SLPS422B March 2013 – August 2016 CSD97376Q4M
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DPC|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4 PWM Pin
The PWM pin incorporates an input tri-state function. The device forces the gate driver outputs to low when PWM is driven into the tri-state window and the driver enters a low-power state with zero exit latency. The pin incorporates a weak pullup to maintain the voltage within the tri-state window during low-power modes. Operation into and out of tri-state mode follows the timing diagram outlined in Figure 14.
When VDD reaches the UVLO_H level, a tri-state voltage range (window) is set for the PWM input voltage. The window is defined the PWM voltage range between PWM logic high (VIH) and logic low (VIL) thresholds. The device sets high-level input voltage and low-level input voltage threshold levels to accommodate both 3.3-V (typical) and 5-V (typical) PWM drive signals.
When the PWM exits tri-state, the driver enters CCM for a period of 4 µs, regardless of the state of the SKIP# pin. Normal operation requires this time period in order for the auto-zero comparator to resume.
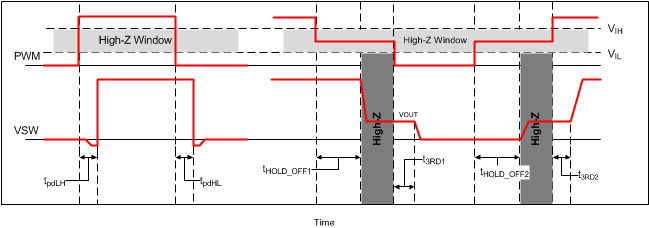 Figure 14. PWM Tri-State Timing Diagram
Figure 14. PWM Tri-State Timing Diagram