SLUSA75B July 2010 – January 2020 BQ24650
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.2 Input Voltage Regulation
- 8.3.3 Battery Current Regulation
- 8.3.4 Battery Precharge
- 8.3.5 Charge Termination and Recharge
- 8.3.6 Power Up
- 8.3.7 Enable and Disable Charging
- 8.3.8 Automatic Internal Soft-Start Charger Current
- 8.3.9 Converter Operation
- 8.3.10 Synchronous and Non-Synchronous Operation
- 8.3.11 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Undercurrent
- 8.3.12 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 8.3.13 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.14 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.15 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.16 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.17 Temperature Qualification
- 8.3.18 Charge Enable
- 8.3.19 Inductor, Capacitor, and Sense Resistor Selection Guidelines
- 8.3.20 Charge Status Outputs
- 8.3.21 Battery Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVA|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVA|16
Orderable Information
9.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
The output capacitor also should have enough ripple current rating to absorb output switching ripple current. The output capacitor RMS current ICOUT is given as:
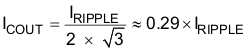
The output capacitor voltage ripple can be calculated in Equation 16:
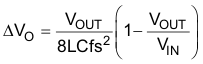
At certain input/output voltages and switching frequencies, the voltage ripple can be reduced by increasing the output filter inductor and capacitor values.
The BQ24650 has an internal loop compensator. To achieve good loop stability, the resonant frequency of the output inductor and output capacitor must be designed between 12 kHz and 17 kHz. The preferred ceramic capacitor has a 35 V or higher rating, X7R or X5R.
Ceramic capacitors show a de-bias effect. This effect reduces the effective capacitance when a DC-bias voltage is applied across a ceramic capacitor, as on the output capacitor of a charger. The effect may lead to a significant capacitance drop, especially for high voltages and small capacitor packages. See the manufacturer’s datasheet about performance with a DC bias voltage applied. It may be necessary to choose a higher voltage rating or nominal capacitance value to achieve the required value at the operating point.