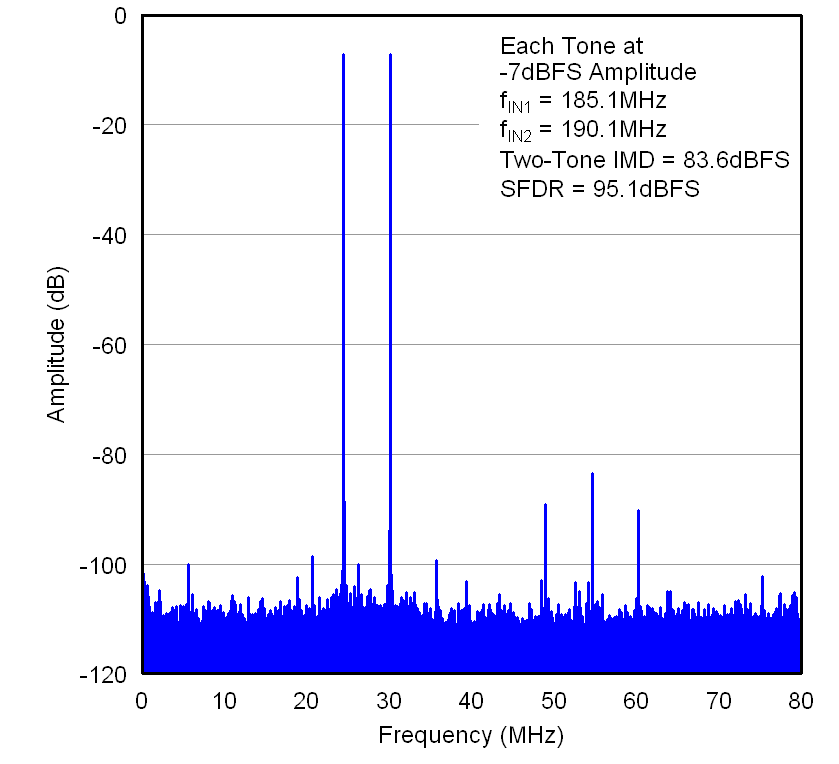 Figure 7-9 FFT
for Two-tone Input Signal
Figure 7-9 FFT
for Two-tone Input Signal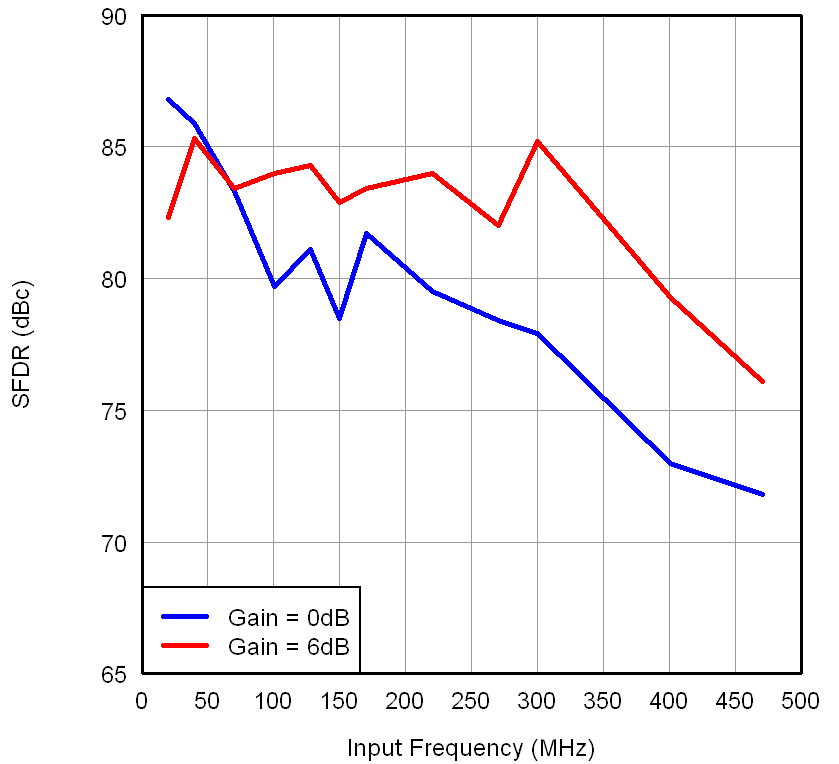 Figure 7-11 SFDR
vs Input Frequency
Figure 7-11 SFDR
vs Input Frequency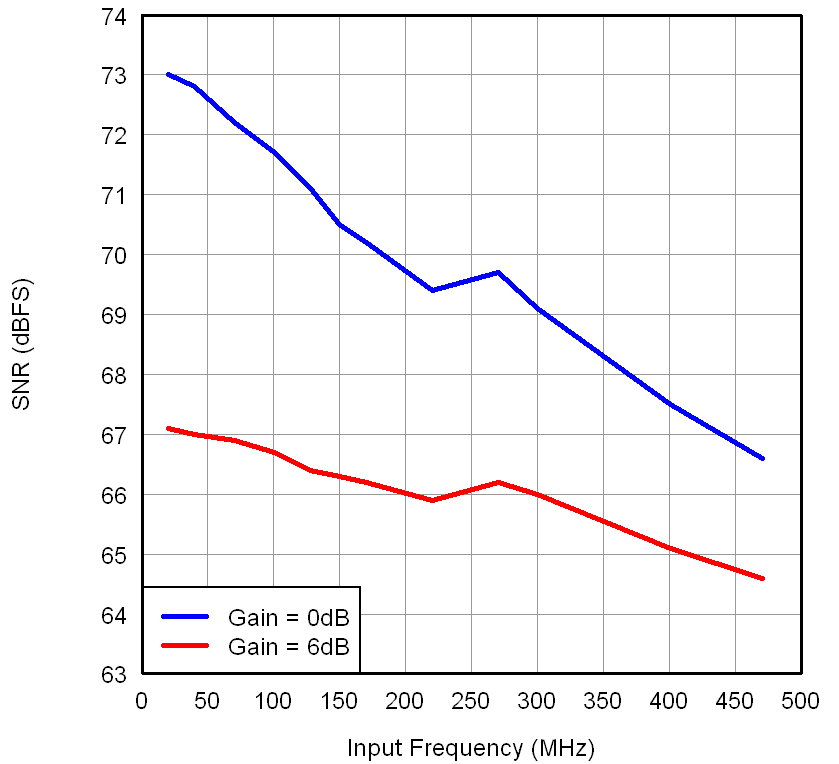 Figure 7-13 SNR
vs Input Frequency (CMOS)
Figure 7-13 SNR
vs Input Frequency (CMOS)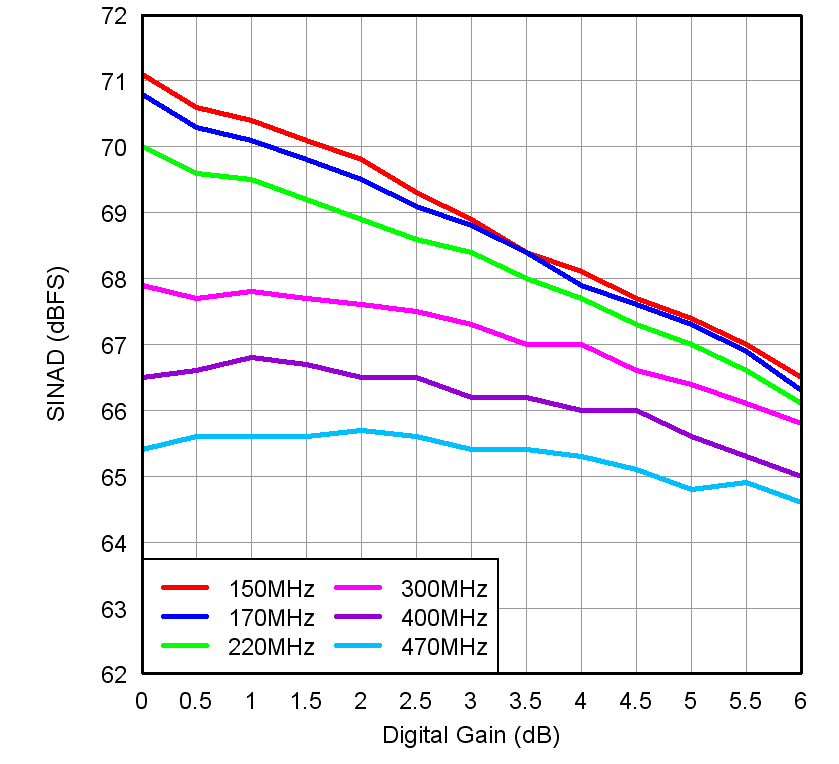 Figure 7-15 SINAD
vs Gain and Input Frequency
Figure 7-15 SINAD
vs Gain and Input Frequency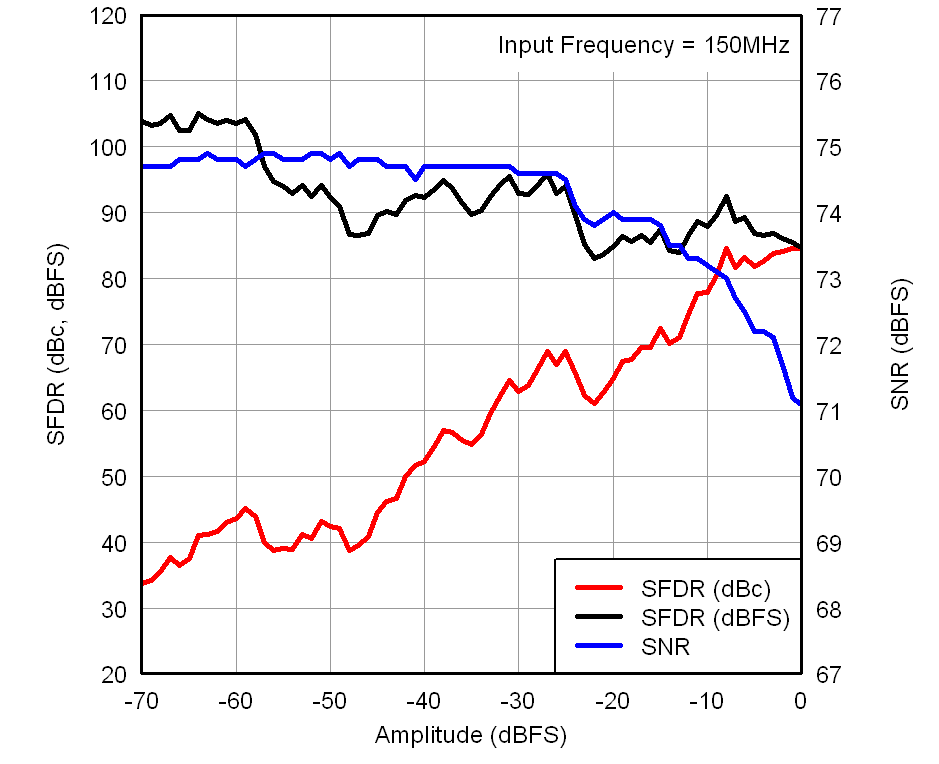 Figure 7-17 Performance vs Input Amplitude
Figure 7-17 Performance vs Input Amplitude Figure 7-19 Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 7-19 Performance vs Input Common-Mode Voltage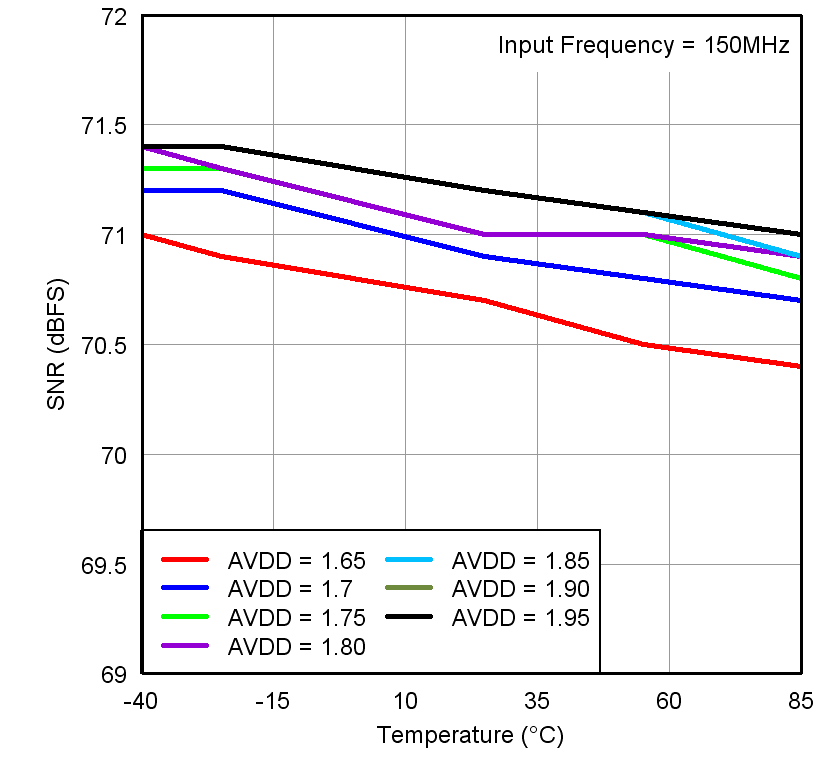 Figure 7-21 SNR
vs Temperature and AVDD Supply
Figure 7-21 SNR
vs Temperature and AVDD Supply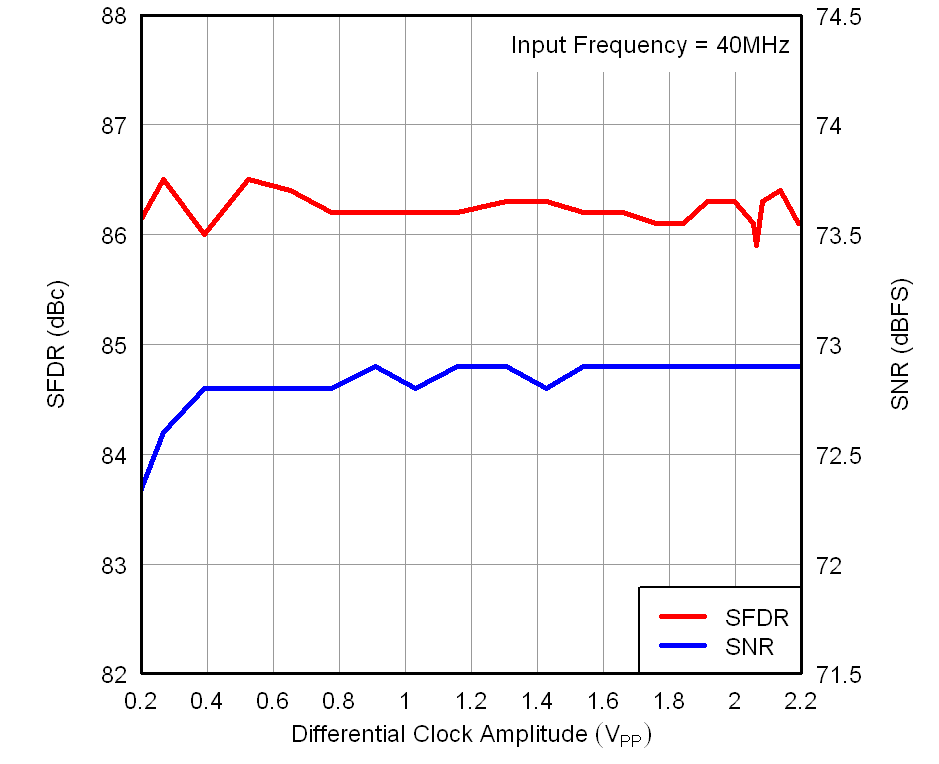 Figure 7-23 Performance vs Input Clock Amplitude
Figure 7-23 Performance vs Input Clock Amplitude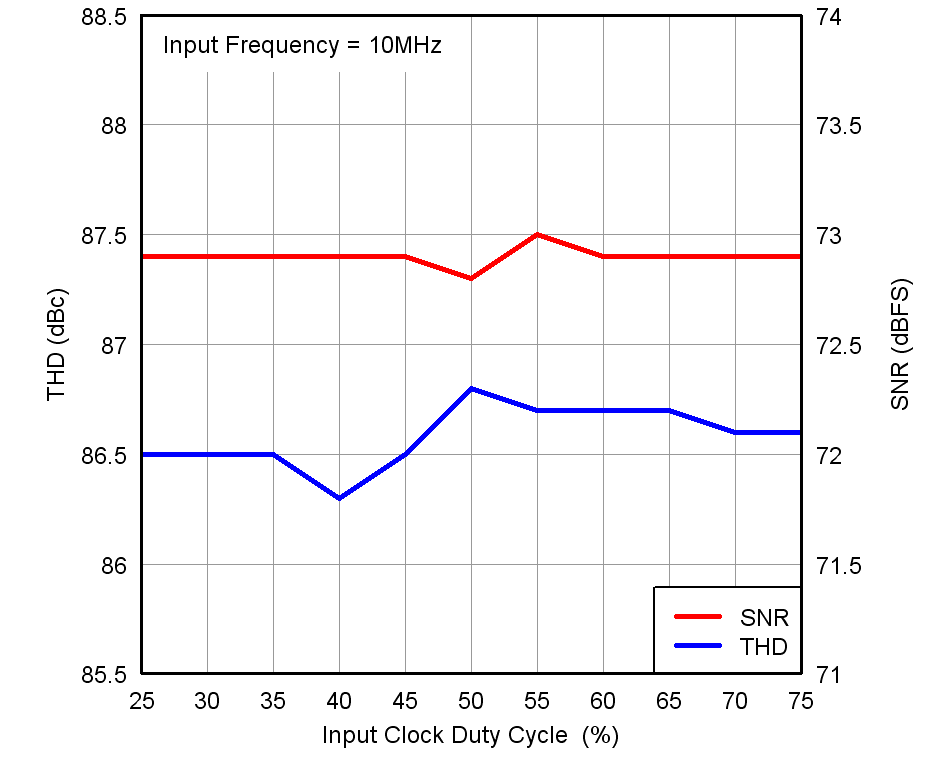 Figure 7-25 Performance vs Input Clock Duty Cycle
Figure 7-25 Performance vs Input Clock Duty Cycle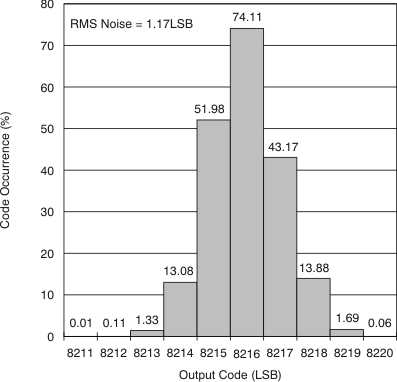 Figure 7-27 Output Noise Histogram (With Inputs Shorted to VCM)
Figure 7-27 Output Noise Histogram (With Inputs Shorted to VCM)