SNLS643C March 2019 – April 2024 DS90UB953A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 CSI-2 Receiver
- 6.3.2 FPD-Link III Forward Channel Transmitter
- 6.3.3 FPD-Link III Back Channel Receiver
- 6.3.4 Serializer Status and Monitoring
- 6.3.5 FrameSync Operation
- 6.3.6 GPIO Support
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Pattern Generation
- 6.7
Register Maps
- 6.7.1
Main Registers
- 6.7.1.1 I2C Device ID Register
- 6.7.1.2 Reset
- 6.7.1.3 General Configuration
- 6.7.1.4 Forward Channel Mode Selection
- 6.7.1.5 BC_MODE_SELECT
- 6.7.1.6 PLL Clock Control
- 6.7.1.7 Clock Output Control 0
- 6.7.1.8 Clock Output Control 1
- 6.7.1.9 Back Channel Watchdog Control
- 6.7.1.10 I2C Control 1
- 6.7.1.11 I2C Control 2
- 6.7.1.12 SCL High Time
- 6.7.1.13 SCL Low Time
- 6.7.1.14 Local GPIO DATA
- 6.7.1.15 GPIO Input Control
- 6.7.1.16 DVP_CFG
- 6.7.1.17 DVP_DT
- 6.7.1.18 Force BIST Error
- 6.7.1.19 Remote BIST Control
- 6.7.1.20 Sensor Voltage Gain
- 6.7.1.21 Sensor Control 0
- 6.7.1.22 Sensor Control 1
- 6.7.1.23 Voltage Sensor 0 Thresholds
- 6.7.1.24 Voltage Sensor 1 Thresholds
- 6.7.1.25 Temperature Sensor Thresholds
- 6.7.1.26 CSI-2 Alarm Enable
- 6.7.1.27 Alarm Sense Enable
- 6.7.1.28 Back Channel Alarm Enable
- 6.7.1.29 CSI-2 Polarity Select
- 6.7.1.30 CSI-2 LP Mode Polarity
- 6.7.1.31 CSI-2 High-Speed RX Enable
- 6.7.1.32 CSI-2 Low Power Enable
- 6.7.1.33 CSI-2 Termination Enable
- 6.7.1.34 CSI-2 Packet Header Control
- 6.7.1.35 Back Channel Configuration
- 6.7.1.36 Datapath Control 1
- 6.7.1.37 Remote Partner Capabilities 1
- 6.7.1.38 Partner Deserializer ID
- 6.7.1.39 Target 0 ID
- 6.7.1.40 Target 1 ID
- 6.7.1.41 Target 2 ID
- 6.7.1.42 Target 3 ID
- 6.7.1.43 Target 4 ID
- 6.7.1.44 Target 5 ID
- 6.7.1.45 Target 6 ID
- 6.7.1.46 Target 7 ID
- 6.7.1.47 Target 0 Alias
- 6.7.1.48 Target 1 Alias
- 6.7.1.49 Target 2 Alias
- 6.7.1.50 Target 3 Alias
- 6.7.1.51 Target 4 Alias
- 6.7.1.52 Target 5 Alias
- 6.7.1.53 Target 6 Alias
- 6.7.1.54 Target 7 Alias
- 6.7.1.55 Back Channel Control
- 6.7.1.56 Revision ID
- 6.7.1.57 Device Status
- 6.7.1.58 General Status
- 6.7.1.59 GPIO Pin Status
- 6.7.1.60 BIST Error Count
- 6.7.1.61 CRC Error Count 1
- 6.7.1.62 CRC Error Count 2
- 6.7.1.63 Sensor Status
- 6.7.1.64 Sensor V0
- 6.7.1.65 Sensor V1
- 6.7.1.66 Sensor T
- 6.7.1.67 CSI-2 Error Count
- 6.7.1.68 CSI-2 Error Status
- 6.7.1.69 CSI-2 Errors Data Lanes 0 and 1
- 6.7.1.70 CSI-2 Errors Data Lanes 2 and 3
- 6.7.1.71 CSI-2 Errors Clock Lane
- 6.7.1.72 CSI-2 Packet Header Data
- 6.7.1.73 Packet Header Word Count 0
- 6.7.1.74 Packet Header Word Count 1
- 6.7.1.75 CSI-2 ECC
- 6.7.1.76 IND_ACC_CTL
- 6.7.1.77 IND_ACC_ADDR
- 6.7.1.78 IND_ACC_DATA
- 6.7.1.79 FPD3_TX_ID0
- 6.7.1.80 FPD3_TX_ID1
- 6.7.1.81 FPD3_TX_ID2
- 6.7.1.82 FPD3_TX_ID3
- 6.7.1.83 FPD3_TX_ID4
- 6.7.1.84 FPD3_TX_ID5
- 6.7.2 Indirect Access Registers
- 6.7.1
Main Registers
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RHB|32
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
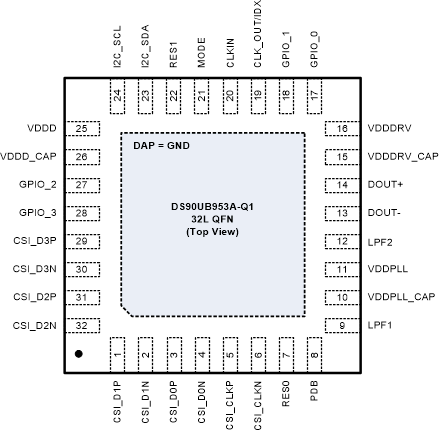 Figure 4-1 RHB Package
Figure 4-1 RHB Package32-Pin VQFN
Top View
Table 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| CSI INTERFACE | |||
| CSI_CLKP | 5 | I, DPHY | CSI-2 clock input pins. Connect to a CSI-2 clock source with matched 100Ω (±5%) impedance interconnects. |
| CSI_CLKN | 6 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D0P | 3 | I, DPHY | CSI-2 data input pins. Connect to a CSI-2 data sources with matched 100Ω (±5%) impedance interconnects. If unused, these pins can be left floating. |
| CSI_D0N | 4 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D1P | 1 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D1N | 2 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D2P | 31 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D2N | 32 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D3P | 29 | I, DPHY | |
| CSI_D3N | 30 | I, DPHY | |
| SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE | |||
| I2C_SDA | 23 | OD | I2C Data and Clock Pins. Pulled up to either 1.8V or 3.3V supply rail depending on IDX setting. See I2C Interface Configuration for further details on the I2C implementation of the DS90UB953A-Q1. See I2C Bus Pullup Resistor Calculation (SVLA689). |
| I2C_SCL | 24 | OD | |
| CONFIGURATION and CONTROL | |||
| RES0 | 7 | I | Reserved pin – Connect to GND |
| RES1 | 22 | I | Reserved pin – Do not connect (leave floating) |
| PDB | 8 | I, PD | Power-down inverted Input Pin.
Internal 1MΩ pulldown. Typically connected to
processor GPIO with pull down. When PDB input is
brought HIGH, the device is enabled and internal
register and state machines are reset to default
values. Asserting PDB signal low powers down the
device and consumes minimum power. The default
function of this pin is PDB = LOW; POWER DOWN. PDB
remains low until after power supplies are applied
and reach minimum required levels. See Power Down (PDB) for further details
on the function of PDB. PDB INPUT IS NOT 3.3V TOLERANT. PDB = 1.8V, device is enabled (normal operation) PDB = 0, device is powered down. |
| MODE | 21 | I, S | Mode select configuration input. Default operational mode is strapped at start-up based on the MODE input voltage when PDB transitions LOW to HIGH. Typically connected to voltage divider through external pullup to VDD18 and pulldown to GND applying an appropriate bias voltage. See MODE for details. |
| CLK_OUT/IDX | 19 | I/O, S | IDX pin sets the I2C pullup voltage and device address; connect to external pullup to VDD and pulldown to GND to create a voltage divider. When PDB transitions LOW to HIGH, the strap input voltage is sensed at the CLOCK_OUT/IDX pin to determine functionality and then converted to CLK_OUT. See I2C Interface Configuration for details. If CLK_OUT is used, the minimum resistance on the pin is 35kΩ. If unused, CLK_OUT/IDX can be tied to GND. |
| FPD-LINK III INTERFACE | |||
| DOUT- | 13 | I/O | FPD-Link III Input/Output pins. These pins must be AC-coupled. See Figure 7-5 and Figure 7-6 for typical connection diagrams and Table 7-3 for recommended capacitor values. |
| DOUT+ | 14 | I/O | |
| POWER AND GROUND | |||
| VDDD_CAP | 26 | D, P | A connection for an internal analog regulator decoupling capacitor. Typically connected to 10µF, 0.1µF, and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. Do not connect to an external supply rail. See Typical Application for more details. |
| VDDDRV_CAP | 15 | D, P | A connection for an internal analog regulator decoupling capacitor. Typically connected to 10µF, 0.1µF, and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. Do not connect to an external supply rail. See Typical Application for more details. |
| VDDPLL_CAP | 10 | D, P | A connection for an internal analog regulator decoupling capacitor. Typically connected to 10µF, 0.1µF, and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. Do not connect to an external supply rail. See Typical Application for more details. |
| VDDD | 25 | P | 1.8V (±5%) Power Supply pin.
Typically connected to 1µF and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. |
| VDDDRV | 16 | P | 1.8V (±5%) Analog Power Supply
pin. Typically connected to 1µF and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. |
| VDDPLL | 11 | P | 1.8V (±5%) Analog Power Supply
pin. Typically connected to 1µF and 0.01µF capacitors to GND. |
| GND | DAP | G | DAP is the large metal contact at the bottom side, located at the center of the VQFN package. Connect to the ground plane (GND). |
| LOOP FILTER | |||
| LPF1 | 9 | P | Loop Filter 1: Connect as described in Section 7.2.2.4. |
| LPF2 | 12 | P | Loop Filter 2: Connect as described in Section 7.2.2.4. |
| CLOCK INTERFACE AND GPIO | |||
| GPIO_0 | 17 | I/O, PD | General-Purpose Input/Output pins. These pins can also be configured to sense the voltage at their inputs. See Voltage and Temperature Sensing. At power up, these GPIO pins default to inputs with a 300kΩ (typical) internal pulldown resistor. These pins can be left floating if unused, but TI recommends to set the GPIOx_INPUT_EN to 0 to disable the pins. See Section 6.3.6 for programmability. |
| GPIO_1 | 18 | I/O, PD | |
| GPIO_2 | 27 | I/O, PD | General-Purpose Input/Output pins. At power up, these GPIO pins default to inputs with a 300kΩ (typical) internal pulldown resistor. These pins can be left floating if unused, but TI recommends to set the GPIOx_INPUT_EN to 0 to disable the pins. See Section 6.3.6 for programmability. |
| GPIO_3 | 28 | I/O. PD | |
| CLKIN | 20 | I | Reference Clock Input pin. If operating in non-sync external clock mode, connect this pin to a local clock source. If unused (like other clocking modes), this pin can be left open. See Table 6-8 for more information on clocking modes. |